Action potential
... Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) Graded hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane ...
... Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) Graded hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... recognition. In this case face recognition is very useful to easily detect the human faces. This face recognition is a very challenging area in computer vision and pattern recognition due to various variations in facial expressions, poses, Illumination, changes in temperature, sweating, aging and sk ...
... recognition. In this case face recognition is very useful to easily detect the human faces. This face recognition is a very challenging area in computer vision and pattern recognition due to various variations in facial expressions, poses, Illumination, changes in temperature, sweating, aging and sk ...
Chapter 3 The Nervous System and the Brain
... The spinal nerves and the peripheral nervous system can be divided into four categories. The Somatic afferent, the Somatic efferent, the Visceral afferent, and the Visceral efferent. Somatic afferent neurons are sensory indicators that conduct impulses and send information to and from receptors in ...
... The spinal nerves and the peripheral nervous system can be divided into four categories. The Somatic afferent, the Somatic efferent, the Visceral afferent, and the Visceral efferent. Somatic afferent neurons are sensory indicators that conduct impulses and send information to and from receptors in ...
Nervous System
... ______ 14. The part of the brain that controls balance, posture, and movement is the a. hypothalamus. b. cortex. c. cerebellum. ______ 15. The part of a neuron that receives information from other neurons is a a. synapse. b. dendrite. c. nucleus. ______ 16. A sudden, rapid, and involuntary self-prot ...
... ______ 14. The part of the brain that controls balance, posture, and movement is the a. hypothalamus. b. cortex. c. cerebellum. ______ 15. The part of a neuron that receives information from other neurons is a a. synapse. b. dendrite. c. nucleus. ______ 16. A sudden, rapid, and involuntary self-prot ...
Neurons - Noba Project
... Photo Credit: Changes in Membrane Potentials of Neurons. Noba Staff. http://nobaproject.com/modules/neurons#action-potential https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-ncsa/4.0/deed.en_US Photo Credit: Version 8.25 from the Textbook OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology Published May 18, 2016 OpenStax ...
... Photo Credit: Changes in Membrane Potentials of Neurons. Noba Staff. http://nobaproject.com/modules/neurons#action-potential https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-ncsa/4.0/deed.en_US Photo Credit: Version 8.25 from the Textbook OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology Published May 18, 2016 OpenStax ...
Session 2 Neurons - Creature and Creator
... Of note is the fact that most of the neurons in the brain are in the cerebellum. The cerebellum is largely cortex and the cortex is packed with tiny cells. The cerebrum contains a lot more connecting fibers – these form the white matter within and between the hemispheres. These links between neurons ...
... Of note is the fact that most of the neurons in the brain are in the cerebellum. The cerebellum is largely cortex and the cortex is packed with tiny cells. The cerebrum contains a lot more connecting fibers – these form the white matter within and between the hemispheres. These links between neurons ...
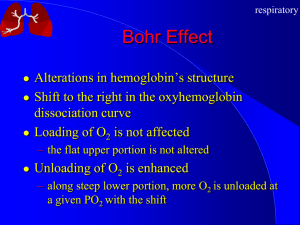
Respiration - Weber State University
... Carbon dioxide pressure in arterial plasma (PaCO2) provides the most important respiratory stimulus at rest. Urge to breathe after 40 s breath-holding results mainly from increased arterial PCO2. Hyperventilation decreases Alveolar PCO2 to 15 mm Hg, which decreases PaCO2 below normal, allows longer ...
... Carbon dioxide pressure in arterial plasma (PaCO2) provides the most important respiratory stimulus at rest. Urge to breathe after 40 s breath-holding results mainly from increased arterial PCO2. Hyperventilation decreases Alveolar PCO2 to 15 mm Hg, which decreases PaCO2 below normal, allows longer ...
The autonomic nervous system
... - It regulates bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, urination, respiratory rate etc. - Within the brain, the ANS regulated by the hypothalamus ...
... - It regulates bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, urination, respiratory rate etc. - Within the brain, the ANS regulated by the hypothalamus ...
Synaptic Transmission and Neurotransmitters
... – Principal excitatory NT in central nervous system – Critical for learning: it is Glutamate and the NMDA receptors that allow for long term potentiation – May play significant role in schizophrenia: disrupts regulation of DA, NE, Ach, 5HT. • Affects memory formation • Affects arousal • Affects proc ...
... – Principal excitatory NT in central nervous system – Critical for learning: it is Glutamate and the NMDA receptors that allow for long term potentiation – May play significant role in schizophrenia: disrupts regulation of DA, NE, Ach, 5HT. • Affects memory formation • Affects arousal • Affects proc ...
The Motor System of the Cortex and the Brain Stem
... attach to the skeleton, and intrafusal fibers, which attach to the extrafusal fibers. Extrafusal fibers produce the force that acts on bones and other structures. Intrafusal fibers also produce force, but they are much smaller than extrafusal fibers and the level of force that they produce is neglig ...
... attach to the skeleton, and intrafusal fibers, which attach to the extrafusal fibers. Extrafusal fibers produce the force that acts on bones and other structures. Intrafusal fibers also produce force, but they are much smaller than extrafusal fibers and the level of force that they produce is neglig ...
