CELLS : the Structural and Functional Units of All Life Forms
... A sphere is the shape with the largest surface area to volume ratio Volume is represented by cytoplasm (site of all reactions) – this unit is ‘cubed’ Need to match supply with demand and import with export, energy amts and pollution also need to be considered IT is more EFFICIENT to have many, small ...
... A sphere is the shape with the largest surface area to volume ratio Volume is represented by cytoplasm (site of all reactions) – this unit is ‘cubed’ Need to match supply with demand and import with export, energy amts and pollution also need to be considered IT is more EFFICIENT to have many, small ...
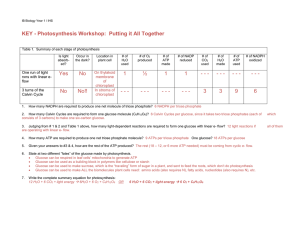
KEY - Photosynthesis Workshop: Putting it All Together
... Glucose can be used to make sucrose, which is the “traveling” form of sugar in a plant, and sent to feed the roots, which don’t do photosynthesis ...
... Glucose can be used to make sucrose, which is the “traveling” form of sugar in a plant, and sent to feed the roots, which don’t do photosynthesis ...
Membranes and Transport - Bio-Guru
... • Ion pumps – like the Na+ / K+ pump and the Proton pump (H+) are an example of active transport • Concentration of Na+ has to be higher outside the cell whereas that of K+ has to be higher inside the cell – so active transport is used to maintain these concentrations (pumping against electrochemica ...
... • Ion pumps – like the Na+ / K+ pump and the Proton pump (H+) are an example of active transport • Concentration of Na+ has to be higher outside the cell whereas that of K+ has to be higher inside the cell – so active transport is used to maintain these concentrations (pumping against electrochemica ...
cell respiration wilk hl ibdp
... • As a result the more and more H+ ions ( protons) are transferred to the inter membrane space. Cytochrome c oxidase ultimately transfers electrons to Oxygen (terminal e acceptor) and water is formed as an end product. ...
... • As a result the more and more H+ ions ( protons) are transferred to the inter membrane space. Cytochrome c oxidase ultimately transfers electrons to Oxygen (terminal e acceptor) and water is formed as an end product. ...
Nervous System
... Membrane is more permeable to K+ than Na+ so diffusion more likely. Na+ channels often closed. ...
... Membrane is more permeable to K+ than Na+ so diffusion more likely. Na+ channels often closed. ...
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration
... We eat a potato which is full of the polysaccharide glycogen which is digested by salivary amylase. The polysaccaride is broken down to monosaccarides glucose which are absorbed into the blood through the wall of the small intestine. As the blood glucose level rises the hormone glucagon is released ...
... We eat a potato which is full of the polysaccharide glycogen which is digested by salivary amylase. The polysaccaride is broken down to monosaccarides glucose which are absorbed into the blood through the wall of the small intestine. As the blood glucose level rises the hormone glucagon is released ...
Proteins in Solution and in Membrane
... lipid layer and restrict the diffusion of neighboring lipid molecules • Proteins in membrane interact with each other more than do proteins in solution ...
... lipid layer and restrict the diffusion of neighboring lipid molecules • Proteins in membrane interact with each other more than do proteins in solution ...
Chapter 10 Outline
... What is photosynthesis? How are the chloroplasts a photosynthetic machine? ...
... What is photosynthesis? How are the chloroplasts a photosynthetic machine? ...
222 Coenzymes.p65
... Just as in photosynthesis, the process of respiration involves a series of reactions that occur in different places. Glycolysis occurs in the cell cytoplasm, Krebs Cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria and electron transport occurs on the crista (Fig.2) ...
... Just as in photosynthesis, the process of respiration involves a series of reactions that occur in different places. Glycolysis occurs in the cell cytoplasm, Krebs Cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria and electron transport occurs on the crista (Fig.2) ...
Name Date____________ Block ___ Movement of Materials
... higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. Whether a substance will diffuse across a membrane depends on the permeability of the membrane to that substance as well as the concentration of the substance on either side of the membrane. Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules through a s ...
... higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. Whether a substance will diffuse across a membrane depends on the permeability of the membrane to that substance as well as the concentration of the substance on either side of the membrane. Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules through a s ...
Cells: The Living Units
... Stabilizes neighboring phospholipids and decrease flexibility of cell membrane Plasma Membrane: Structure ...
... Stabilizes neighboring phospholipids and decrease flexibility of cell membrane Plasma Membrane: Structure ...
Power, Sex, Suicide. Mitochondria and the Meaning
... – “…give striking new insights into why we are here at all, whether we are alone in the universe, why we have our sense of individuality, why we should make love, where we trace our ancestral roots, why we must age and die––in short, into the meaning of life.” ...
