1-Student`s Refexes
... impulses to the Intrafusal Fibers inside the muscle spindle leading to shortening of the peripheral contractile parts of the intrafusal fibres increase the sensitivity of the receptor to muscle stretch . ...
... impulses to the Intrafusal Fibers inside the muscle spindle leading to shortening of the peripheral contractile parts of the intrafusal fibres increase the sensitivity of the receptor to muscle stretch . ...
21. Basal ganglion
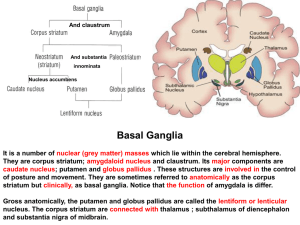
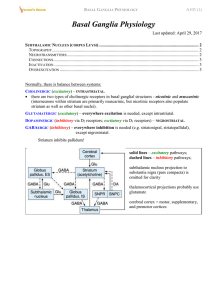
... They are corpus striatum; amygdaloid nucleus and claustrum. Its major components are caudate nucleus; putamen and globus pallidus . These structures are involved in the control of posture and movement. They are sometimes referred to anatomically as the corpus striatum but clinically, as basal gangli ...
... They are corpus striatum; amygdaloid nucleus and claustrum. Its major components are caudate nucleus; putamen and globus pallidus . These structures are involved in the control of posture and movement. They are sometimes referred to anatomically as the corpus striatum but clinically, as basal gangli ...
nervous system physiology 7
... Normally, the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems are continually active, and the basal rates of activity are known, respectively, as sympathetic tone and parasympathetic tone. The value of tone is that it allows a single nervous system both to increase and to decrease the activity of a stimulat ...
... Normally, the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems are continually active, and the basal rates of activity are known, respectively, as sympathetic tone and parasympathetic tone. The value of tone is that it allows a single nervous system both to increase and to decrease the activity of a stimulat ...
The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST), a structure
... processing, such as the prefrontal cortex and the hippocampal formation. This information only becomes a stressor once it has been processed and compared to prior events in one’s experience. The BNST also receives “systemic” stressor information, i.e. hypotension or hemorrhage. This input comes dire ...
... processing, such as the prefrontal cortex and the hippocampal formation. This information only becomes a stressor once it has been processed and compared to prior events in one’s experience. The BNST also receives “systemic” stressor information, i.e. hypotension or hemorrhage. This input comes dire ...
The All or None Law - twynham a level pe
... The problem with this is that fatigue will soon occur. ...
... The problem with this is that fatigue will soon occur. ...
Two Kinds of Reverse Inference in Cognitive Neuroscience
... overlap in part of the neural pattern observed in both conditions (execution and observation) but neither makes specific predictions regarding the fine-grained structure of this pattern. Next, consider location, the result that MN (the set of mirror neurons that selectively fire at the same rate in ...
... overlap in part of the neural pattern observed in both conditions (execution and observation) but neither makes specific predictions regarding the fine-grained structure of this pattern. Next, consider location, the result that MN (the set of mirror neurons that selectively fire at the same rate in ...
BN16 Neural plasticity
... Purkinje cells only output from cerebellar cortex inhibit deep cerebellar nuclei Input to Purkinje cells Mossy fibers via parallel fibers ...
... Purkinje cells only output from cerebellar cortex inhibit deep cerebellar nuclei Input to Purkinje cells Mossy fibers via parallel fibers ...
Time cited
... Abstract: Neurotrophic factors, such as nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor, are members of the structurally related neurotrophin family that play important roles in pain modulation. Although there are also indications for the involvement of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic ...
... Abstract: Neurotrophic factors, such as nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor, are members of the structurally related neurotrophin family that play important roles in pain modulation. Although there are also indications for the involvement of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic ...
What We Can and What We Can`t Do with fMRI
... about synapses, neurons, and their interconnections. In the same way, to understand the functioning of a distributed large-scale system, such as that underlying our memory or linguistic capacities, one must first understand the architectural units that organize neural populations of similar properti ...
... about synapses, neurons, and their interconnections. In the same way, to understand the functioning of a distributed large-scale system, such as that underlying our memory or linguistic capacities, one must first understand the architectural units that organize neural populations of similar properti ...
Marginal chimera state at cross-frequency locking of pulse
... Studies of the dynamics of globally coupled populations of oscillators, pioneered more than 40 years ago by Winfree and Kuramoto [1], are the focus of current research due to numerous applications in diverse fields from physics to neuroscience, but also due to striking effects such as synchronizatio ...
... Studies of the dynamics of globally coupled populations of oscillators, pioneered more than 40 years ago by Winfree and Kuramoto [1], are the focus of current research due to numerous applications in diverse fields from physics to neuroscience, but also due to striking effects such as synchronizatio ...
This is all we can do!
... shows single neuron but pain would stimulate many neurons that are become bundled together in nerve. Motor output would also be carried by many neurons that stimulate many muscle cells causing movement response. ...
... shows single neuron but pain would stimulate many neurons that are become bundled together in nerve. Motor output would also be carried by many neurons that stimulate many muscle cells causing movement response. ...
The Spinal Cord
... – depends on location, extent of damage – monoplegia: 1 limb – paraplegia: both lower limbs – hemiplegia: upper limb, trunk, lower limb on 1 side of body – quadriplegia: all 4 limbs & trunk ...
... – depends on location, extent of damage – monoplegia: 1 limb – paraplegia: both lower limbs – hemiplegia: upper limb, trunk, lower limb on 1 side of body – quadriplegia: all 4 limbs & trunk ...
Sensory Pathways
... 1. Most often, these two divisions have opposing effects • If the sympathetic division causes excitation, the ...
... 1. Most often, these two divisions have opposing effects • If the sympathetic division causes excitation, the ...
Michael Arbib: CS564 - Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence
... Michael Arbib CS564 - Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence, USC, Fall 2001. Lecture 20. Schemas 1 ...
... Michael Arbib CS564 - Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence, USC, Fall 2001. Lecture 20. Schemas 1 ...
Probing scale interaction in brain dynamics through synchronization
... dynamics, as initially proposed by Hodgkin & Huxley [1,2], or by more abstract models of neural excitation such as the integrate-and-fire model [3,4] or the FitzHugh–Nagumo model [5,6]. The set of equations representing each neuron’s membrane potential can be coupled in a way that mimics the synapti ...
... dynamics, as initially proposed by Hodgkin & Huxley [1,2], or by more abstract models of neural excitation such as the integrate-and-fire model [3,4] or the FitzHugh–Nagumo model [5,6]. The set of equations representing each neuron’s membrane potential can be coupled in a way that mimics the synapti ...
Action potential
... Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) Graded hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane ...
... Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) Graded hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane ...
Funkcje ruchowe
... the same patterns of activity in the premotor and posterior parietal cortical areas as those that occur during performance of the movement Fourth, the premotor areas activated during a particular task are not the same over time but change progressively as performance becomes automatic. ...
... the same patterns of activity in the premotor and posterior parietal cortical areas as those that occur during performance of the movement Fourth, the premotor areas activated during a particular task are not the same over time but change progressively as performance becomes automatic. ...