Chapter 10
... where a nerve impulse is transmitted • occurs between the axon of one neuron and dendrite or cell body of a second neuron • Note that the two neurons do not touch There is a gap between them = synaptic cleft ...
... where a nerve impulse is transmitted • occurs between the axon of one neuron and dendrite or cell body of a second neuron • Note that the two neurons do not touch There is a gap between them = synaptic cleft ...
chapter48
... 7. Removal of neurotransmitters closes the ion channels and terminates the synaptic response. Neural integration Neural integration occurs at the cellular level. It is the process of adding and subtracting signals, and determining whether or not to fire an impulse. Each neuron may synapse with hundr ...
... 7. Removal of neurotransmitters closes the ion channels and terminates the synaptic response. Neural integration Neural integration occurs at the cellular level. It is the process of adding and subtracting signals, and determining whether or not to fire an impulse. Each neuron may synapse with hundr ...
Slide 1 - MisterSyracuse.com
... 16. Many tasks in the body are taken care of by the unconscious part of the brain, so that the brain’s owner doesn’t have to think about them. These tasks are performed by the A. Cerebrum B. Malpighian tubule C. Cortex D. Cerebellum _________ 17. Name three tasks that might be performed by the stru ...
... 16. Many tasks in the body are taken care of by the unconscious part of the brain, so that the brain’s owner doesn’t have to think about them. These tasks are performed by the A. Cerebrum B. Malpighian tubule C. Cortex D. Cerebellum _________ 17. Name three tasks that might be performed by the stru ...
Nervous System Reading from SparkNotes
... out of the neuron, they also diffuse along the neuron’s length. These sodium ions depolarize the surrounding areas of the neuron’s cell membrane to the threshold potential, at which point the voltage-gated sodium channels in those regions open, creating an action potential. This cycle continues to o ...
... out of the neuron, they also diffuse along the neuron’s length. These sodium ions depolarize the surrounding areas of the neuron’s cell membrane to the threshold potential, at which point the voltage-gated sodium channels in those regions open, creating an action potential. This cycle continues to o ...
Brain calculus: neural integration and persistent activity
... changes in firing rate induced with the intracellular injection of current. This supports the network hypothesis, because if the step changes were generated through mechanisms intrinsic to the cell recorded, such as through the activation of a persistent depolarizing current, then hyperpolarization ...
... changes in firing rate induced with the intracellular injection of current. This supports the network hypothesis, because if the step changes were generated through mechanisms intrinsic to the cell recorded, such as through the activation of a persistent depolarizing current, then hyperpolarization ...
Brain Plasticity and Behavior
... neurological and psychiatric disorders, are correlated with localized changes in neural circuits. Finally, therapies that are intended to alter behavior, such as treatment for addiction, stroke, or schizophrenia, are likely to be most effective if they are able to further reorganize relevant brain c ...
... neurological and psychiatric disorders, are correlated with localized changes in neural circuits. Finally, therapies that are intended to alter behavior, such as treatment for addiction, stroke, or schizophrenia, are likely to be most effective if they are able to further reorganize relevant brain c ...
Neuron Anatomy
... • Particularly important at the Nodes of Ranvier. • Why might such K+ buffering be important anyway? ...
... • Particularly important at the Nodes of Ranvier. • Why might such K+ buffering be important anyway? ...
feedback-poster
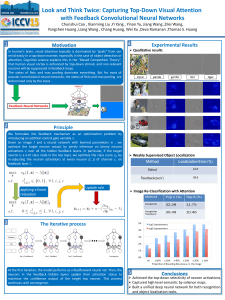
... Yongzhen Huang ,Liang Wang , Chang Huang, Wei Xu ,Deva Ramanan ,Thomas S. Huang ...
... Yongzhen Huang ,Liang Wang , Chang Huang, Wei Xu ,Deva Ramanan ,Thomas S. Huang ...
Structures and Functions Lecture 2
... fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft occurs • Higher impulse frequency more released ...
... fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft occurs • Higher impulse frequency more released ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Welcome to the Health Science Program
... transmission takes place, thus communication Impulses from one neuron are transmitted across the synapse to another neuron by a chemical called a neurotransmitter ...
... transmission takes place, thus communication Impulses from one neuron are transmitted across the synapse to another neuron by a chemical called a neurotransmitter ...
Unit Test Neuro: Core ( Topic 6.5) and Options E ( Topics 1,2,4) HL
... E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdraw reflex including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, motor neuron and effector. (1) ...
... E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdraw reflex including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, motor neuron and effector. (1) ...
Readings to Accompany “Nerves” Worksheet (adapted from France
... When dendrites of a neuron receive sufficient stimulation, the axon hillock of the neuron will transmit that impulse toward the axon. This is the first step in transmitting a stimulus called the action potential. Sodium (Na+) ions will rush into the axon through Na+ channels resulting in a change in ...
... When dendrites of a neuron receive sufficient stimulation, the axon hillock of the neuron will transmit that impulse toward the axon. This is the first step in transmitting a stimulus called the action potential. Sodium (Na+) ions will rush into the axon through Na+ channels resulting in a change in ...
