25-1
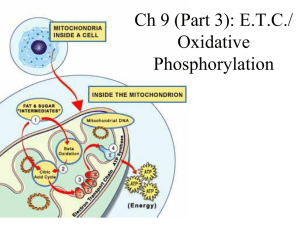
... • Mobile shuttles pass electrons between complexes • Last complex passes its electrons (2H+) to a half of O2 molecule to form a water molecule (H2O) ...
... • Mobile shuttles pass electrons between complexes • Last complex passes its electrons (2H+) to a half of O2 molecule to form a water molecule (H2O) ...
No Slide Title
... • Mobile shuttles pass electrons between complexes • Last complex passes its electrons (2H+) to a half of O2 molecule to form a water molecule (H2O) ...
... • Mobile shuttles pass electrons between complexes • Last complex passes its electrons (2H+) to a half of O2 molecule to form a water molecule (H2O) ...
Ch 9: E.T.C./ Oxidative Phosphorylation
... they accept and donate electrons • each successive group is more electronegative than the group before it, so the electrons are “pulled downhill” towards OXYGEN (the final electron carrier!) ...
... they accept and donate electrons • each successive group is more electronegative than the group before it, so the electrons are “pulled downhill” towards OXYGEN (the final electron carrier!) ...
Document
... In the process of respiration, energy stored in organic food molecules is transferred to the molecule Adenosine Triphosphate ATP. ATP in turn supplies the energy for metabolic processes in the cell. Synthesizing ATP uses a series of linked oxidation and reduction reaction. 8.1.1 Oxidation and Reduct ...
... In the process of respiration, energy stored in organic food molecules is transferred to the molecule Adenosine Triphosphate ATP. ATP in turn supplies the energy for metabolic processes in the cell. Synthesizing ATP uses a series of linked oxidation and reduction reaction. 8.1.1 Oxidation and Reduct ...
aminoacyl-tRNA
... • Protein synthesis occurs on ribosomes: having a large and small subunits, both composing one or two rRNA and many protein molecules. • Protein synthesis can be divided into five stages: activation of amino acids (ATP dependent, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase catalyzed); formation of the initiation com ...
... • Protein synthesis occurs on ribosomes: having a large and small subunits, both composing one or two rRNA and many protein molecules. • Protein synthesis can be divided into five stages: activation of amino acids (ATP dependent, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase catalyzed); formation of the initiation com ...
Notes - Learner
... When the electrons pass from one carrier to another via complex I to IV in the electron transport chain, they are coupled to ATP synthase (complex V). This coupling is necessary for the production of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. The nature of the electron donor decides the number of ATP mol ...
... When the electrons pass from one carrier to another via complex I to IV in the electron transport chain, they are coupled to ATP synthase (complex V). This coupling is necessary for the production of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. The nature of the electron donor decides the number of ATP mol ...
Respiration Respiration Respiration
... -energy is released from oxidation reaction in the form of electrons -electrons are shuttled by electron carriers (e.g. NAD+) to an electron transport chain -electron energy is converted to ATP at the electron transport chain ...
... -energy is released from oxidation reaction in the form of electrons -electrons are shuttled by electron carriers (e.g. NAD+) to an electron transport chain -electron energy is converted to ATP at the electron transport chain ...
Photosynthesis- Photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR)
... pH stroma goes up from 7 Æ 8 Mg2+ increases in stroma NADPH allosteric activator Rubisco Activase catalyzes carbamate formation – CO2 required ...
... pH stroma goes up from 7 Æ 8 Mg2+ increases in stroma NADPH allosteric activator Rubisco Activase catalyzes carbamate formation – CO2 required ...
How Cells Harvest Energy
... DG = -686kcal/mol of glucose DG can be even higher than this in a cell This large amount of energy must be released in small steps rather than all at once. ...
... DG = -686kcal/mol of glucose DG can be even higher than this in a cell This large amount of energy must be released in small steps rather than all at once. ...
chapter-23
... 25. There are many biological molecules that contain high-energy phosphate bonds. ATP is used to power life processes because the energy of hydrolysis of ATP is ________. a. intermediate between the energies of hydrolysis of other organophosphate molecules b. small enough that ADP can easily be recy ...
