Chapter 11: Nervous System
... Neurotransmitter receptors mediate changes in membrane potential according to: The amount of neurotransmitter released The amount of time the neurotransmitter is bound to receptors ...
... Neurotransmitter receptors mediate changes in membrane potential according to: The amount of neurotransmitter released The amount of time the neurotransmitter is bound to receptors ...
Homeostasis Test%28CNS%29-Tawsif Hossain
... channels open and sodium ions move down the gradient into the axon. The potential difference of 40mV is reached. 2) As a result the sodium channels close and voltage gated potassium channels open. The potassium ions move down their concentration outside the axon carrying the positive charge out. Thi ...
... channels open and sodium ions move down the gradient into the axon. The potential difference of 40mV is reached. 2) As a result the sodium channels close and voltage gated potassium channels open. The potassium ions move down their concentration outside the axon carrying the positive charge out. Thi ...
Chapter 11: Nervous System
... Neurotransmitter receptors mediate changes in membrane potential according to: The amount of neurotransmitter released The amount of time the neurotransmitter is bound to receptors ...
... Neurotransmitter receptors mediate changes in membrane potential according to: The amount of neurotransmitter released The amount of time the neurotransmitter is bound to receptors ...
Nerve activates contraction - Silver Falls School District
... stimulus depolarizes the neuron’s membrane allows Na+ to flow inside membrane exchange of ions initiates an action potential in neuron ...
... stimulus depolarizes the neuron’s membrane allows Na+ to flow inside membrane exchange of ions initiates an action potential in neuron ...
Ch45--Neurons and Nervous Systems v2015
... “voltage-gated” channels channel Na+ ions continue to diffuse into cell channel closed open “wave” moves down neuron = action potential ...
... “voltage-gated” channels channel Na+ ions continue to diffuse into cell channel closed open “wave” moves down neuron = action potential ...
AP Biology - Pleasantville High School
... -presynaptic means anything before the synapse and postsynaptic means anything after the synapse. Therefore the cell transmitting the nerve impulse is called the presynaptic cell and the cell receiving the information is called the postsynaptic cell. -nerve impulses reaching the presynaptic ending c ...
... -presynaptic means anything before the synapse and postsynaptic means anything after the synapse. Therefore the cell transmitting the nerve impulse is called the presynaptic cell and the cell receiving the information is called the postsynaptic cell. -nerve impulses reaching the presynaptic ending c ...
Action potential - Solon City Schools
... – Neurotransmitters cross synapse: different ones send different impulses and need to find receptors – It can either excite (fire) or inhibit (prevent firing) ...
... – Neurotransmitters cross synapse: different ones send different impulses and need to find receptors – It can either excite (fire) or inhibit (prevent firing) ...
Molecular basis of learning in the hippocampus and the amygdala
... synaptic plasticity is essential for brain development. Short-term synaptic plasticity relies on accumulation of calcium ions in pre-synapse and neurotransmitter release, leading to short-term memory. Long-term plasticity relates to long-term memory andis described further in detail (Citri et al., 2 ...
... synaptic plasticity is essential for brain development. Short-term synaptic plasticity relies on accumulation of calcium ions in pre-synapse and neurotransmitter release, leading to short-term memory. Long-term plasticity relates to long-term memory andis described further in detail (Citri et al., 2 ...
CH 8 Nervous part 1
... The name “endorphin” comes from endo- and -orphin; intended to mean "a morphine-like substance originating from within the body. ...
... The name “endorphin” comes from endo- and -orphin; intended to mean "a morphine-like substance originating from within the body. ...
Slide ()
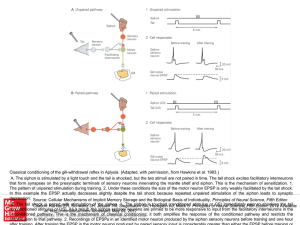
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
Answers - Mosaiced.org
... Follows that significant –ve potential needed to balance tendency of K+ to diffuse down concentration gradient out of cell. Membrane slightly permeable to Na+, so memb potential slightly more positive than K+ eqm potential (to balance flow of Na+ into cell down conc gradient). 85. closed 86. depolar ...
... Follows that significant –ve potential needed to balance tendency of K+ to diffuse down concentration gradient out of cell. Membrane slightly permeable to Na+, so memb potential slightly more positive than K+ eqm potential (to balance flow of Na+ into cell down conc gradient). 85. closed 86. depolar ...
nervous system ppt
... Can be produced from exercise. The name “endorphin” comes from endo- and -orphin; intended to mean "a morphinelike substance originating from within the body. ...
