BIOLOGY COMPETITION REVIEW QUESTIONS PRACTICE EXAM
... 30. Which statement about ATP synthesis is FALSE? a. ATP is synthesized only in chloroplasts and mitochondria. b. ATP synthesis in the chloroplast occurs in the thylakoid region of this organelle. c. Proton motive force (proton gradient) drives the formation of ATP in mitochondria. d. ATP synthases ...
... 30. Which statement about ATP synthesis is FALSE? a. ATP is synthesized only in chloroplasts and mitochondria. b. ATP synthesis in the chloroplast occurs in the thylakoid region of this organelle. c. Proton motive force (proton gradient) drives the formation of ATP in mitochondria. d. ATP synthases ...
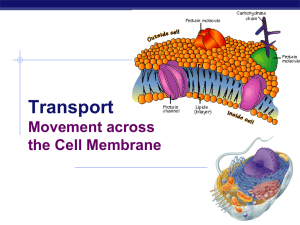
Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane
... Membrane Proteins Proteins determine most of membrane’s specific functions ...
... Membrane Proteins Proteins determine most of membrane’s specific functions ...
Respiration - Dr. Annette M. Parrott
... 1. Glyco lysis (sugar breaking) 2. Kreb’s Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) ...
... 1. Glyco lysis (sugar breaking) 2. Kreb’s Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 Part A
... 1. What are cytochromes? 2. Write a note on the amphoteric nature of proteins. 3. Comment on the following: (i) Isomerization (ii) Tautomerization. 4. What is called line Weaker Burk equation? 5. What is V-Max? 6. Differentiate LDL from HDL. 7. What is chemi-osmotic hypothesis? 8. Comment on auto ox ...
... 1. What are cytochromes? 2. Write a note on the amphoteric nature of proteins. 3. Comment on the following: (i) Isomerization (ii) Tautomerization. 4. What is called line Weaker Burk equation? 5. What is V-Max? 6. Differentiate LDL from HDL. 7. What is chemi-osmotic hypothesis? 8. Comment on auto ox ...
Chapter 5 Membrane Structure and Function
... – A hypotonic solution is one with higher water concentration or ___________________ particle concentration • Water moves across a membrane _____ from the hypotonic solution ...
... – A hypotonic solution is one with higher water concentration or ___________________ particle concentration • Water moves across a membrane _____ from the hypotonic solution ...
Bacterial Rhodopsin Light-driven Proton Pump
... 2. The internal cavity is divided into two half channels, cytoplasmic and external (the H+ pathway) 3. The internal half channel is more hydrophobic. 4. The external half channel is more hydrophilic. 5. The N-terminus of the protein is outside; the C-terminus is inside. Rhodopsin: K296 (out of 348aa ...
... 2. The internal cavity is divided into two half channels, cytoplasmic and external (the H+ pathway) 3. The internal half channel is more hydrophobic. 4. The external half channel is more hydrophilic. 5. The N-terminus of the protein is outside; the C-terminus is inside. Rhodopsin: K296 (out of 348aa ...
Ch. 8 Honors PP
... translocate Na+ and K+ one for one, but pumps 3 sodium ions out for every 2 potassium ions it pumps in - There is a net transfer of 1 positive charge from inside the cell to the outside of the cell with each crank of the pump - This stores energy in the form of voltage ...
... translocate Na+ and K+ one for one, but pumps 3 sodium ions out for every 2 potassium ions it pumps in - There is a net transfer of 1 positive charge from inside the cell to the outside of the cell with each crank of the pump - This stores energy in the form of voltage ...
05 Bioelectrical phenomena in nervous cells
... Depolarization: the membrane potential becomes less negative than the resting potential (close to zero). Hyperpolarization: the membrane potential is more negative than the resting level. ...
... Depolarization: the membrane potential becomes less negative than the resting potential (close to zero). Hyperpolarization: the membrane potential is more negative than the resting level. ...
File
... Exocytosis: movement of materials out of cell through the fusion of the plasma membrane and a transport vesicle Endosytosis: movement of large molecules into the cell by infolding of plasma membrane ...
... Exocytosis: movement of materials out of cell through the fusion of the plasma membrane and a transport vesicle Endosytosis: movement of large molecules into the cell by infolding of plasma membrane ...
Cell Organisation
... • Selectively permeable • Inner membranes have similar structure • Proteins: integral vs peripheral • Modifications • Anchors ...
... • Selectively permeable • Inner membranes have similar structure • Proteins: integral vs peripheral • Modifications • Anchors ...
Ans 518_class 4
... – Low circulating concentrations of insulin: GLUT4 is sequestered within cytosolic vesicles in myocytes and adipocytes – Accumulation of glucose in blood triggers insulin release from pancreatic ß-cells; Insulin-receptor signaling induces the redistribution of GLUT4 from intracellular storage sites ...
... – Low circulating concentrations of insulin: GLUT4 is sequestered within cytosolic vesicles in myocytes and adipocytes – Accumulation of glucose in blood triggers insulin release from pancreatic ß-cells; Insulin-receptor signaling induces the redistribution of GLUT4 from intracellular storage sites ...