... 25. There are many biological molecules that contain high-energy phosphate bonds. ATP is used to power life processes because the energy of hydrolysis of ATP is ________. a. intermediate between the energies of hydrolysis of other organophosphate molecules b. small enough that ADP can easily be recy ...
Microbial physiology. Microbial metabolism. Enzymes. Nutrition
... precursors for amino acids, carbohydrates and fats ...
... precursors for amino acids, carbohydrates and fats ...
Self-Organizing Bio-structures
... What about chains longer than 10 amino-acids? What about chain sequence specificity? ...
... What about chains longer than 10 amino-acids? What about chain sequence specificity? ...
Photosynthesis
... Photosynthesis is broken down into 2 stages: 1. Light-dependent reactions – take place in thylakoid membrane 2. Calvin Cycle – uses ATP and NADPH from lightdependent reactions to produce high energy sugars (glucose) ...
... Photosynthesis is broken down into 2 stages: 1. Light-dependent reactions – take place in thylakoid membrane 2. Calvin Cycle – uses ATP and NADPH from lightdependent reactions to produce high energy sugars (glucose) ...
ch8and9notes2011
... • The principal plant pigment is__________________.-chlorophyll a and b • Chlorophyll absorbs light well in the blue-violet and red regions,but not well in the _______________region,which is reflected by leaves • Contain red and orange pigments like _________________,that absorb light in other regio ...
... • The principal plant pigment is__________________.-chlorophyll a and b • Chlorophyll absorbs light well in the blue-violet and red regions,but not well in the _______________region,which is reflected by leaves • Contain red and orange pigments like _________________,that absorb light in other regio ...
Cells and Systems - Topic 1 Practice Quiz
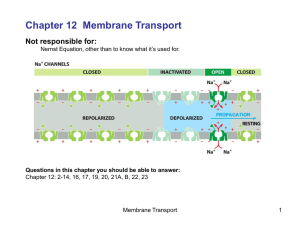
... Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. This process occurs because water will move from an area of ... low concentration to high concentration high concentration to low concentration (Text p. 131) Water moves from a region of high concentration to an area of low ...
... Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. This process occurs because water will move from an area of ... low concentration to high concentration high concentration to low concentration (Text p. 131) Water moves from a region of high concentration to an area of low ...
File
... of amino acids; genetically determined • Secondary Structure – repeated twisting or folding of neighboring amino acids in the polypeptide chain; alpha helixes (spirals) or pleated sheets; ...
... of amino acids; genetically determined • Secondary Structure – repeated twisting or folding of neighboring amino acids in the polypeptide chain; alpha helixes (spirals) or pleated sheets; ...
Slide 1
... Copyright © 2012, American Society for Neurochemistry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Copyright © 2012, American Society for Neurochemistry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
Chapter 9-2 Guided Reading
... 15. What does the electron transport chain use the high-energy electrons from the Krebs cycle for? The chain uses the electrons to convert ADP into ATP. 16. How does the location of the electron transport chain differ in eukaryotes and prokaryotes? In eukaryotes, the chain is composed of a series of ...
... 15. What does the electron transport chain use the high-energy electrons from the Krebs cycle for? The chain uses the electrons to convert ADP into ATP. 16. How does the location of the electron transport chain differ in eukaryotes and prokaryotes? In eukaryotes, the chain is composed of a series of ...
PhotosynthesisCalving CycleON
... twice in order to make a molecule of glucose. (Actually 6 times). 1. Carbon dioxide combines with ribulose biphosphate. Ru-Bp is a pentose monosacharide with 2 ...
... twice in order to make a molecule of glucose. (Actually 6 times). 1. Carbon dioxide combines with ribulose biphosphate. Ru-Bp is a pentose monosacharide with 2 ...
9/14
... Many proteins need to be transported across the bacterial membrane These include flagella and pilus subunits Gram negative bacteria have evolved several systems for the secretion of proteins to the external environment ...
... Many proteins need to be transported across the bacterial membrane These include flagella and pilus subunits Gram negative bacteria have evolved several systems for the secretion of proteins to the external environment ...
Outline - Utexas
... a. glucose completely dismantled b. CO2 produced c. 2 ATP, 6 NADH and 2 FADH2 generated ...
... a. glucose completely dismantled b. CO2 produced c. 2 ATP, 6 NADH and 2 FADH2 generated ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.