... – “…give striking new insights into why we are here at all, whether we are alone in the universe, why we have our sense of individuality, why we should make love, where we trace our ancestral roots, why we must age and die––in short, into the meaning of life.” ...
unit-4-notes-cell-membranes
... – These connections are called junctions; they may include gap junctions or tight junctions. ...
... – These connections are called junctions; they may include gap junctions or tight junctions. ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS & RESPIRATION
... a. Light dependent rxns b. electron transport chain c. light independent rxns The Calvin Cycle takes place in the a. mitochondria b. stroma c. nucleus d. thylakoid membrane What product of the light dependent rxn is used in the Calvin Cycle a. oxygen b. carbon dioxide c. NADPH d. chlorophyll What is ...
... a. Light dependent rxns b. electron transport chain c. light independent rxns The Calvin Cycle takes place in the a. mitochondria b. stroma c. nucleus d. thylakoid membrane What product of the light dependent rxn is used in the Calvin Cycle a. oxygen b. carbon dioxide c. NADPH d. chlorophyll What is ...
CHAPTER 7
... ACTIVE TRANSPORT [Lower] → [Higher]; Energy required ~ allows cell to maintain internal conditions that differ from environment Ex: Normal animal cell- higher K+/lower Na+ inside Two forces drive movement (~ electrochemical gradient) 1. chemical force (concentration gradient) 2. electrical force (m ...
... ACTIVE TRANSPORT [Lower] → [Higher]; Energy required ~ allows cell to maintain internal conditions that differ from environment Ex: Normal animal cell- higher K+/lower Na+ inside Two forces drive movement (~ electrochemical gradient) 1. chemical force (concentration gradient) 2. electrical force (m ...
The cell membrane
... Sodium-potassium protein pump Sodium-‐potassium pump = electrogenic pump = Generates a voltage across the membrane -‐More nega@vely charged inside a cell than outside -‐creates an “electrochemical” gradient ...
... Sodium-potassium protein pump Sodium-‐potassium pump = electrogenic pump = Generates a voltage across the membrane -‐More nega@vely charged inside a cell than outside -‐creates an “electrochemical” gradient ...
hyaluronan–plasma membrane direct interaction modulates
... Glycosaminoglycans are the most abundant compounds of the glycocalyx, a highly charged layer of biological macromolecules attached to a cell membrane. This layer functions as a barrier between a cell and its surroundings, meaning that any molecule entering or leaving a cell permeates through it [1]. ...
... Glycosaminoglycans are the most abundant compounds of the glycocalyx, a highly charged layer of biological macromolecules attached to a cell membrane. This layer functions as a barrier between a cell and its surroundings, meaning that any molecule entering or leaving a cell permeates through it [1]. ...
Cell boundaries
... of cell membrane : water in equals water out HYPERTONIC = High concentration of solute molecules than water molecules : water moves out of cell to achieve equilibrium – cell shrinks, dies HYPOTONIC = lower concentration of solute molecules than water molecules : water moves into cell to achieve ...
... of cell membrane : water in equals water out HYPERTONIC = High concentration of solute molecules than water molecules : water moves out of cell to achieve equilibrium – cell shrinks, dies HYPOTONIC = lower concentration of solute molecules than water molecules : water moves into cell to achieve ...
Document
... "Membrane protein folding and oligomerization: the two-stage model" JL Popot and DM Engelman Biochemistry (1990) 29, 4031-7. ...
... "Membrane protein folding and oligomerization: the two-stage model" JL Popot and DM Engelman Biochemistry (1990) 29, 4031-7. ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS - Green Local Schools
... in plants and algae. Absorbs violet, blue, and red lights. Reflect and Transmit Green light – giving plants their GREEN color. – Chlorophyll a – primary photosynthetic pigment – Accessory Pigments – Chlorophyll b and carotenoids ...
... in plants and algae. Absorbs violet, blue, and red lights. Reflect and Transmit Green light – giving plants their GREEN color. – Chlorophyll a – primary photosynthetic pigment – Accessory Pigments – Chlorophyll b and carotenoids ...
Carbohydrates and Lipids - Washington State University
... A. the length of the hydrocarbon chain: as it moves from 10 to 20, the membrane becomes less fluid. B. For a given number of carbons, the presence of unsaturation increases the fluidity of the membrane, because the fatty acids do not pack as tightly. ...
... A. the length of the hydrocarbon chain: as it moves from 10 to 20, the membrane becomes less fluid. B. For a given number of carbons, the presence of unsaturation increases the fluidity of the membrane, because the fatty acids do not pack as tightly. ...
Cell Membrane Jeopardy Review
... Give examples of the three different types of solutions and explain how water molecules would move if a cell was placed in each one. ...
... Give examples of the three different types of solutions and explain how water molecules would move if a cell was placed in each one. ...
Lectures 6 & 7: Powerpoint
... ATP required (has own binding site) Note movement of particles (Ca++) against their concentration gradient ...
... ATP required (has own binding site) Note movement of particles (Ca++) against their concentration gradient ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.