neuron
... • Threshold: refers to the minimal level of stimulation required for a neural impulse to fire. ...
... • Threshold: refers to the minimal level of stimulation required for a neural impulse to fire. ...
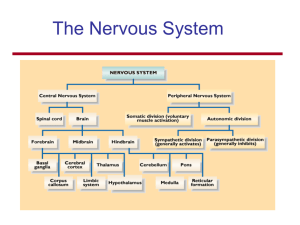
Nerves Ganglia Spinal nerves Cranial nerves Afferent neurons
... Division of the ANS that regulates resting and nutrition-related functions such as digestion, defecation, and urination ...
... Division of the ANS that regulates resting and nutrition-related functions such as digestion, defecation, and urination ...
1050927abstract
... intrinsic excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. In addition, silent cells show long-lasting activity in respond to past experience of encountering novel objects. Such reverberating activity is reminiscent of engram cell activity that reflects storage of the memory. Using two-photon imaging ...
... intrinsic excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. In addition, silent cells show long-lasting activity in respond to past experience of encountering novel objects. Such reverberating activity is reminiscent of engram cell activity that reflects storage of the memory. Using two-photon imaging ...
Part1
... Resting potential maintained by concentration differences of ions inside and outside of cell There are channels in membrane selective to different ions. Channels may be open or closed. ...
... Resting potential maintained by concentration differences of ions inside and outside of cell There are channels in membrane selective to different ions. Channels may be open or closed. ...
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
... In order to generate an action potential, a certain level of depolarization must be achieved, known as the threshold. ...
... In order to generate an action potential, a certain level of depolarization must be achieved, known as the threshold. ...
Chapter 48 Worksheet
... 1. The part of a neuron that carries nerve impulses toward the cell body is called _____. a. a nerve b. white matter c. a neurotransmitter d. a dendrite e. an axon 2. Which one of the following statements is not true about the resting potential? a. The neuron's plasma membrane is much more permeabl ...
... 1. The part of a neuron that carries nerve impulses toward the cell body is called _____. a. a nerve b. white matter c. a neurotransmitter d. a dendrite e. an axon 2. Which one of the following statements is not true about the resting potential? a. The neuron's plasma membrane is much more permeabl ...
Nerve Impulses - Tamalpais Union High School District
... K+ channels open and K+ moves outward causing inside of membrane to become negative again. K+ Potassium channels open ...
... K+ channels open and K+ moves outward causing inside of membrane to become negative again. K+ Potassium channels open ...
Candy Neurons Activity
... Students work in pairs of two to create their candy neurons. They must be labeled and contain all key parts. Once they are done they must link of their diagram with another two groups. When you have a group of 6 come by for some direct instruction showing that neurons fire DAT way. Dendrites t ...
... Students work in pairs of two to create their candy neurons. They must be labeled and contain all key parts. Once they are done they must link of their diagram with another two groups. When you have a group of 6 come by for some direct instruction showing that neurons fire DAT way. Dendrites t ...
How is the Nervous System Organized? a Class Objectives a What
... To transmit information to other neurons, a brief electrical current impulses through its axon. ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ - This current causes the neuron to “fire” ...
... To transmit information to other neurons, a brief electrical current impulses through its axon. ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ - This current causes the neuron to “fire” ...
1 Introduction to Neurobiology Rudolf Cardinal NST 1B
... typically 0.4 mV, and even at the postsynaptic neuron’s most sensitive site near the cell body, 10 mV of depolarization is required to bring the neuron to threshold and fire an AP. However, if enough EPSPs arrive at the neuron and are close enough to each other in space and time (and overcome any in ...
... typically 0.4 mV, and even at the postsynaptic neuron’s most sensitive site near the cell body, 10 mV of depolarization is required to bring the neuron to threshold and fire an AP. However, if enough EPSPs arrive at the neuron and are close enough to each other in space and time (and overcome any in ...
File
... usually (not always) the Axon terminal. The axon terminals are also called the bouton terminaux or synaptic knob. The synaptic knobs have synaptic vesicles that contain the NT (neurotransmitters). The NT are produced in the body & conducted along the axon (anterograde flow). The NT can be inhibitory ...
... usually (not always) the Axon terminal. The axon terminals are also called the bouton terminaux or synaptic knob. The synaptic knobs have synaptic vesicles that contain the NT (neurotransmitters). The NT are produced in the body & conducted along the axon (anterograde flow). The NT can be inhibitory ...
