$doc.title
... excess or unnecessary connections (and potentially nodes as well). This technique allows for robustness in nodes and connections that appear together, an effect of learning. If there are not enough occurrence ...
... excess or unnecessary connections (and potentially nodes as well). This technique allows for robustness in nodes and connections that appear together, an effect of learning. If there are not enough occurrence ...
A novel neuroprosthetic interface with the peripheral nervous system
... In this paper, we describe a novel hybrid neuroprosthetic interface platform, consisting of biocompatible electrodes coupled to neural tissue constructs. For this to become clinically feasible, however, much work remains to be done. In addition to looking for markers of host axon ingrowth and synapt ...
... In this paper, we describe a novel hybrid neuroprosthetic interface platform, consisting of biocompatible electrodes coupled to neural tissue constructs. For this to become clinically feasible, however, much work remains to be done. In addition to looking for markers of host axon ingrowth and synapt ...
Distributed Modular Architectures Linking Basal Ganglia
... spiny neurons (SP). This feature is well suited for contextual pattern recognition (Houk and Wise, 1993; Wise and Houk, 1994). We postulate that, through the mediation of reinforcement training signals provided by the dopaminergic cells of the midbrain, this neuronal architecture learns to recognize ...
... spiny neurons (SP). This feature is well suited for contextual pattern recognition (Houk and Wise, 1993; Wise and Houk, 1994). We postulate that, through the mediation of reinforcement training signals provided by the dopaminergic cells of the midbrain, this neuronal architecture learns to recognize ...
Article
... compared to the time scale of an action potential or synaptic transmission [6–8]. Moreover, the duration of each cycle can change according to the circumstances [9]. In general, CPG networks consist of interconnected interneurons that generate motor patterns underlying rhythmic behaviors. Since inte ...
... compared to the time scale of an action potential or synaptic transmission [6–8]. Moreover, the duration of each cycle can change according to the circumstances [9]. In general, CPG networks consist of interconnected interneurons that generate motor patterns underlying rhythmic behaviors. Since inte ...
presentation
... The cell body of one neuron is located in the spinal cord and brain and the second extends to a visceral effector. The Preganglionic fiber is the axon within the cell body that is located in the brain and spinal cord in which it travels through the CNS and synapse with the neurons within an autonomi ...
... The cell body of one neuron is located in the spinal cord and brain and the second extends to a visceral effector. The Preganglionic fiber is the axon within the cell body that is located in the brain and spinal cord in which it travels through the CNS and synapse with the neurons within an autonomi ...
Changes in GABA Modulation During a Theta Cycle May Be
... inhibitory interneuron; W, the strength of recurrent excitatory connections from a2 to a2 and a3 to a3 ; W 0 , the strength of excitatory connections from a2 and a3 to the interneuron; −H, the strength of the inhibitory connections from this interneuron to a2 and a3 ; h, activation of the model inte ...
... inhibitory interneuron; W, the strength of recurrent excitatory connections from a2 to a2 and a3 to a3 ; W 0 , the strength of excitatory connections from a2 and a3 to the interneuron; −H, the strength of the inhibitory connections from this interneuron to a2 and a3 ; h, activation of the model inte ...
14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... The largest part of the brain is the cerebrum, which controls the higher mental functions such as thought, memory and conscious movement. The cerebrum is divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres, and covered by a surface layer of gray matter or neural cortex (cerebral cortex). The surface is ...
... The largest part of the brain is the cerebrum, which controls the higher mental functions such as thought, memory and conscious movement. The cerebrum is divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres, and covered by a surface layer of gray matter or neural cortex (cerebral cortex). The surface is ...
the requirements of the neuroanatomy exam for dentistry students
... - membraneous labyrinth: utricle and saccule, ant., post. and lat. semicircular ducts, cochlear duct, - auditory tube: spaces connected by it, its function, - for recapitulation: facial canal, facial nerve and its branches, tympanic nerve. ...
