Introduction to neural computation
... Modularity and the brain • Different bits of the cortex do different things. – Local damage to the brain has specific effects – Specific tasks increase the blood flow to specific regions. • But cortex looks pretty much the same all over. – Early brain damage makes functions relocate • Cortex is mad ...
... Modularity and the brain • Different bits of the cortex do different things. – Local damage to the brain has specific effects – Specific tasks increase the blood flow to specific regions. • But cortex looks pretty much the same all over. – Early brain damage makes functions relocate • Cortex is mad ...
Unit A: Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... accept 2K+ from outside the membrane. 4. P (phosphate) is released from the carrier protein 5. Carrier protein changes shape to release 2K+ and accept 3Na+ again NET GAIN = 1+ out (keeps resting potential -70mV) ...
... accept 2K+ from outside the membrane. 4. P (phosphate) is released from the carrier protein 5. Carrier protein changes shape to release 2K+ and accept 3Na+ again NET GAIN = 1+ out (keeps resting potential -70mV) ...
Slide 1
... because certain ions can cross at certain times but there is not a free exchange The opening and closing of specific ion channels can be controlled by chemical signals including neurotransmitter ...
... because certain ions can cross at certain times but there is not a free exchange The opening and closing of specific ion channels can be controlled by chemical signals including neurotransmitter ...
Responses to stimulating multiple inputs
... the early neurobiologists to understand basic mechanisms underliying synaptic transmission and action potential generation. A) What features of these two aspects of the squid nervous system made them so amenable to experimental analysis. B) What is the neuroethological principle that is revealed her ...
... the early neurobiologists to understand basic mechanisms underliying synaptic transmission and action potential generation. A) What features of these two aspects of the squid nervous system made them so amenable to experimental analysis. B) What is the neuroethological principle that is revealed her ...
Turning neurons into a nervous system
... multiple climbing fibers that contact the immature Purkinje cell. Only one climbing fiber will innervate the mature neuron. If climbing fibers are inefficiently removed in mouse mutants, or if they are synchronously activated, the multiplanar tree is not remodeled. Dendritic trees form under two bro ...
... multiple climbing fibers that contact the immature Purkinje cell. Only one climbing fiber will innervate the mature neuron. If climbing fibers are inefficiently removed in mouse mutants, or if they are synchronously activated, the multiplanar tree is not remodeled. Dendritic trees form under two bro ...
36.1 The Nervous System Neurons: Basic units of
... The inside is more negatively charged than the outside ...
... The inside is more negatively charged than the outside ...
CH005a NERVOUS SYS - INTRO 10-22
... Nutrients, such as glucose, essential amino acids, and some electrolytes, move passively by facilitated diffusion through the endothelial cell membranes Bloodborne metabolic wastes, such as urea and creatinine as well as proteins, certain toxins, and most drugs, are prevented from entering brain ...
... Nutrients, such as glucose, essential amino acids, and some electrolytes, move passively by facilitated diffusion through the endothelial cell membranes Bloodborne metabolic wastes, such as urea and creatinine as well as proteins, certain toxins, and most drugs, are prevented from entering brain ...
neurotransmitters
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump, using ATP, restores the ...
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump, using ATP, restores the ...
Respiratory and Nervous Systems
... The neurotransmitters diffuse across the cleft. The neurotransmitters bind with specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. Depolarization occurs on the postsynaptic membrane if threshold is reached. The neurotransmitter is destroyed by an enzyme (ex. acetylcholinesterase) or reabsorbed back in ...
... The neurotransmitters diffuse across the cleft. The neurotransmitters bind with specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. Depolarization occurs on the postsynaptic membrane if threshold is reached. The neurotransmitter is destroyed by an enzyme (ex. acetylcholinesterase) or reabsorbed back in ...
Teacher Guide
... synapse - the gap between two neurons forming the site of information transfer, via neurotransmitters, from one neuron to another, including the presynaptic nerve terminal and the post-synaptic dendritic site; at synapses, neurotransmitters released from pre-synaptic axon terminals bind to receptors ...
... synapse - the gap between two neurons forming the site of information transfer, via neurotransmitters, from one neuron to another, including the presynaptic nerve terminal and the post-synaptic dendritic site; at synapses, neurotransmitters released from pre-synaptic axon terminals bind to receptors ...
Central nervous system
... •Myelin will get laid down in segments along the axon, leaving unmyelinated gaps known as “nodes of Ranvier” ...
