Module I. Introduction to biophysical models of individual cells and... plane analysis important to capture phenomenology and sometimes – biophysical mechanisms
... 1. Read about neurons, or about phase-plane methods. We are learning terminology, getting everybody on the same page 2. Simulate a Hodgkin-huxley model in matlab, make it spike. 3. Consider other currents. e.g. IK-Ca, IAHP, IA, Ih, IM, IKLT,IT. Pick 2 of the currents. Explain what happens at differe ...
... 1. Read about neurons, or about phase-plane methods. We are learning terminology, getting everybody on the same page 2. Simulate a Hodgkin-huxley model in matlab, make it spike. 3. Consider other currents. e.g. IK-Ca, IAHP, IA, Ih, IM, IKLT,IT. Pick 2 of the currents. Explain what happens at differe ...
chapt12-nervous system
... The action potential occurs in each successive portion of an axon. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. The Synapse Transmission of the nerve ...
... The action potential occurs in each successive portion of an axon. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. The Synapse Transmission of the nerve ...
LESSON 3.3 WORKBOOK
... receptors at the synaptic cleft are referred to as postsynaptic potentials. Interestingly, the kind of postsynaptic potential a particular synapse produces does not depend on the neurotransmitter itself. Instead, it is determined by the characteristics of the postsynaptic receptors the neurotransmit ...
... receptors at the synaptic cleft are referred to as postsynaptic potentials. Interestingly, the kind of postsynaptic potential a particular synapse produces does not depend on the neurotransmitter itself. Instead, it is determined by the characteristics of the postsynaptic receptors the neurotransmit ...
File
... 6.5.1 State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed of cells called neurons that can carry rapid electrical impulses. 6.5.2 Draw and label the structure of a motor neuron, include; dendrites, cell body with nucleus, axon, myelin sh ...
... 6.5.1 State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed of cells called neurons that can carry rapid electrical impulses. 6.5.2 Draw and label the structure of a motor neuron, include; dendrites, cell body with nucleus, axon, myelin sh ...
Part 1: The Strange Tale of Phineas Gage
... it- it’s very important). Make sure you take care of both. Tomorrow, you will upload this file to turnitin.com and it will be checked for completion. Part 1: The Strange Tale of Phineas Gage (the beginning of modern brain science) Go to: http://brainconnection.positscience.com/topics/?main=fa/phinea ...
... it- it’s very important). Make sure you take care of both. Tomorrow, you will upload this file to turnitin.com and it will be checked for completion. Part 1: The Strange Tale of Phineas Gage (the beginning of modern brain science) Go to: http://brainconnection.positscience.com/topics/?main=fa/phinea ...
File
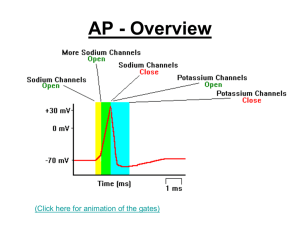
... Depolarization is stopped When the membrane voltage reaches 35 mV, the inactivation gates close in response to depolarization and the sodium ions can’t enter the cell anymore. The Na+ can only come in during a brief period when both activation and inactivation ...
... Depolarization is stopped When the membrane voltage reaches 35 mV, the inactivation gates close in response to depolarization and the sodium ions can’t enter the cell anymore. The Na+ can only come in during a brief period when both activation and inactivation ...
Nervous System
... the amount of acetylcholine in synaptic cleft increases with each successive nerve impulse repeated stimulation of muscle life-threatening spasms The acetylcholine from one axon terminal is usually not enough to cause depolarization of the post-synaptic neuron. Usually, neurotransmitters f ...
... the amount of acetylcholine in synaptic cleft increases with each successive nerve impulse repeated stimulation of muscle life-threatening spasms The acetylcholine from one axon terminal is usually not enough to cause depolarization of the post-synaptic neuron. Usually, neurotransmitters f ...
a14b NeuroPhysII
... o Axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron, which contains synaptic vesicles o Receptor region on the postsynaptic neuron ...
... o Axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron, which contains synaptic vesicles o Receptor region on the postsynaptic neuron ...
1. The main function of myelin is to a. form a protective coating over
... Q: Neurons send signals to…. A: the brain, muscles, and glands Q: Write the definition for the following neurons.. -Sensory Neurons ...
... Q: Neurons send signals to…. A: the brain, muscles, and glands Q: Write the definition for the following neurons.. -Sensory Neurons ...
to find the lecture notes for lecture 6 nervous tissue click here
... – because a local area has begun to depolarize – charge of this area changes – specifically the inside area gets more positive in relation to the surrounding areas that are at rest – the outer area becomes more negative in relation to the surrounding areas that are at ...
... – because a local area has begun to depolarize – charge of this area changes – specifically the inside area gets more positive in relation to the surrounding areas that are at rest – the outer area becomes more negative in relation to the surrounding areas that are at ...
