III. 5 Test Fotosíntesi
... 16) In the thylakoid membranes, what is the main role of the antenna pigment molecules? A) split water and release oxygen to the reaction-center chlorophyll B) harvest photons and transfer light energy to the reaction-center chlorophyll C) synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi D) transfer electrons to ferr ...
... 16) In the thylakoid membranes, what is the main role of the antenna pigment molecules? A) split water and release oxygen to the reaction-center chlorophyll B) harvest photons and transfer light energy to the reaction-center chlorophyll C) synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi D) transfer electrons to ferr ...
Measuring Mitochondrial Membrane Potential using
... In most eukaryotic cells the majority of ATP production is via oxidative phosphorylation by the respiratory chain. In this way, sugars, such as glucose, and free fatty acids are oxidised, resulting in the pumping of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, creating an electro-chemical gradie ...
... In most eukaryotic cells the majority of ATP production is via oxidative phosphorylation by the respiratory chain. In this way, sugars, such as glucose, and free fatty acids are oxidised, resulting in the pumping of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, creating an electro-chemical gradie ...
Small G-protein
... Rab-GTPases - small GTP binding proteins on vesicles. Related to the oncogene product Ras. Act as tethering factors that mediate initial interaction between membrane Bind to Rab effectors on target membrane. Over 30 diferent Rab proteins specific to different membranes. Another protein (guanine-nuc. ...
... Rab-GTPases - small GTP binding proteins on vesicles. Related to the oncogene product Ras. Act as tethering factors that mediate initial interaction between membrane Bind to Rab effectors on target membrane. Over 30 diferent Rab proteins specific to different membranes. Another protein (guanine-nuc. ...
ch9sec1n2_2013
... If all the energy was released in one step… most would be lost as light and heat ____________________! ...
... If all the energy was released in one step… most would be lost as light and heat ____________________! ...
Lecture 5 & 6 Metabolism S11 Chpt. 6 for HO
... •Oxidizes NADH, generating NAD for use in further rounds of glucose breakdown •Stops short of the transition step and the TCA cycle, which together generate 5X more reducing power ...
... •Oxidizes NADH, generating NAD for use in further rounds of glucose breakdown •Stops short of the transition step and the TCA cycle, which together generate 5X more reducing power ...
Robustness of the model
... among bottlenecks (33% vs. 21% among all nodes, p-value of one-sided Fisher’s exact test: 0.07, see Table S6). However, when we considered bottlenecks that are not hubs, coiled-coil proteins were most over-represented (25% vs. 13%, pvalue 0.11). To control for hubs regardless of their functional cla ...
... among bottlenecks (33% vs. 21% among all nodes, p-value of one-sided Fisher’s exact test: 0.07, see Table S6). However, when we considered bottlenecks that are not hubs, coiled-coil proteins were most over-represented (25% vs. 13%, pvalue 0.11). To control for hubs regardless of their functional cla ...
PDF
... Proteins that belong to the protein phosphatase 1 and actin regulator (phactr) family are involved in cell motility and morphogenesis. However, the mechanisms that regulate the actin cytoskeleton are poorly understood. We have previously shown that phactr3, also known as scapinin, localizes to the p ...
... Proteins that belong to the protein phosphatase 1 and actin regulator (phactr) family are involved in cell motility and morphogenesis. However, the mechanisms that regulate the actin cytoskeleton are poorly understood. We have previously shown that phactr3, also known as scapinin, localizes to the p ...
Salting in and salting out of proteins and dialysis
... •Salting out with ammonium sulfate is a technique that is used as an early step in purification scheme. • Significant purification is not achieved, but broad ammonium sulfate cut at least a volume of unwanted proteins. ...
... •Salting out with ammonium sulfate is a technique that is used as an early step in purification scheme. • Significant purification is not achieved, but broad ammonium sulfate cut at least a volume of unwanted proteins. ...
File
... Option 2 Directions and RubricI will provide you with the basic structure of a unit plan that you must complete. All activities must connect to each other and make sense in the flow of the unit. For each activity you must provide supple- ...
... Option 2 Directions and RubricI will provide you with the basic structure of a unit plan that you must complete. All activities must connect to each other and make sense in the flow of the unit. For each activity you must provide supple- ...
Respiration and Fermentation
... dioxide, some ATP molecules are synthesized directly and some by chemiosmotic phosphorylation via the electron transport system. What approximate percentage of the total number of ATP molecules formed comes from the latter process? a. 90% b. 66% c. 50% d. 25% 15. Despite the name, oxygen is not nece ...
... dioxide, some ATP molecules are synthesized directly and some by chemiosmotic phosphorylation via the electron transport system. What approximate percentage of the total number of ATP molecules formed comes from the latter process? a. 90% b. 66% c. 50% d. 25% 15. Despite the name, oxygen is not nece ...
An overview of Metabolism - Harford Community College
... • Krebs cycle (TCA) • Electron transport chain ...
... • Krebs cycle (TCA) • Electron transport chain ...
No Slide Title
... 9) The 2 ATP produced in glycolysis account for only 2.2% of the energy in 1 glucose. Where is the rest of the energy? Program 4: The Krebs Cycle (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nOR_EAzFkfo) 1) Let’s review: In glycolysis, 1 glucose reacts to produce ...