... •Myelin will get laid down in segments along the axon, leaving unmyelinated gaps known as “nodes of Ranvier” ...
20-NervousSystem
... membrane of a resting neuron is generated by different concentrations of Na+, K+, and Cl ...
... membrane of a resting neuron is generated by different concentrations of Na+, K+, and Cl ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump, using ATP, restores the ...
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump, using ATP, restores the ...
What is real? How do you define real?
... • Vm: difference in potential between interior and exterior of the neuron. • at rest, Vm~-70 mV (more Na+ outside, more K+ inside, due to N+/K+ pump) • Following activation of (Glutamatergic) synapses, depolarization occurs. • if depolarization > threshold, neuron generates an action potential (spik ...
... • Vm: difference in potential between interior and exterior of the neuron. • at rest, Vm~-70 mV (more Na+ outside, more K+ inside, due to N+/K+ pump) • Following activation of (Glutamatergic) synapses, depolarization occurs. • if depolarization > threshold, neuron generates an action potential (spik ...
Name: Date: Period:
... types are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons send information to the brain. Motor neurons carry out instructions from the brain. Interneurons carry the messages ‘in between’ the sensory and motor neurons. In today’s activity, we will be modeling how neurons work using ...
... types are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons send information to the brain. Motor neurons carry out instructions from the brain. Interneurons carry the messages ‘in between’ the sensory and motor neurons. In today’s activity, we will be modeling how neurons work using ...
The Nervous System
... from the sense organs to the spinal cord and the brain – Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands – Interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses ...
... from the sense organs to the spinal cord and the brain – Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands – Interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses ...
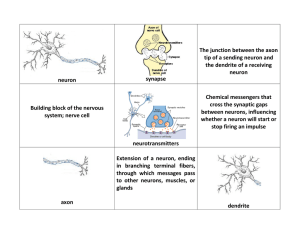
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending
... linked to emotion; thought to determine whether we should emotionally react to sensory stimuli, especially with rage or fear; processes emotional memories ...
... linked to emotion; thought to determine whether we should emotionally react to sensory stimuli, especially with rage or fear; processes emotional memories ...
Chapter 10: Nervous System I
... membrane and is measured in millivolts. 7. Resting potential is the membrane potential of a resting neuron and has a value of –70 millivolts. 8. The negative sign of a resting membrane potential is relative to the inside of the cell and is due to the excess negative charges on the inside of the cell ...
... membrane and is measured in millivolts. 7. Resting potential is the membrane potential of a resting neuron and has a value of –70 millivolts. 8. The negative sign of a resting membrane potential is relative to the inside of the cell and is due to the excess negative charges on the inside of the cell ...
Option E Neurobiology and Behaviour
... A change in the internal or external environment that is detected by a receptor and causes a response. Response A change in an organism as a result of a stimulus. Reflex A rapid and unconscious response to a stimulus. ...
... A change in the internal or external environment that is detected by a receptor and causes a response. Response A change in an organism as a result of a stimulus. Reflex A rapid and unconscious response to a stimulus. ...
The Neural Mechanisms of Learning
... Babies born with all 100 billion nerve cells Each cell at birth synapses with around 2500 other neurons By late childhood the number of connections increases to around 15,000 per neuron By adulthood this number decreases to around 8,000 as unused connections are destroyed ...
... Babies born with all 100 billion nerve cells Each cell at birth synapses with around 2500 other neurons By late childhood the number of connections increases to around 15,000 per neuron By adulthood this number decreases to around 8,000 as unused connections are destroyed ...
CH 48 Nervous systemnotes2010
... 2. interneuron- a nerve cell within the central nervous system responsible for the integration of neural input and output 3. motor neuron transmits signals from the brain or spinal column to muscles or glands How do nerve cells send impulses along itself? All deals with membrane potentials it’s the ...
... 2. interneuron- a nerve cell within the central nervous system responsible for the integration of neural input and output 3. motor neuron transmits signals from the brain or spinal column to muscles or glands How do nerve cells send impulses along itself? All deals with membrane potentials it’s the ...
Answer Key
... 5. People can simultaneously process many aspects of sensory information such as color, shape, and size. This best illustrates the functioning of multiple A) ACh agonists. B) dendrites. C) endorphins. D) neural networks. E) ACh antagonists. ...
... 5. People can simultaneously process many aspects of sensory information such as color, shape, and size. This best illustrates the functioning of multiple A) ACh agonists. B) dendrites. C) endorphins. D) neural networks. E) ACh antagonists. ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.