Slides - gserianne.com
... • absolute - time when threshold stimulus does not start another action potential (Na+ channels inactivated) • relative – time when stronger threshold stimulus can start another action potential (Na+ channels restored, K+ channels begin ...
... • absolute - time when threshold stimulus does not start another action potential (Na+ channels inactivated) • relative – time when stronger threshold stimulus can start another action potential (Na+ channels restored, K+ channels begin ...
Voltage-Dependent Switching of Sensorimotor Integration by a
... integration and behavioral adaptations. The present study explored a novel form of sensory-induced plasticity by which the resulting changes in motor output depend essentially on the preexisting functional state of an identified neuron of an endogenously active central network. In the isolated lobst ...
... integration and behavioral adaptations. The present study explored a novel form of sensory-induced plasticity by which the resulting changes in motor output depend essentially on the preexisting functional state of an identified neuron of an endogenously active central network. In the isolated lobst ...
amy-2a-2016-cryders-rmp-and-generation-of-action
... pulls ions back into the cell. K+ ions will continue to diffuse out of the cell until the electrical potential is equal but opposite. Once equilibrium is reached, there will be no net movement of ions. -90mv is the equilibrium potential for K+ and -70mv is the resting membrane potential for a neuro ...
... pulls ions back into the cell. K+ ions will continue to diffuse out of the cell until the electrical potential is equal but opposite. Once equilibrium is reached, there will be no net movement of ions. -90mv is the equilibrium potential for K+ and -70mv is the resting membrane potential for a neuro ...
Passive Conduction - Cable Theory
... October 7, 2013 Biological Structure Theoretical models describing propagation of synaptic potentials have evolved significantly over the past century. Synaptic potentials are the root of neural activity, electrical potential differences caused by fluxes of biological ions across the neural membrane ...
... October 7, 2013 Biological Structure Theoretical models describing propagation of synaptic potentials have evolved significantly over the past century. Synaptic potentials are the root of neural activity, electrical potential differences caused by fluxes of biological ions across the neural membrane ...
Modeling the brain
... Neuronal reuse offers a reasonable explanation to the mechanism of the remarkable ability of the human to develop new and advanced skills over evolutionary very short periods of time. The combined hypotheses of Neural plasticity and Neural reuse offers a reasonable explanation to social/cultural inh ...
... Neuronal reuse offers a reasonable explanation to the mechanism of the remarkable ability of the human to develop new and advanced skills over evolutionary very short periods of time. The combined hypotheses of Neural plasticity and Neural reuse offers a reasonable explanation to social/cultural inh ...
Title: Nervous System
... 1. The role of synapses – synapses determine the directions that the nervous signals will spread in to the nervous system. 2. Physiologic anatomy of synapses (presynaptic terminals, synaptic cleft, postsynaptic neuron). 3. The major type of synapses a) the chemical synapse (transmitters, “one-way” c ...
... 1. The role of synapses – synapses determine the directions that the nervous signals will spread in to the nervous system. 2. Physiologic anatomy of synapses (presynaptic terminals, synaptic cleft, postsynaptic neuron). 3. The major type of synapses a) the chemical synapse (transmitters, “one-way” c ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... in myelinated than nonmyelinated axons. Transmission Across a Synapse Every axon branches into many fine endings, each tipped by an axon terminal. Each terminal lies very close to either the dendrite or cell body of another neuron. This region is called a synapse, the two neurons are separated by th ...
... in myelinated than nonmyelinated axons. Transmission Across a Synapse Every axon branches into many fine endings, each tipped by an axon terminal. Each terminal lies very close to either the dendrite or cell body of another neuron. This region is called a synapse, the two neurons are separated by th ...
Sensory neurons
... Myelin Sheath • Some important nerve cells have an axon that is covered in Myelin. • Myelin is a fatty substance that acts as an insulator and allows an nerve impulse to travel very quickly. • Multiple Sclerosis is a disease where the Myelin Sheath is damaged causing some signals to ‘short-circuit’ ...
... Myelin Sheath • Some important nerve cells have an axon that is covered in Myelin. • Myelin is a fatty substance that acts as an insulator and allows an nerve impulse to travel very quickly. • Multiple Sclerosis is a disease where the Myelin Sheath is damaged causing some signals to ‘short-circuit’ ...
Cellular Mechanisms of Learning and Memory
... another transcription factor C/EBP. This binds to the DNA response element CAAT, which activates genes that encode proteins important for the growth of new synaptic connections. ...
... another transcription factor C/EBP. This binds to the DNA response element CAAT, which activates genes that encode proteins important for the growth of new synaptic connections. ...
Unit 2: Nervous System
... • Message sent out of axon terminal • FOCUS: – Get message to CNS – Let CNS process and decide (NO need to have cell body right by dendrites) ...
... • Message sent out of axon terminal • FOCUS: – Get message to CNS – Let CNS process and decide (NO need to have cell body right by dendrites) ...
Terms being described
... 41. The summation of IPSPs produce this type of inhibition. 43. It’s the energy molecule used by the Na+/K+ pumps to restore the concentration of Na+ and K+ after the action potential is complete. 45. It’s another name for the sheath of Schwann. 47. The physiology of these cells is the basis of nerv ...
... 41. The summation of IPSPs produce this type of inhibition. 43. It’s the energy molecule used by the Na+/K+ pumps to restore the concentration of Na+ and K+ after the action potential is complete. 45. It’s another name for the sheath of Schwann. 47. The physiology of these cells is the basis of nerv ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... Cerebral nuclei do not exert direct control over lower motor neurons; instead, they adjust the motor commands issued in other nuclei and provide a background pattern and rhythm once a movement is under way. The cerebral nuclei also play a key role in cognition and in emotions. The cerebellum influen ...
... Cerebral nuclei do not exert direct control over lower motor neurons; instead, they adjust the motor commands issued in other nuclei and provide a background pattern and rhythm once a movement is under way. The cerebral nuclei also play a key role in cognition and in emotions. The cerebellum influen ...
Chapter 31 The Nervous System
... cell body: largest part of a typical neuron, contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm Dendrite: extension of the cell body of a neuron that carries impulses from the environment or from other neurons toward the cell body Axon: long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body of a neuro ...
... cell body: largest part of a typical neuron, contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm Dendrite: extension of the cell body of a neuron that carries impulses from the environment or from other neurons toward the cell body Axon: long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body of a neuro ...
Checkpoint Answers
... A. after-hyperpolarization B. all-or-none-law *C. Na+/K+ pump D. refractory period • 3. The membrane of resting nerve cells is more permeable to ____K+_____ ions than _____Na+_____ ions. • 4. The minimum depolarization needed to open Na+ gates is called the _threshold__ • 5. Action potentials would ...
... A. after-hyperpolarization B. all-or-none-law *C. Na+/K+ pump D. refractory period • 3. The membrane of resting nerve cells is more permeable to ____K+_____ ions than _____Na+_____ ions. • 4. The minimum depolarization needed to open Na+ gates is called the _threshold__ • 5. Action potentials would ...
BIOLOGY 12: U NIT M/N - C A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. What are the
... 14. a) What happens when a nerve impulse reaches the axon’s presynaptic membrane? _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 14. a) What happens when a nerve impulse reaches the axon’s presynaptic membrane? _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
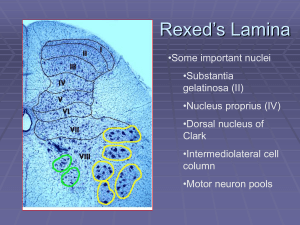
Rexed`s Lamina
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...
www.translationalneuromodeling.org
... response and pre-synaptic input Impulse response. H is the synaptic gain, t is the time constant Membrane potential to rate for kth subpopulation. c, r and e are population parametrs (e.g. volatge sensitivity) ...
... response and pre-synaptic input Impulse response. H is the synaptic gain, t is the time constant Membrane potential to rate for kth subpopulation. c, r and e are population parametrs (e.g. volatge sensitivity) ...
Background: Classical fear conditioning is a phenomenon in which
... addition to the functional images, we will also collect online subjective ratings of perceived level of risk for shock, as well as skin conductance as a measure of physiological arousal, in order to determine how well the subject has learned the connection between the shock US and the CS+ . Anticip ...
... addition to the functional images, we will also collect online subjective ratings of perceived level of risk for shock, as well as skin conductance as a measure of physiological arousal, in order to determine how well the subject has learned the connection between the shock US and the CS+ . Anticip ...
Chapter 12 - Mesa Community College
... Generation of action potential is now more difficult Must add up all the excitatory and inhibitory stimuli (summation) that are influencing the neuron to determine if an action potential will be sent (Fig 12.17 & 12.26) Action Potentials Action Potential (AP) = rapid change in membrane potential (po ...
... Generation of action potential is now more difficult Must add up all the excitatory and inhibitory stimuli (summation) that are influencing the neuron to determine if an action potential will be sent (Fig 12.17 & 12.26) Action Potentials Action Potential (AP) = rapid change in membrane potential (po ...
Chapter 11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... Generation of action potential is now more difficult Must add up all the excitatory and inhibitory stimuli (summation) that are influencing the neuron to determine if an action potential will be sent (Fig 12.17 & 12.26) Action Potentials Action Potential (AP) = rapid change in membrane potential (po ...
... Generation of action potential is now more difficult Must add up all the excitatory and inhibitory stimuli (summation) that are influencing the neuron to determine if an action potential will be sent (Fig 12.17 & 12.26) Action Potentials Action Potential (AP) = rapid change in membrane potential (po ...
File - Mr. Jacobson`s Site
... terminal of a neuron and a target, such as another neuron, a muscle cell, or a gland, is called a ...
... terminal of a neuron and a target, such as another neuron, a muscle cell, or a gland, is called a ...
Nervous system - Lancaster High School
... Neurons are not stimulated, not transmitting signals 1. Fixed anions Proteins, carbohydrates & nucleic acids More abundant inside 2. Sodium/potassium pump ...
... Neurons are not stimulated, not transmitting signals 1. Fixed anions Proteins, carbohydrates & nucleic acids More abundant inside 2. Sodium/potassium pump ...
Study/Review * Nervous System Part 2 * CNS and PNS
... 5. Which of these correctly describes the distribution of ions on either side of an axon when it is not conducting a nerve impulse? a. More sodium ions outside and more potassium ions inside b. More potassium ions outside and less sodium ions inside c. Charged proteins outside and sodium and potass ...
... 5. Which of these correctly describes the distribution of ions on either side of an axon when it is not conducting a nerve impulse? a. More sodium ions outside and more potassium ions inside b. More potassium ions outside and less sodium ions inside c. Charged proteins outside and sodium and potass ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.