Action Potentials
... • EPSP and IPSP travel to the base of the axon hillock where they are summed • Two EPSPs in rapid succession at one synapse are additive • Same for IPSPs ...
... • EPSP and IPSP travel to the base of the axon hillock where they are summed • Two EPSPs in rapid succession at one synapse are additive • Same for IPSPs ...
PPTX - Bonham Chemistry
... Hormone: A chemical messenger released by an endocrine gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse ...
... Hormone: A chemical messenger released by an endocrine gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse ...
10synapse & neurotransmitter
... • A single neuron maybe connected to 5000 to 10,000 other neurons. • Brain is responsible for different activities like sensations, movements of muscle, thought, emotion, memory – all these depend on electrical and chemical signaling between neurons along wired neural pathways. ...
... • A single neuron maybe connected to 5000 to 10,000 other neurons. • Brain is responsible for different activities like sensations, movements of muscle, thought, emotion, memory – all these depend on electrical and chemical signaling between neurons along wired neural pathways. ...
Nervous System - APBio
... • The inside is negative relative to the outside • Maintained by the sodium potassium pump, which pumps 3 Na+ out of the cell for every 2 K+ it pumps in, and K+ ion channels that allow for the diffusion of K+ out of the cell • Na+ is not allowed in (the Na+ ion channels are closed) ...
... • The inside is negative relative to the outside • Maintained by the sodium potassium pump, which pumps 3 Na+ out of the cell for every 2 K+ it pumps in, and K+ ion channels that allow for the diffusion of K+ out of the cell • Na+ is not allowed in (the Na+ ion channels are closed) ...
The Nervous System
... • There are more than 40 known types • Different neurotransmitters have different effects • Drugs, neural diseases often affect neurotransmitters ...
... • There are more than 40 known types • Different neurotransmitters have different effects • Drugs, neural diseases often affect neurotransmitters ...
7. Describe what membrane potential is, and how
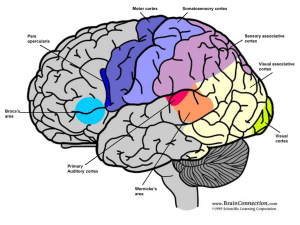
... blood-brain barrier? • This restricts the passage of most substances into the brain • Allows the chemical environment of the CNS to be well controlled ...
... blood-brain barrier? • This restricts the passage of most substances into the brain • Allows the chemical environment of the CNS to be well controlled ...
Central nervous system
... – Neuron I releases inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA • prevents voltage-gated calcium channels from opening in neuron S so it releases less or no neurotransmitter onto neuron R and fails to stimulate it ...
... – Neuron I releases inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA • prevents voltage-gated calcium channels from opening in neuron S so it releases less or no neurotransmitter onto neuron R and fails to stimulate it ...
File - Mr. Haan`s Science
... d. K+ diffuses out quickly causing the outside to be + and inside to be – in comparison e. Resting potential = difference in charges ...
... d. K+ diffuses out quickly causing the outside to be + and inside to be – in comparison e. Resting potential = difference in charges ...
Chapter 3
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
ActionPotentialWebquestCompleteGarrettIan
... Click on the “Other Cells in the Brain” link and answer the following questions: 5. There are about ______________ neurons in the brain as well as ______________ of support cells called _____________________. 6. There are 3 types of glial cells. Name each of the 3 and explain their function: 1. ____ ...
... Click on the “Other Cells in the Brain” link and answer the following questions: 5. There are about ______________ neurons in the brain as well as ______________ of support cells called _____________________. 6. There are 3 types of glial cells. Name each of the 3 and explain their function: 1. ____ ...
Document
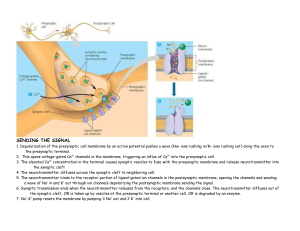
... 1. Depolarization of the presynaptic cell membrane by an action potential pushes a wave (Na+ ions rushing in/K+ ions rushing out) along the axon to the presynaptic terminal. 2. This opens voltage–gated Ca2+ channels in the membrane, triggering an influx of Ca2+ into the presynaptic cell. 3. The elev ...
... 1. Depolarization of the presynaptic cell membrane by an action potential pushes a wave (Na+ ions rushing in/K+ ions rushing out) along the axon to the presynaptic terminal. 2. This opens voltage–gated Ca2+ channels in the membrane, triggering an influx of Ca2+ into the presynaptic cell. 3. The elev ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.