... Can be produced from exercise. The name “endorphin” comes from endo- and -orphin; intended to mean "a morphinelike substance originating from within the body. ...
Nervous System
... • Nerve impulses pass from neuron to neuron at synapses, moving from a pre-synaptic neuron to a post-synaptic neuron. ...
... • Nerve impulses pass from neuron to neuron at synapses, moving from a pre-synaptic neuron to a post-synaptic neuron. ...
Neurons - Honors Biology 10 - 2222-03
... A neuron remains in its resting state until it receives a stimulus large enough to start a nerve impulse. Once this happens ion channels open and the electrical charge inside and outside the neuron reverse. ...
... A neuron remains in its resting state until it receives a stimulus large enough to start a nerve impulse. Once this happens ion channels open and the electrical charge inside and outside the neuron reverse. ...
COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE Medical Diagnostic Systems
... impulses originate in the cell body, and are propagated along the axon, which may have one or more branches. This axon, which is folded for diagrammatic purposes, would be a centimeter long at actual size. Some axons are more than a meter long. The axon’s terminal branches form synapses with as many ...
... impulses originate in the cell body, and are propagated along the axon, which may have one or more branches. This axon, which is folded for diagrammatic purposes, would be a centimeter long at actual size. Some axons are more than a meter long. The axon’s terminal branches form synapses with as many ...
C8003 Psychobiology sample paper 2016-17
... into nerve cells Benzodiazepines may reduce anxiety by acting on receptors for the neurotransmitter GABA Benzodiazepines may reduce anxiety by acting on areas of the visual cortex involved in processing threat-related stimuli ...
... into nerve cells Benzodiazepines may reduce anxiety by acting on receptors for the neurotransmitter GABA Benzodiazepines may reduce anxiety by acting on areas of the visual cortex involved in processing threat-related stimuli ...
6.1 Overview of the Nervous System
... appear white (White matter); Gray matter is non-myelinated nerve fibers c. insulated gaps between Schwann Cells are call nodes of Ranvier ...
... appear white (White matter); Gray matter is non-myelinated nerve fibers c. insulated gaps between Schwann Cells are call nodes of Ranvier ...
Lecture 9
... • Joined by specific protein structures called gap junctions (specialized ionic channels that connect the cytoplasm of both cells) • Action potential comes to gap junction depolarizes or hyperpolarizes the membrane induces opening of the channels diffusion of ions from one neuron to the other ...
... • Joined by specific protein structures called gap junctions (specialized ionic channels that connect the cytoplasm of both cells) • Action potential comes to gap junction depolarizes or hyperpolarizes the membrane induces opening of the channels diffusion of ions from one neuron to the other ...
Media:oreilly_genpsych_ch2_neuron
... Neurons integrate electrical signals (depolarization) received via synapses on their dendrites, from axons of other neurons When membrane potential exceeds threshold, action potential (spike) is sent down axon, triggering release of neurotransmitter in synapse, which opens ion channels on receiving ...
... Neurons integrate electrical signals (depolarization) received via synapses on their dendrites, from axons of other neurons When membrane potential exceeds threshold, action potential (spike) is sent down axon, triggering release of neurotransmitter in synapse, which opens ion channels on receiving ...
Overview Functions of the Nervous System
... • 2. Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open and Ca2+ enters the axon terminal • 3. Ca2+ entry causes neurotransmitter-containing vesicles to release their contents by exocytosis • 4. Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane • 5. Bindi ...
... • 2. Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open and Ca2+ enters the axon terminal • 3. Ca2+ entry causes neurotransmitter-containing vesicles to release their contents by exocytosis • 4. Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane • 5. Bindi ...
Unit – M Neuron, Impulse Generation, and Reflex Arc Structures and
... When the axon or dendrite is stimulated, sodium gates open which allows some Na+ to enter the axoplasm (interior). Now, the inside becomes more positive than the outside by 40 mv. This is called the Upswing Phase of the action potential. The charge changes from –60 mv to +40 mv. The change is calle ...
... When the axon or dendrite is stimulated, sodium gates open which allows some Na+ to enter the axoplasm (interior). Now, the inside becomes more positive than the outside by 40 mv. This is called the Upswing Phase of the action potential. The charge changes from –60 mv to +40 mv. The change is calle ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.