... - membraneous labyrinth: utricle and saccule, ant., post. and lat. semicircular ducts, cochlear duct, - auditory tube: spaces connected by it, its function, - for recapitulation: facial canal, facial nerve and its branches, tympanic nerve. ...
neuropharmacology of spasticity
... Supraspinal or higher spinal lesion results in a net loss of inhibition below lesion – Dorsal Reticulospinal tract ( - ) – Medial Reticulospinal tract (+) – Corticospinal tract (+) – Vestibulospinal tract (+) – Coerulospinal tract (+) ...
... Supraspinal or higher spinal lesion results in a net loss of inhibition below lesion – Dorsal Reticulospinal tract ( - ) – Medial Reticulospinal tract (+) – Corticospinal tract (+) – Vestibulospinal tract (+) – Coerulospinal tract (+) ...
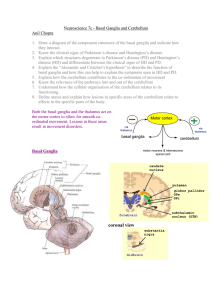
Neuroscience 7c – Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum
... bending a lead pipe- lead pipe rigidity Gait slow, small steps, reduced arm swing. Huntington’s Disease Huntington’s disease is caused by a defective “Huntington Gene” on chromosome 4. This results in the degradation of the spiny GABAergic neurons in the striatum. It is an autosomal dominant disea ...
... bending a lead pipe- lead pipe rigidity Gait slow, small steps, reduced arm swing. Huntington’s Disease Huntington’s disease is caused by a defective “Huntington Gene” on chromosome 4. This results in the degradation of the spiny GABAergic neurons in the striatum. It is an autosomal dominant disea ...
The evolution of nervous system centralization
... by axon tracts (neuropil). The CNS may be subdivided into separate parts (ganglia). It connects to the periphery via nerves. A CNS thus defined is found in various shapes and degrees of complexity in different animal phyla, including vertebrates and many invertebrates, such as echinoderms, arthropod ...
... by axon tracts (neuropil). The CNS may be subdivided into separate parts (ganglia). It connects to the periphery via nerves. A CNS thus defined is found in various shapes and degrees of complexity in different animal phyla, including vertebrates and many invertebrates, such as echinoderms, arthropod ...
Neural Nets
... Inputs are transmitted electrochemically across the input synapses Input potentials are summed. If the potential reaches a threshold, a pulse or action potential moves down the axon. (The neuron has “fired”.) The pulse is distributed at the axonal arborization to the input synapses of other neurons. ...
... Inputs are transmitted electrochemically across the input synapses Input potentials are summed. If the potential reaches a threshold, a pulse or action potential moves down the axon. (The neuron has “fired”.) The pulse is distributed at the axonal arborization to the input synapses of other neurons. ...
Florence Bareyre - scientia.global
... vivo imaging techniques that allow the direct visualisation of regrowing spinal axons and their path to the target cells in vivo, Dr Bareyre joined the Institute of Clinical Neuroimmunology at the LMU Munich. Chasing the Peripheral Vision There are clearly differences in the CNS and PNS that explai ...
... vivo imaging techniques that allow the direct visualisation of regrowing spinal axons and their path to the target cells in vivo, Dr Bareyre joined the Institute of Clinical Neuroimmunology at the LMU Munich. Chasing the Peripheral Vision There are clearly differences in the CNS and PNS that explai ...
56 Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia
... The Purkinje cells learn to correct motor errors: role of climbing fibers ...
... The Purkinje cells learn to correct motor errors: role of climbing fibers ...
Spinal Cord Injury - Deranged Physiology
... Changes associated with loss of reflex activity: Loss of somatic reflexes leads to loss of deep tendon reflexes and a flaccid paralysis of the affected limbs (lower limbs in paraplegics and upper and lower limbs in tetraplegics). Loss of reflex activity in viscera so that the bladder and bowel lose ...
... Changes associated with loss of reflex activity: Loss of somatic reflexes leads to loss of deep tendon reflexes and a flaccid paralysis of the affected limbs (lower limbs in paraplegics and upper and lower limbs in tetraplegics). Loss of reflex activity in viscera so that the bladder and bowel lose ...
Ch 3 Vision - Texas A&M University
... • On a scratch paper, draw two vertical lines of about 2 inches (1/2 inch apart). • Close your left eye, and focus your right eye on your index figure, and move the figure. • At some point, you can’t distinguish the two vertical lines. ...
... • On a scratch paper, draw two vertical lines of about 2 inches (1/2 inch apart). • Close your left eye, and focus your right eye on your index figure, and move the figure. • At some point, you can’t distinguish the two vertical lines. ...
Motor systems(W)
... Motor output comes from the motor cortex Projects through pyramidal tracts to spinal cord, where it synapses with peripheral motor neurones Other pathways run parallel from cortex, basal ganglia and cerebellum via brainstem and spinal cord - these run outside the pyramidal tract and are called the e ...
... Motor output comes from the motor cortex Projects through pyramidal tracts to spinal cord, where it synapses with peripheral motor neurones Other pathways run parallel from cortex, basal ganglia and cerebellum via brainstem and spinal cord - these run outside the pyramidal tract and are called the e ...
14. Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... anterior ramus, and rami communicantes. Each of these latter three structures carries both sensory and motor information. Because each spinal nerve carries both sensory and motor information, spinal nerves are referred to as “mixed nerves.” Posterior rami carry visceral motor, somatic motor, and sen ...
... anterior ramus, and rami communicantes. Each of these latter three structures carries both sensory and motor information. Because each spinal nerve carries both sensory and motor information, spinal nerves are referred to as “mixed nerves.” Posterior rami carry visceral motor, somatic motor, and sen ...
NEURO PresentationWORKING students A
... • extracts from damaged tissue cause pain when injected under the skin • bradykinin causes the most pain and may be the single agent most responsible for causing the tissue damage type of pain – also the local increase in potassium ion concentration and action of enzymes can contribute to pain ...
... • extracts from damaged tissue cause pain when injected under the skin • bradykinin causes the most pain and may be the single agent most responsible for causing the tissue damage type of pain – also the local increase in potassium ion concentration and action of enzymes can contribute to pain ...
Comparative study of indriyas in relation to functional
... The cerebellum is involved in maintaining balance and muscle tone and in coordinating fine motor movements. A major function of the cerebellum is that of a comparator. A comparator is a sensing device that compares the data from two sources- in this case, the motor cortex and peripheral structures. ...
... The cerebellum is involved in maintaining balance and muscle tone and in coordinating fine motor movements. A major function of the cerebellum is that of a comparator. A comparator is a sensing device that compares the data from two sources- in this case, the motor cortex and peripheral structures. ...
Dopamine control of pyramidal neuron activity in the primary motor
... NaCl solution containing 2.5% neurobiotin (Vector Labs, USA). Electrodes had an in vivo resistance of 12-20 MΩ. Recording electrodes were lowered in M1 (1.3 to 1.5 mm lateral and 1.0 to 1.5 mm anterior to bregma) at a depth of between 0.65 mm and 1 mm from the brain surface. Neuronal activity was am ...
... NaCl solution containing 2.5% neurobiotin (Vector Labs, USA). Electrodes had an in vivo resistance of 12-20 MΩ. Recording electrodes were lowered in M1 (1.3 to 1.5 mm lateral and 1.0 to 1.5 mm anterior to bregma) at a depth of between 0.65 mm and 1 mm from the brain surface. Neuronal activity was am ...
Cough, Expiration and Aspiration Reflexes following
... Shannon et al. (1998, 2000). According to this model neuronal circuitries of the Respiratory Central Pattern Generator can also produce the cough motor pattern. However, the possibility that other brainstem circuits overlapping the main respiratory networks may also participate has not been excluded ...
... Shannon et al. (1998, 2000). According to this model neuronal circuitries of the Respiratory Central Pattern Generator can also produce the cough motor pattern. However, the possibility that other brainstem circuits overlapping the main respiratory networks may also participate has not been excluded ...
PowerPoint to accompany Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... music, and complex patterns • Parietal lobe association areas • Occipital lobe association areas • Understanding speech • Analyze and combine visual • Choosing words to express images with other sensory thought experiences ...
... music, and complex patterns • Parietal lobe association areas • Occipital lobe association areas • Understanding speech • Analyze and combine visual • Choosing words to express images with other sensory thought experiences ...