Insights into the inner side: new facettes of endocytosis
... cluster numerous receptors, channels, carriers, but also nonproteinaceous molecules that are involved in signalling. One would presume that such a complex structure is strictly preserved once it has been established. One of the surprises from live cell imaging is the insight into a shockingly high t ...
... cluster numerous receptors, channels, carriers, but also nonproteinaceous molecules that are involved in signalling. One would presume that such a complex structure is strictly preserved once it has been established. One of the surprises from live cell imaging is the insight into a shockingly high t ...
Ch3-4 Cell membrane
... Active Transport - uses ATP energy to move solutes across a membrane. It also requires the assistance of carrier proteins. 1) Channel proteins Channel proteins: form pores in the lipid bi-layer allowing certain ions to cross the membrane. These channel proteins are specialized and allow only part ...
... Active Transport - uses ATP energy to move solutes across a membrane. It also requires the assistance of carrier proteins. 1) Channel proteins Channel proteins: form pores in the lipid bi-layer allowing certain ions to cross the membrane. These channel proteins are specialized and allow only part ...
Biology-1 Exam Two You can write on this exam. Please put a W at
... a. power the synthesis of ATP in photosynthesis b. power the synthesis of ATP in cellular respiration c. involve the transfer of electrons to more electronegative atoms d. b and c e. all of the above 28. During aerobic respiration, electrons travel downhill in which sequence? a. food → citric acid c ...
... a. power the synthesis of ATP in photosynthesis b. power the synthesis of ATP in cellular respiration c. involve the transfer of electrons to more electronegative atoms d. b and c e. all of the above 28. During aerobic respiration, electrons travel downhill in which sequence? a. food → citric acid c ...
Outline - Membranes 1. Fluid Mosaic Model of Membrane Structure
... Facilitated Diffusion in Red Blood Cells 1) Cl- and bicarbonate ions ...
... Facilitated Diffusion in Red Blood Cells 1) Cl- and bicarbonate ions ...
MEMBRANE-BOUND ELECTRON TRANSFER AND ATP …
... diffuses rapidly within the IMM. Electrons are carried from Complex III to Complex IV by cytochrome c, a small hydrophilic peripheral membrane protein located on the cytosolic or P side of the IMM. Complex II (Succinate-UQ oxidoreductase) is membrane bound and contains the FADH2 as a prosthetic grou ...
... diffuses rapidly within the IMM. Electrons are carried from Complex III to Complex IV by cytochrome c, a small hydrophilic peripheral membrane protein located on the cytosolic or P side of the IMM. Complex II (Succinate-UQ oxidoreductase) is membrane bound and contains the FADH2 as a prosthetic grou ...
Practice Questions
... 16. C - The Nuclear Localization Sequence (II) and start transfer (III) sequence are both part of the primary sequence of a polypeptide and are therefore incorporated during translation. Targeting to the lysosome or for extracellular export require the addition of carbohydrate tags which are added p ...
... 16. C - The Nuclear Localization Sequence (II) and start transfer (III) sequence are both part of the primary sequence of a polypeptide and are therefore incorporated during translation. Targeting to the lysosome or for extracellular export require the addition of carbohydrate tags which are added p ...
HERE
... is called a(n) _lipid bilayer __. 3. The lipid bilayer forms because there is __water__ both inside and _outside_ of the cell. 4. The phosphate _head_ of a phospholipid is polar. It is _attracted_ to water. 5. The long fatty acid _tails_ of a phospholipid are nonpolar. They are _afraid of/ repelled ...
... is called a(n) _lipid bilayer __. 3. The lipid bilayer forms because there is __water__ both inside and _outside_ of the cell. 4. The phosphate _head_ of a phospholipid is polar. It is _attracted_ to water. 5. The long fatty acid _tails_ of a phospholipid are nonpolar. They are _afraid of/ repelled ...
The main points that you should learn from the problems in øvelse 2
... The ER retention signal (ER retrieval signal) is a four amino acid sequence (KDEL) at the C-terminus of ER resident proteins (page 517). The KDEL receptor, which is present in the Golgi and in the ER recognizes the KDEL sequence and binds to it in the Golgi but does not bind to it in the ER (due to ...
... The ER retention signal (ER retrieval signal) is a four amino acid sequence (KDEL) at the C-terminus of ER resident proteins (page 517). The KDEL receptor, which is present in the Golgi and in the ER recognizes the KDEL sequence and binds to it in the Golgi but does not bind to it in the ER (due to ...
Membrane targeting of proteins
... 3.20 Communication between the ER and nucleus prevents the accumulation of unfolded proteins in the lumen • The unfolded protein response: – monitors folding conditions in the ER lumen – initiates a signaling pathway that increases the expression of genes for ER chaperones ...
... 3.20 Communication between the ER and nucleus prevents the accumulation of unfolded proteins in the lumen • The unfolded protein response: – monitors folding conditions in the ER lumen – initiates a signaling pathway that increases the expression of genes for ER chaperones ...
5 Eukaryotic Microbial Structure and Function
... site where ATP is generated by electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation about the same size as bacterial cells reproduce by binary fission as do bacterial cells Mitochondrial Structure ...
... site where ATP is generated by electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation about the same size as bacterial cells reproduce by binary fission as do bacterial cells Mitochondrial Structure ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.