Drosophila melanogaster
... food preference switch, we manipulated activities of neurons producing hugin peptides or its two receptors, CG8784 and CG8795. Virgin females carrying hugin cell-knockout (hugin-KO) showed the strong preference toward yeast, reminiscent of that of the mated. This phenotype is also observed in virgin ...
... food preference switch, we manipulated activities of neurons producing hugin peptides or its two receptors, CG8784 and CG8795. Virgin females carrying hugin cell-knockout (hugin-KO) showed the strong preference toward yeast, reminiscent of that of the mated. This phenotype is also observed in virgin ...
B) Nervous System Introduction NtG Spring
... Narrows to form a slender process the rest of the length In some neurons the axon is very short and in others it is very long Ex: axons of toes extend from your spine to your foot (about 3-4 feet) – the longest cells in your body Axons and Axonal Terminals Axons can branch many times but all ...
... Narrows to form a slender process the rest of the length In some neurons the axon is very short and in others it is very long Ex: axons of toes extend from your spine to your foot (about 3-4 feet) – the longest cells in your body Axons and Axonal Terminals Axons can branch many times but all ...
Nervous System – Ch 7
... Cervical enlargement is the thickening of the spinal cord in the neck region that supplies nerves to upper limbs The lumbar enlargement is in the lower back giving nerves to lower limbs. Divided into right and left halves by the anterior median fissure and posterior median sulcus grooves. ...
... Cervical enlargement is the thickening of the spinal cord in the neck region that supplies nerves to upper limbs The lumbar enlargement is in the lower back giving nerves to lower limbs. Divided into right and left halves by the anterior median fissure and posterior median sulcus grooves. ...
Chapter 12- Intro to NS
... 4. Somatic sensory: afferent impulses that originate from non-visceral areas such as skin and muscle. Proprioceptive senses sends sensory information from muscle, ligaments, tendons, and indicate body position. Special somatic senses are localized receptors such as those of the ear and eyes. 5. Visc ...
... 4. Somatic sensory: afferent impulses that originate from non-visceral areas such as skin and muscle. Proprioceptive senses sends sensory information from muscle, ligaments, tendons, and indicate body position. Special somatic senses are localized receptors such as those of the ear and eyes. 5. Visc ...
Document
... Nucleus raphe magnus neurons release serotonin at their nerve endings. Neurons with cell bodies located within the spinal cord that are stimulated by input from nucleus raphe magnus neurons release -endorphin at their nerve endings. d. All of the above are true. 10. Massaging the skin or applicatio ...
... Nucleus raphe magnus neurons release serotonin at their nerve endings. Neurons with cell bodies located within the spinal cord that are stimulated by input from nucleus raphe magnus neurons release -endorphin at their nerve endings. d. All of the above are true. 10. Massaging the skin or applicatio ...
Results Introduction! Conclusions!
... include IPSC-derived motor neurons in experiments because they are very similar to their real counterparts in terms of their shape, size, and genetic expression levels. Furthermore, it is interesting to explore differences between IPSC cell lines because expression levels are different between the l ...
... include IPSC-derived motor neurons in experiments because they are very similar to their real counterparts in terms of their shape, size, and genetic expression levels. Furthermore, it is interesting to explore differences between IPSC cell lines because expression levels are different between the l ...
File - Lucinda Supernavage
... • Sensory Nerves – conduct impulses into the brain or spinal cord from senses; AFFERENT nerves • Motor Nerves – carry impulses to muscles or glands; cause a response; EFFERENT nerves • Interneurons – connect sensory and motor nerves NEUROPATHY – damage to nerves in the PNS usually from underlying me ...
... • Sensory Nerves – conduct impulses into the brain or spinal cord from senses; AFFERENT nerves • Motor Nerves – carry impulses to muscles or glands; cause a response; EFFERENT nerves • Interneurons – connect sensory and motor nerves NEUROPATHY – damage to nerves in the PNS usually from underlying me ...
Nervous System PowerPoint
... •Reflexes are autonomic responses to certain stimuli. •They are not under conscious control, they are involuntary. •The pathway that a nerve impulse takes is called a reflex arc. •We need to identify the stimulus, receptor, sensory neuron, motor neuron, effector, and the response. ...
... •Reflexes are autonomic responses to certain stimuli. •They are not under conscious control, they are involuntary. •The pathway that a nerve impulse takes is called a reflex arc. •We need to identify the stimulus, receptor, sensory neuron, motor neuron, effector, and the response. ...
Handout_Master_11
... large differences individually can culturally, but the differences typically disappear over time. 2. True. Infants have reached half of their adult height by age 2. If the continued to grow throughout their life as quickly as they do in the first two years, they would end up more than 12 feet tall. ...
... large differences individually can culturally, but the differences typically disappear over time. 2. True. Infants have reached half of their adult height by age 2. If the continued to grow throughout their life as quickly as they do in the first two years, they would end up more than 12 feet tall. ...
