05_Boyle_compiled
... b. The extracellular membrane has a higher concentration of sodium compared with the intercellular space. c. The extracellular membrane has a higher concentration of potassium compared with the intercellular space. d. The membrane potential must pass a certain threshold in order to fire an action po ...
... b. The extracellular membrane has a higher concentration of sodium compared with the intercellular space. c. The extracellular membrane has a higher concentration of potassium compared with the intercellular space. d. The membrane potential must pass a certain threshold in order to fire an action po ...
Neuroglia - wsscience
... control non-motor symptoms (those that do not affect movement) of Parkinson's.” •“Surgical Treatments and Other Therapies Pallidotomy was once the most common surgery for Parkinson's. In this procedure, a surgeon destroys a portion of the brain called the globus pallidus. Pallidotomy can improve sym ...
... control non-motor symptoms (those that do not affect movement) of Parkinson's.” •“Surgical Treatments and Other Therapies Pallidotomy was once the most common surgery for Parkinson's. In this procedure, a surgeon destroys a portion of the brain called the globus pallidus. Pallidotomy can improve sym ...
Central Nervous System
... Myelinated neurons faster than unmyelinated Myelinated fibers conduct impulses from one Node of Ranvier to the next, a phenomenon called saltatory conduction. Speed of impulse conduction is proportional to the diameter of the axon a.Thick, myelinated motor axons conduct at 120 m/s b.Thin, unmyeli ...
... Myelinated neurons faster than unmyelinated Myelinated fibers conduct impulses from one Node of Ranvier to the next, a phenomenon called saltatory conduction. Speed of impulse conduction is proportional to the diameter of the axon a.Thick, myelinated motor axons conduct at 120 m/s b.Thin, unmyeli ...
13.2 part 2
... Action potentials are used to carry the message along one neuron, however action potentials end when the message reaches the end of the neuron. The end of the neuron is made up of terminal branches with end plates. In order to carry the message across the gap to the next neuron, a chemical called a ...
... Action potentials are used to carry the message along one neuron, however action potentials end when the message reaches the end of the neuron. The end of the neuron is made up of terminal branches with end plates. In order to carry the message across the gap to the next neuron, a chemical called a ...
Name
... 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of neuron cell bodies found in the PNS 16. a chemical which diffuses across the synapse in order to affect a postsynaptic neuron 17. stimulus strength NOT strong enough to cause a response 18. when these “ ...
... 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of neuron cell bodies found in the PNS 16. a chemical which diffuses across the synapse in order to affect a postsynaptic neuron 17. stimulus strength NOT strong enough to cause a response 18. when these “ ...
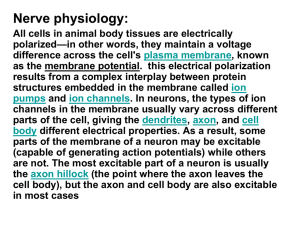
NERVOUS SYSTEMS – FUNCTION AT THE CELLULAR LEVEL
... membrane potential of cell body - amount of change varies (graded) depending on how many channels open and number of ions moving in or out If graded potential exceeds threshold (~10mV above resting potential, or -60 mV) , an action potential is initiated in the axon ...
... membrane potential of cell body - amount of change varies (graded) depending on how many channels open and number of ions moving in or out If graded potential exceeds threshold (~10mV above resting potential, or -60 mV) , an action potential is initiated in the axon ...
are involved in a few types of action potentials
... be reached whereby both solutions have 25 sodium ions and 25 chloride ions. If, however, the barrier is selective to which ions are let through, then diffusion alone will not determine the resulting solution. Returning to the previous example, let's now construct a barrier that is permeable only to ...
... be reached whereby both solutions have 25 sodium ions and 25 chloride ions. If, however, the barrier is selective to which ions are let through, then diffusion alone will not determine the resulting solution. Returning to the previous example, let's now construct a barrier that is permeable only to ...
Document
... Nerve Impulse Transmission Two ways to increase velocity of conduction: 1. Axon has a large diameter -Less resistance to current flow -Found primarily in invertebrates 2. Axon is myelinated -Action potential is only produced at the nodes of Ranvier -Impulse jumps from node to node ...
... Nerve Impulse Transmission Two ways to increase velocity of conduction: 1. Axon has a large diameter -Less resistance to current flow -Found primarily in invertebrates 2. Axon is myelinated -Action potential is only produced at the nodes of Ranvier -Impulse jumps from node to node ...
1. Cell body - greinerudsd
... • The terminals contain tiny sacs (vesicles) that contain neurotransmitters chemical signals • