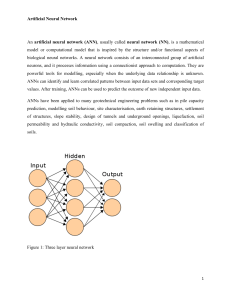
Artificial Neural Network An artificial neural network (ANN)
... one feedback loop. Thus, in these networks, for example, there could exist one layer with feedback connections as shown in figure below. There could also be neurons with self feed back links, i.e. the output of a neuron is fed back into itself as input. Recurrent neural networks that do contain feed ...
... one feedback loop. Thus, in these networks, for example, there could exist one layer with feedback connections as shown in figure below. There could also be neurons with self feed back links, i.e. the output of a neuron is fed back into itself as input. Recurrent neural networks that do contain feed ...
20. Nervous system. Spinal cord
... • Posterior horns contain interneurons. • Anterior horns contain some • interneurons as well as the cell bodies of motor neurons. – These cell bodies project their axons via the ventral roots of the spinal cord to the skeletal muscles. – The amount of ventral gray matter at a given level of the spi ...
... • Posterior horns contain interneurons. • Anterior horns contain some • interneurons as well as the cell bodies of motor neurons. – These cell bodies project their axons via the ventral roots of the spinal cord to the skeletal muscles. – The amount of ventral gray matter at a given level of the spi ...
Control of Wake and Sleep States
... thalamus through CT projections. They consist of prolonged depolarizations associated with extracellular gamma activity (up) separated by prolonged hyperpolarizations (down states) when most cortical neurons are silent. Up State is caused by excitatory glutamatergic synaptic input. ...
... thalamus through CT projections. They consist of prolonged depolarizations associated with extracellular gamma activity (up) separated by prolonged hyperpolarizations (down states) when most cortical neurons are silent. Up State is caused by excitatory glutamatergic synaptic input. ...
Laboratory 7: Medulla
... laminae II and III of the spinal cord. The raphe also send ascending fibers to the forebrain. The midline location of this nucleus suggests an older phylogenetic origin. It’s location next to and within the reticular formation indicates a role in the reticular modulation of pain. The raphe slow reti ...
... laminae II and III of the spinal cord. The raphe also send ascending fibers to the forebrain. The midline location of this nucleus suggests an older phylogenetic origin. It’s location next to and within the reticular formation indicates a role in the reticular modulation of pain. The raphe slow reti ...
A Fast, Reciprocal Pathway between the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
... Consistent with past results (Bullier and Henry, 1980), spike propagation in the geniculocortical pathway was fast, as the mean orthodromic latency among GR neurons was 4.0 ⫾ 0.2 ms (Fig. 3A, dashed line). Orthodromic latencies for GRCG neurons were similar with an average latency of 4.2 ⫾ 0.4 ms ( ...
... Consistent with past results (Bullier and Henry, 1980), spike propagation in the geniculocortical pathway was fast, as the mean orthodromic latency among GR neurons was 4.0 ⫾ 0.2 ms (Fig. 3A, dashed line). Orthodromic latencies for GRCG neurons were similar with an average latency of 4.2 ⫾ 0.4 ms ( ...
A lineage-related reciprocal inhibition circuitry for sensory
... Table 1). These data suggest that c232 and EB1 R neurons are inhibitory GABAergic interneurons. To test this hypothesis, we carried out functional imaging using the bioluminescent photoprotein GFP-aequorin (GA)40. We expressed GA in c232 neurons and measured photon emission related to calciuminduced ...
... Table 1). These data suggest that c232 and EB1 R neurons are inhibitory GABAergic interneurons. To test this hypothesis, we carried out functional imaging using the bioluminescent photoprotein GFP-aequorin (GA)40. We expressed GA in c232 neurons and measured photon emission related to calciuminduced ...
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
... on the opposite side of the body. The crossover occurs in the medulla, after a synapse in the nucleus gracilis or nucleus cuneatus. ...