AP – All or nothing
... – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one direction only. – Produces discrete impulses. – Limits the frequency of impulses. ...
... – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one direction only. – Produces discrete impulses. – Limits the frequency of impulses. ...
Biological synaptic functioning ordering activity
... The Biological approach to Psychology Synaptic functioning Put these processes in the correct order ...
... The Biological approach to Psychology Synaptic functioning Put these processes in the correct order ...
Slide 1
... Advantages: Spikes of biological neurons are well localized in time and not very frequent. Thus low number of events (sparse coding). Disadvantages: We need a mathematical expression (or method) to calculate the value of each state variable after an arbitrary time (the time of the next event). ...
... Advantages: Spikes of biological neurons are well localized in time and not very frequent. Thus low number of events (sparse coding). Disadvantages: We need a mathematical expression (or method) to calculate the value of each state variable after an arbitrary time (the time of the next event). ...
Biopsychology
... Are two kinds: 1. Hyperpolarization - increased polarity (voltage difference). 2. Depolarization - decreased polarity. Threshold Refers to the voltage level that needs to be reached for an action potential to occur. While the resting potential of the cell is about -70 mV, the threshold is ab ...
... Are two kinds: 1. Hyperpolarization - increased polarity (voltage difference). 2. Depolarization - decreased polarity. Threshold Refers to the voltage level that needs to be reached for an action potential to occur. While the resting potential of the cell is about -70 mV, the threshold is ab ...
Neuroanatomy- anatomy of nerve cell (neuron)
... Terminal Buttons of axon (aka end buttons, terminal branches, synaptic knobs))- branched end of the axon that contains neurotransmitters ...
... Terminal Buttons of axon (aka end buttons, terminal branches, synaptic knobs))- branched end of the axon that contains neurotransmitters ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... Neurons that receive information from the external world and convey this information to the brain via the spinal cord. Motor Neurons Neurons that carry signals from the spinal cord and produce movement. ...
... Neurons that receive information from the external world and convey this information to the brain via the spinal cord. Motor Neurons Neurons that carry signals from the spinal cord and produce movement. ...
neuron is
... Neuron May Fail to Fire • threshold of excitation: (firing threshold) level of “depolarization” that must be reached for neuron to fire • graded potential: stimulation of dendrites was too weak to reach threshold and neuron fails to fire (depolarization just “fades away”) ...
... Neuron May Fail to Fire • threshold of excitation: (firing threshold) level of “depolarization” that must be reached for neuron to fire • graded potential: stimulation of dendrites was too weak to reach threshold and neuron fails to fire (depolarization just “fades away”) ...
AP Psychology - Ms. Hofmann`s Website
... Peripheral Nervous system on this website. Read the two scenarios on the right that begin with, “It’s a nice sunny day…” Draw yourself in each of these situations and in the caption explain what is going on in your body. ...
... Peripheral Nervous system on this website. Read the two scenarios on the right that begin with, “It’s a nice sunny day…” Draw yourself in each of these situations and in the caption explain what is going on in your body. ...
Sensory Physiology
... – Did you activate neurons with low as well as high threshold for activation? ...
... – Did you activate neurons with low as well as high threshold for activation? ...
שקופית 1
... Which of the many parameters that influence the input-output behavior should be viewed as being adjustable for a specific protocol for inducing synaptic plasticity (i.e., “learning”)? STDP adjust the following parameters: ◦ scaling factors w of the amplitudes ◦ initial release probabilities U ...
... Which of the many parameters that influence the input-output behavior should be viewed as being adjustable for a specific protocol for inducing synaptic plasticity (i.e., “learning”)? STDP adjust the following parameters: ◦ scaling factors w of the amplitudes ◦ initial release probabilities U ...
Chapter 12- Intro to NS
... A. The Neuron- these types of cells are excitable and can send an impulse (electrical signal). Neurons have three major parts: cell body, dendrites, axon. These cells live for many years, do not under mitosis, and are highly dependant on oxygen due to a high metabolic rate. 1. The cell body (soma)- ...
... A. The Neuron- these types of cells are excitable and can send an impulse (electrical signal). Neurons have three major parts: cell body, dendrites, axon. These cells live for many years, do not under mitosis, and are highly dependant on oxygen due to a high metabolic rate. 1. The cell body (soma)- ...
AP Biology Animal Form and Function
... In most animals, the synapse between two neurons are traversed by chemicals in the following steps: 1. Calcium (Ca2+) gates open. When an action potential reaches the end of an axon, the depolarization of the membrane causes gated channels to open and allows Ca2+ to enter the cell 2. Synaptic vesicl ...
... In most animals, the synapse between two neurons are traversed by chemicals in the following steps: 1. Calcium (Ca2+) gates open. When an action potential reaches the end of an axon, the depolarization of the membrane causes gated channels to open and allows Ca2+ to enter the cell 2. Synaptic vesicl ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.