Biology 231
... neuroglandular junction – synapse between neuron and gland most synapses are between one neuron and another neuron Synapses Between Neurons presynaptic neuron – sending neuron (axon terminal) postsynaptic neuron – receiving neuron (dendrite or cell body) synaptic cleft – small space between 2 commun ...
... neuroglandular junction – synapse between neuron and gland most synapses are between one neuron and another neuron Synapses Between Neurons presynaptic neuron – sending neuron (axon terminal) postsynaptic neuron – receiving neuron (dendrite or cell body) synaptic cleft – small space between 2 commun ...
The Nervous System
... axon terminal of the presynaptic cell and causes V-gated Ca2+ channels to open. • Ca2+ rushes in, binds to regulatory proteins & initiates NT exocytosis. • NTs diffuse across the synaptic cleft and then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and initiate some sort of response on the postsyna ...
... axon terminal of the presynaptic cell and causes V-gated Ca2+ channels to open. • Ca2+ rushes in, binds to regulatory proteins & initiates NT exocytosis. • NTs diffuse across the synaptic cleft and then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and initiate some sort of response on the postsyna ...
Plasticity and Functional Recovery of the Brain After
... Our increased understanding in this area has contributed to the field of neurorehabilitation. In other words, it has helped in the treatment of those who have suffered brain trauma. The fact that we know that spontaneous brain recovery slows down after a few weeks, means that we are aware of when it ...
... Our increased understanding in this area has contributed to the field of neurorehabilitation. In other words, it has helped in the treatment of those who have suffered brain trauma. The fact that we know that spontaneous brain recovery slows down after a few weeks, means that we are aware of when it ...
CHAPTER 2 RAPID REVIEW
... thirst, hunger, sleeping, sexual activity, and mood. It appears that the hippocampus is critical for the formation of long-term memories and for memories of the locations of objects. The amygdala is a small almond-shaped structure that is involved in our response to fear. The outer part of the brain ...
... thirst, hunger, sleeping, sexual activity, and mood. It appears that the hippocampus is critical for the formation of long-term memories and for memories of the locations of objects. The amygdala is a small almond-shaped structure that is involved in our response to fear. The outer part of the brain ...
Nervous System - University of Nevada, Las Vegas
... – Interneurons (association neurons) — shuttle signals through CNS pathways ...
... – Interneurons (association neurons) — shuttle signals through CNS pathways ...
Neurotransmitter proteins
... Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse and attach to receptors of a neighboring neuron ...
... Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse and attach to receptors of a neighboring neuron ...
Chapter 24
... carry an impulse from the CNS to a sense organ. carry a nerve impulse from a sense organ to the CNS. carry a nerve impulse to a muscle. carry a nerve impulse both to and from a sense organ. ...
... carry an impulse from the CNS to a sense organ. carry a nerve impulse from a sense organ to the CNS. carry a nerve impulse to a muscle. carry a nerve impulse both to and from a sense organ. ...
Neurotransmitters
... Dilaudid, Demerol, Codeine But can also cause pain if taken over a long period of time ...
... Dilaudid, Demerol, Codeine But can also cause pain if taken over a long period of time ...
Neural Conduction - U
... • Small-molecule transmitters are usually released each time an action potential arrives at the terminal; by contrast, large molecule transmitters are released gradually in response to multiple action potentials ...
... • Small-molecule transmitters are usually released each time an action potential arrives at the terminal; by contrast, large molecule transmitters are released gradually in response to multiple action potentials ...
Motor Neuron
... • Na+ ions rush into the cell and K+ ions rush out depolarizing the region of the membrane • This region of depolarization is an Action Potential • An action potential in one region stimulates adjacent regions to depolarize and the action potential moves away from the point of stimulus • This moving ...
... • Na+ ions rush into the cell and K+ ions rush out depolarizing the region of the membrane • This region of depolarization is an Action Potential • An action potential in one region stimulates adjacent regions to depolarize and the action potential moves away from the point of stimulus • This moving ...
Module 04
... Tens of billions of neurons, each communicating with thousands of other neurons, yield an everchanging wiring diagram. The complexity of the central nervous system allows or makes possible (enables) our thinking, feeling, and behavior. In this way, it is similar to the electronic circuitry (wiring ...
... Tens of billions of neurons, each communicating with thousands of other neurons, yield an everchanging wiring diagram. The complexity of the central nervous system allows or makes possible (enables) our thinking, feeling, and behavior. In this way, it is similar to the electronic circuitry (wiring ...
Nerve Tissue Part 1
... CNS Regeneration Why does the CNS lack the ability for nerve cell regeneration? 1) Lack of neurolemma 2) Axon regrowth inhibition 3) Scar tissue formation ...
... CNS Regeneration Why does the CNS lack the ability for nerve cell regeneration? 1) Lack of neurolemma 2) Axon regrowth inhibition 3) Scar tissue formation ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.