... on the opposite side of the body. The crossover occurs in the medulla, after a synapse in the nucleus gracilis or nucleus cuneatus. ...
Ch12 notes Martini 9e
... • Somatic nervous system (SNS); Includes all somatic motor neurons that innervate skeletal muscles © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Somatic nervous system (SNS); Includes all somatic motor neurons that innervate skeletal muscles © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_9_lecture
... Prepares the body for intense physical activity in emergencies by increasing heart rate and blood glucose levels and by diverting blood to skeletal muscles Tonically regulates heart, blood vessels, and ...
... Prepares the body for intense physical activity in emergencies by increasing heart rate and blood glucose levels and by diverting blood to skeletal muscles Tonically regulates heart, blood vessels, and ...
Connectivity in Real and Simulated Associative Memories
... connectivity (Bollobas, 2001). Recently, however, there has been an explosion of interest in networks with non-random connectivity graphs, such as small-world and scale-free networks. The seminal paper of Watts and Strogatz (Watts & Strogatz, 1998) formalised the notion of a small-world network. The ...
... connectivity (Bollobas, 2001). Recently, however, there has been an explosion of interest in networks with non-random connectivity graphs, such as small-world and scale-free networks. The seminal paper of Watts and Strogatz (Watts & Strogatz, 1998) formalised the notion of a small-world network. The ...
Lamprey cranial neural crest migration (fore/midbrain)
... Gain and loss of function approaches: 1) Antisense morpholino-mediated knock down 2) Over-expession by electroporation 3) Over-expression of dominant negative constructs 4) RNAi ...
... Gain and loss of function approaches: 1) Antisense morpholino-mediated knock down 2) Over-expession by electroporation 3) Over-expression of dominant negative constructs 4) RNAi ...
Neuroscience 7b – Cortical Motor Function
... A small population of cortical neurones in M1 controls small movements. These are movements that are specific, distal (i.e. fingers) and delicate/precise. ...
... A small population of cortical neurones in M1 controls small movements. These are movements that are specific, distal (i.e. fingers) and delicate/precise. ...
Non- directed synapses
... • An acute infectious disease of humans, particularly children, caused by any of three serotypes of human poliovirus (POLIOVIRUS). Usually the infection is limited to the gastrointestinal tract and nasopharynx, and is often asymptomatic. The central nervous system, primarily the spinal cord, may be ...
... • An acute infectious disease of humans, particularly children, caused by any of three serotypes of human poliovirus (POLIOVIRUS). Usually the infection is limited to the gastrointestinal tract and nasopharynx, and is often asymptomatic. The central nervous system, primarily the spinal cord, may be ...
BIo 218 Lecture Outline Tortora Ch18
... travel inferiorly to form the cauda equina. vi. Each of the 31 pairs of spinal nerves emerge from a spinal segment; the spinal nerves are named and numbered according to the region and level of the spinal cord from which they emerge: a. 8 pairs of cervical nerves (the first pair emerge between the a ...
... travel inferiorly to form the cauda equina. vi. Each of the 31 pairs of spinal nerves emerge from a spinal segment; the spinal nerves are named and numbered according to the region and level of the spinal cord from which they emerge: a. 8 pairs of cervical nerves (the first pair emerge between the a ...
homeostasis - TeacherWeb
... a complete structure; never static; is in perpetual inner selfconstruction and selfdestruction; we destroy in order to make it ...
... a complete structure; never static; is in perpetual inner selfconstruction and selfdestruction; we destroy in order to make it ...
Brainwaves ("40 Hz") Research
... Frisbee. A more plausible idea for how we accomplish such tasks is that transient "binding" functionally links the often discontinuous cortical networks needed to analyze the many features that make up real objects [7] and, conversely, "scene segmentation" functionally separates the networks encodin ...
... Frisbee. A more plausible idea for how we accomplish such tasks is that transient "binding" functionally links the often discontinuous cortical networks needed to analyze the many features that make up real objects [7] and, conversely, "scene segmentation" functionally separates the networks encodin ...