NeuralCell-Neurons.stud
... Neurons differ from Other Cells 1. Neurons have specialized projections called dendrites and axons. Dendrites take information to the cell body and axons take information away from the cell body 2. Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process 3. Neurons contain some specia ...
... Neurons differ from Other Cells 1. Neurons have specialized projections called dendrites and axons. Dendrites take information to the cell body and axons take information away from the cell body 2. Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process 3. Neurons contain some specia ...
NERVES
... the nervous system, having structure and properties that allow it to conduct signals by taking advantage of the electrical charge across its cell membrane › In the simplest animals with a nervous system (ex. cnidarians), the neurons controlling the contraction and expansion of their gastrovascular c ...
... the nervous system, having structure and properties that allow it to conduct signals by taking advantage of the electrical charge across its cell membrane › In the simplest animals with a nervous system (ex. cnidarians), the neurons controlling the contraction and expansion of their gastrovascular c ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... system. The somatic system serves the skin, skeletal muscles, and tendons. Some actions in the somatic system are due to reflexes, which are automatic responses to a stimulus. The Reflex Arc Reflexes are programmed, built-in circuits that allow for protection and survival. They require no conscious ...
... system. The somatic system serves the skin, skeletal muscles, and tendons. Some actions in the somatic system are due to reflexes, which are automatic responses to a stimulus. The Reflex Arc Reflexes are programmed, built-in circuits that allow for protection and survival. They require no conscious ...
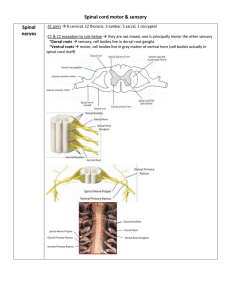
Changes in spinal cord
... *branches or interneurons at terminal level *mainly function to control “automatic functions” such as walking or posture -tectospinal *from superior colliculus to ventral horn of cervical region *decussates at level of colliculus *only functions in upper limb/neck *tectum is associated with visual m ...
... *branches or interneurons at terminal level *mainly function to control “automatic functions” such as walking or posture -tectospinal *from superior colliculus to ventral horn of cervical region *decussates at level of colliculus *only functions in upper limb/neck *tectum is associated with visual m ...
Nervous Tissue
... – neurons from cutaneous and special sensory receptors to the CNS – motor neurons to skeletal muscle tissue ...
... – neurons from cutaneous and special sensory receptors to the CNS – motor neurons to skeletal muscle tissue ...
Hypothalamic arcuate nucleus: neurons in the meeting
... and autonomic regulatory mechanisms of the central nervous system. More than 50 years ago. the parvicellular neurosecretion. as a concept has been introduced on the basis of studies by what the secretory activity of arcute neurons into the pituitary portal vessels had been clearly demonstrated. The ...
... and autonomic regulatory mechanisms of the central nervous system. More than 50 years ago. the parvicellular neurosecretion. as a concept has been introduced on the basis of studies by what the secretory activity of arcute neurons into the pituitary portal vessels had been clearly demonstrated. The ...
MyersExpPsych7e_IM_Module 03 garber edited
... • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
... • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
Chapter 2 - davis.k12.ut.us
... 7. The minimum level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse is called the A) reflex. B) threshold. C) synapse. D) action potential. E) refractory period. 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will not affect the intensity of an action potential. This ...
... 7. The minimum level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse is called the A) reflex. B) threshold. C) synapse. D) action potential. E) refractory period. 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will not affect the intensity of an action potential. This ...
The Boltzmann Machine
... • This reduces the difference between what the network settles to when the inputs are clamped, and what it settles to when its allowed to free-run. • So, the weights learn about what kinds of visible units go together. • Recruits hidden units to help learn higher ...
... • This reduces the difference between what the network settles to when the inputs are clamped, and what it settles to when its allowed to free-run. • So, the weights learn about what kinds of visible units go together. • Recruits hidden units to help learn higher ...
Nervous System
... Processes that conduct electrical currents toward the cell body are dendrites (depending on type, a neuron may have hundreds of dendrites) Processes that generate nerve impulses and conduct them away from the cell body are axons (only one axon) (some have a collateral branch along its length) (all b ...
... Processes that conduct electrical currents toward the cell body are dendrites (depending on type, a neuron may have hundreds of dendrites) Processes that generate nerve impulses and conduct them away from the cell body are axons (only one axon) (some have a collateral branch along its length) (all b ...
Brain Regions
... together in a highly organized fashion to form the rapid control center of the body. • Functions include: – Integrating center for homeostasis, movement, and almost all other body functions. – The mysterious source of those traits that we think of as setting humans apart from animals ...
... together in a highly organized fashion to form the rapid control center of the body. • Functions include: – Integrating center for homeostasis, movement, and almost all other body functions. – The mysterious source of those traits that we think of as setting humans apart from animals ...
The Nervous System
... The CNS receives and analyzes this information and initiates responses. PNS then picks up and carries the response signals. The information is transmitted throughout our body by means of electrical charges called impulses. (up to 248 mph) The messengers and receivers of these transmissions are neuro ...
... The CNS receives and analyzes this information and initiates responses. PNS then picks up and carries the response signals. The information is transmitted throughout our body by means of electrical charges called impulses. (up to 248 mph) The messengers and receivers of these transmissions are neuro ...
36.1: The Nervous System
... Controls and coordinates the body’s responses to changes in the environment HOW: Stimulus: a change in the external or internal environment which initiates an impulse Impulse~ an electro-chemical charge generated along a neuron Receptors~ structures specialized to detect certain stimuli Response~ a ...
... Controls and coordinates the body’s responses to changes in the environment HOW: Stimulus: a change in the external or internal environment which initiates an impulse Impulse~ an electro-chemical charge generated along a neuron Receptors~ structures specialized to detect certain stimuli Response~ a ...
The Nervous System - leavingcertbiology.net
... • The central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system both consist of nerve cells • Nerve cells are the fundamental structural and functional units of the nervous system • There are many different types of nerve cell – an important one being the neuron • The neuron is a specialised nerve ce ...
... • The central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system both consist of nerve cells • Nerve cells are the fundamental structural and functional units of the nervous system • There are many different types of nerve cell – an important one being the neuron • The neuron is a specialised nerve ce ...
The Nervous System
... • There are 4 specific types of cells that form the tissues of the nervous system. – 1) sensory neurons transmit incoming impulses from receptors in sense organs (eyes, ears, skin, nose) to the brain or spinal cord, where they are interpreted. – 2) motor neurons act once the sensory neuron sends its ...
... • There are 4 specific types of cells that form the tissues of the nervous system. – 1) sensory neurons transmit incoming impulses from receptors in sense organs (eyes, ears, skin, nose) to the brain or spinal cord, where they are interpreted. – 2) motor neurons act once the sensory neuron sends its ...
A horizontal spinal cord slice preparation for studying descending
... synaptic transmission in spinal neurons have concentrated on inputs from two sources; those from primary afferents and local circuit neurons. This focus is due largely to practical considerations. For example, peripheral inputs can be readily activated by stimulation of dorsal roots that often remai ...
... synaptic transmission in spinal neurons have concentrated on inputs from two sources; those from primary afferents and local circuit neurons. This focus is due largely to practical considerations. For example, peripheral inputs can be readily activated by stimulation of dorsal roots that often remai ...