Neural Networks
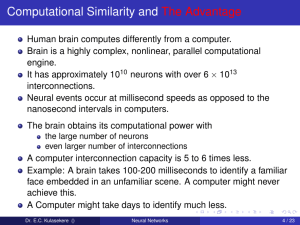
... To build a neuron based computer with as little as 0.1% of the performance of the human brain. Use this model to perform tasks that would be difficult to achieve using conventional computations. ...
... To build a neuron based computer with as little as 0.1% of the performance of the human brain. Use this model to perform tasks that would be difficult to achieve using conventional computations. ...
to specify axonal trajectories and target specificity of Jessell, 2000; Shira-
... provide new insight into how these pathways may operate as “choice points” between incompatible behaviors. The pathway-specific projections of Lhx6expressing neurons in the MEApd show preferential activation by reproductive olfactory cues such as female urine. In contrast, these cells appear unrespo ...
... provide new insight into how these pathways may operate as “choice points” between incompatible behaviors. The pathway-specific projections of Lhx6expressing neurons in the MEApd show preferential activation by reproductive olfactory cues such as female urine. In contrast, these cells appear unrespo ...
Upper and Lower Motor Neuron Lesions
... axon terminals are now separate from the main axon and hence, from each other. • Injury potentials are still generated along the terminals leading to asynchronous contraction of the individual ms fibers attached to terminals. • Invisible to the observer and detected only by electromyogram (EMG). ...
... axon terminals are now separate from the main axon and hence, from each other. • Injury potentials are still generated along the terminals leading to asynchronous contraction of the individual ms fibers attached to terminals. • Invisible to the observer and detected only by electromyogram (EMG). ...
neuron
... Neuron Classification • Neurons are classified in two ways: structural differences and functional differences • There are 3 structural classifications: multipolar, bipolar and unipolar • There are also 3 functional classifications: sensory, interneuron and motor • How they are connected is found o ...
... Neuron Classification • Neurons are classified in two ways: structural differences and functional differences • There are 3 structural classifications: multipolar, bipolar and unipolar • There are also 3 functional classifications: sensory, interneuron and motor • How they are connected is found o ...
Unit Outline_Ch17 - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... system. The somatic system serves the skin, skeletal muscles, and tendons. Some actions in the somatic system are due to reflexes, which are automatic responses to a stimulus. The Reflex Arc Reflexes are programmed, built-in circuits that allow for protection and survival. They require no conscious ...
... system. The somatic system serves the skin, skeletal muscles, and tendons. Some actions in the somatic system are due to reflexes, which are automatic responses to a stimulus. The Reflex Arc Reflexes are programmed, built-in circuits that allow for protection and survival. They require no conscious ...
Central nervous system
... As in other types of cells, a neuron’s cell body (or soma) contains the nucleus and ribosomes and thus has the genetic information and machinery necessary for protein synthesis. The dendrites are a series of highly branched outgrowths of the cell body. They and the cell body receive most of the i ...
... As in other types of cells, a neuron’s cell body (or soma) contains the nucleus and ribosomes and thus has the genetic information and machinery necessary for protein synthesis. The dendrites are a series of highly branched outgrowths of the cell body. They and the cell body receive most of the i ...
Nervous System
... Composed of least permeable capillaries in body Brain depends on a very constant internal environment • Allows: water, glucose, and essential amino acids • Disallows: urea, protein and most drugs • Cannot block: fats, respiratory gases and fat soluble molecules (alcohol, nicotine and anesthetics) ...
... Composed of least permeable capillaries in body Brain depends on a very constant internal environment • Allows: water, glucose, and essential amino acids • Disallows: urea, protein and most drugs • Cannot block: fats, respiratory gases and fat soluble molecules (alcohol, nicotine and anesthetics) ...
Integrate and Fire Neural Network
... – Simulation specifics, intro to neural network models, suggestions for this presentation ...
... – Simulation specifics, intro to neural network models, suggestions for this presentation ...
Sensory pathways
... • Sensory systems allow us to detect, analyze and respond to our environment • “ascending pathways” • Carry information from sensory receptors to the brain • Conscious: reach cerebral cortex • Unconscious: do not reach cerebral ...
... • Sensory systems allow us to detect, analyze and respond to our environment • “ascending pathways” • Carry information from sensory receptors to the brain • Conscious: reach cerebral cortex • Unconscious: do not reach cerebral ...
How the Brain Works And Why it Probably Doesn`t Work this way!
... different pathways in different patients; while patients may show very individual patterns of demyelination (and therefore different signs/symptoms), there are some sites that appear to be more commonly affected; for example, the optic nerve is commonly involved, as is the deep white matter of the h ...
... different pathways in different patients; while patients may show very individual patterns of demyelination (and therefore different signs/symptoms), there are some sites that appear to be more commonly affected; for example, the optic nerve is commonly involved, as is the deep white matter of the h ...
12-nervoussystemintro - Alexmac
... • Injured neurons in the central nervous system don’t regenerate easily. • Some neurons in peripheral nervous system can regrow and repair a small gap. ...
... • Injured neurons in the central nervous system don’t regenerate easily. • Some neurons in peripheral nervous system can regrow and repair a small gap. ...