... 9) The 2 ATP produced in glycolysis account for only 2.2% of the energy in 1 glucose. Where is the rest of the energy? Program 4: The Krebs Cycle (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nOR_EAzFkfo) 1) Let’s review: In glycolysis, 1 glucose reacts to produce ...
The inner ear The inner ear can be divided into
... The inner ear can be divided into three parts: the semicircular canals, vestibule and the cochlea all of which are located in the temporal bone of the skull. Vibrations from the ossicles are transmitted to the cochlea via the stapes bone. The inner ear changes mechanical vibrations from the middle e ...
... The inner ear can be divided into three parts: the semicircular canals, vestibule and the cochlea all of which are located in the temporal bone of the skull. Vibrations from the ossicles are transmitted to the cochlea via the stapes bone. The inner ear changes mechanical vibrations from the middle e ...
Biology 105
... Electron transport chain 4th stage - takes place in the mitochondria Results in chemiosmosis - formation of ATP as protons diffuse through transmembrane channels. This process is known as oxidative phosphorylation Results in 32-34 ATP formed ...
... Electron transport chain 4th stage - takes place in the mitochondria Results in chemiosmosis - formation of ATP as protons diffuse through transmembrane channels. This process is known as oxidative phosphorylation Results in 32-34 ATP formed ...
Major Metabolic Pathway
... Autotrophs and Heterotrophs •Organisms are divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs according to their energy pathways. •Autotrophs are those organisms that are able to make energy-containing organic molecules from inorganic raw material by using basic energy sources such as sunlight. Plants are th ...
... Autotrophs and Heterotrophs •Organisms are divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs according to their energy pathways. •Autotrophs are those organisms that are able to make energy-containing organic molecules from inorganic raw material by using basic energy sources such as sunlight. Plants are th ...
Chapter 2: Major Metabolic Pathway
... Autotrophs and Heterotrophs •Organisms are divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs according to their energy pathways. •Autotrophs are those organisms that are able to make energy-containing organic molecules from inorganic raw material by using basic energy sources such as sunlight. Plants are th ...
... Autotrophs and Heterotrophs •Organisms are divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs according to their energy pathways. •Autotrophs are those organisms that are able to make energy-containing organic molecules from inorganic raw material by using basic energy sources such as sunlight. Plants are th ...
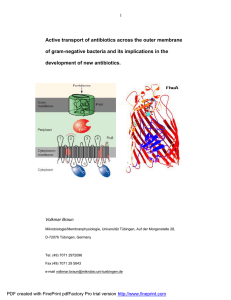
Active transport of antibiotics across the outer membrane of gram
... siderophores, which are taken up across the outer membrane by transport systems of Fe3+-siderophores. A well-studied example is albomycin, which has structural similarities to the natural substrate ferrichrome; albomycin and ferrichrome are both transported by the FhuA protein. A semisynthetic rifam ...
... siderophores, which are taken up across the outer membrane by transport systems of Fe3+-siderophores. A well-studied example is albomycin, which has structural similarities to the natural substrate ferrichrome; albomycin and ferrichrome are both transported by the FhuA protein. A semisynthetic rifam ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... breathing. The cessation of cellular respiration deprives the cell of energy, eventually killing the cell. 6. In a properly functioning mitochondrion, is the pH in the matrix lower than, higher than, or the same as the pH in the intermembrane compartment? If you add one or more poisons described in ...
... breathing. The cessation of cellular respiration deprives the cell of energy, eventually killing the cell. 6. In a properly functioning mitochondrion, is the pH in the matrix lower than, higher than, or the same as the pH in the intermembrane compartment? If you add one or more poisons described in ...
ER, Golgi and Vesicles :
... Once a polypeptide has been translated and released from the ribosome, it may be ready for use, but often it must undergo post-translational processing in order to become fully functional. While many of these processes are carried out in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the presence of organelles pr ...
... Once a polypeptide has been translated and released from the ribosome, it may be ready for use, but often it must undergo post-translational processing in order to become fully functional. While many of these processes are carried out in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the presence of organelles pr ...
Modeling the Structural Consequences of BEST1 Missense Mutations
... Bestrophinopathies are a group of inherited retinal disorders primarily caused by point mutations scattered throughout the entire BEST1 gene. In humans, most of these sequence alterations lead to Best vitelliform macular dystrophy (BVMD), and in dogs cause cmr, a retinal phenotype modeling BVMD (Guz ...
... Bestrophinopathies are a group of inherited retinal disorders primarily caused by point mutations scattered throughout the entire BEST1 gene. In humans, most of these sequence alterations lead to Best vitelliform macular dystrophy (BVMD), and in dogs cause cmr, a retinal phenotype modeling BVMD (Guz ...
PersPeCTIves
... (barbed end or plus end (+)) is localized adjacent to the membrane — this means that the insertion of while being attached to the membrane new monomers occurs at this site. Of the different mechanisms and processes shown, only two can be surface, providing a force that contributes to considered to b ...
... (barbed end or plus end (+)) is localized adjacent to the membrane — this means that the insertion of while being attached to the membrane new monomers occurs at this site. Of the different mechanisms and processes shown, only two can be surface, providing a force that contributes to considered to b ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.