View PDF - CiteSeerX
... Abstract Mushroom bodies are central brain structures and essentially involved in insect olfactory learning. Within the mushroom bodies c-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-immunoreactive feedback neurons are the most prominent neuron group. The plasticity of inhibitory neural activity within the mushroom bod ...
... Abstract Mushroom bodies are central brain structures and essentially involved in insect olfactory learning. Within the mushroom bodies c-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-immunoreactive feedback neurons are the most prominent neuron group. The plasticity of inhibitory neural activity within the mushroom bod ...
01-Spinal Reflexes Student`s Copy
... stimulus for a considerable time . (2) augments ( reinforces ) the response . It eventually stops or wanes out due to fatigue or due to inhibitory impulses from other parts of CNS with inhibitory interneurons . ...
... stimulus for a considerable time . (2) augments ( reinforces ) the response . It eventually stops or wanes out due to fatigue or due to inhibitory impulses from other parts of CNS with inhibitory interneurons . ...
Anatomy Written Exam #2 Cranial Nerves Introduction Embryological
... i. Afferents from thalamus and cerebral cortex ii. GABA efferents back to thalamus c. Functional Organization of Thalamic Nuclei All thalamic nuclei, except or the reticular nucleus, project to IPSILATERAL cerebral cortex 1. Specific Nuclei- have point to point projections between individual thala ...
... i. Afferents from thalamus and cerebral cortex ii. GABA efferents back to thalamus c. Functional Organization of Thalamic Nuclei All thalamic nuclei, except or the reticular nucleus, project to IPSILATERAL cerebral cortex 1. Specific Nuclei- have point to point projections between individual thala ...
Parts of the Nervous System
... Pyramidal cells of the cerebral cortex All of the cortical output is mediated through pyramidal neurons which are the major excitatory neurons Pyramidal cells can be subdivided into numerous classes based on morphology, laminar location and connectivity Purkinje cells of the cerebellum Anterior horn ...
... Pyramidal cells of the cerebral cortex All of the cortical output is mediated through pyramidal neurons which are the major excitatory neurons Pyramidal cells can be subdivided into numerous classes based on morphology, laminar location and connectivity Purkinje cells of the cerebellum Anterior horn ...
Neurons with Two Sites of Synaptic Integration Learn Invariant
... described by two main variables, corresponding to the two sites of integration (see Figure 1F): A is referred to as the activity of the neuron, and D represents the average potential at the apical dendrite. We simulate a rate coding neural network where a unit’s output is a real number representing ...
... described by two main variables, corresponding to the two sites of integration (see Figure 1F): A is referred to as the activity of the neuron, and D represents the average potential at the apical dendrite. We simulate a rate coding neural network where a unit’s output is a real number representing ...
Neuropeptide-Mediated Facilitation and Inhibition of Sensory Inputs
... acetate and with resistances of 40 – 60 MV. To facilitate intracellular recordings, in some experiments approximately three segments of the rostral end of the spinal cord were isolated from the notochord. This region of the spinal cord was stabilized by placing a plastic net over it, which was secur ...
... acetate and with resistances of 40 – 60 MV. To facilitate intracellular recordings, in some experiments approximately three segments of the rostral end of the spinal cord were isolated from the notochord. This region of the spinal cord was stabilized by placing a plastic net over it, which was secur ...
CHAPTER 13- The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... B) It allows an individual to maintain balance when withdrawing from harm’s way. C) It is contralateral. D) It involves only one spinal segment. E) It is polysynaptic. 43) Which of the following is NOT a reflex typically used for diagnosing neurological disorders? A) patellar reflex B) Babinski sign ...
... B) It allows an individual to maintain balance when withdrawing from harm’s way. C) It is contralateral. D) It involves only one spinal segment. E) It is polysynaptic. 43) Which of the following is NOT a reflex typically used for diagnosing neurological disorders? A) patellar reflex B) Babinski sign ...
Osteo-genesis
... Autonomic Nervous System • It is part of motor section of Visceral PNS. It is exclusively the motor system controlling the activity of cardiac muscle, smooth muscles and glands. • It has two components. Sympathetic System and Para-Sympathetic System. Sympathetic system is activated during fight, fl ...
... Autonomic Nervous System • It is part of motor section of Visceral PNS. It is exclusively the motor system controlling the activity of cardiac muscle, smooth muscles and glands. • It has two components. Sympathetic System and Para-Sympathetic System. Sympathetic system is activated during fight, fl ...
(B) rosiglitazone
... a, Structure of the Kir6.2[DN2–30,K185Q]–GFP transgene. Mice. For generation of POMC-mut-Kir6.2 mice, the mut-Kir6.2 cassette (Kir[D2–30,K185Q]–GFP)7 was inserted into a POMC BAC genomic clone so that the ATG codon replaced that of POMC, as described previously. POMC-mut-Kir6.2 BAC DNA was prepared ...
... a, Structure of the Kir6.2[DN2–30,K185Q]–GFP transgene. Mice. For generation of POMC-mut-Kir6.2 mice, the mut-Kir6.2 cassette (Kir[D2–30,K185Q]–GFP)7 was inserted into a POMC BAC genomic clone so that the ATG codon replaced that of POMC, as described previously. POMC-mut-Kir6.2 BAC DNA was prepared ...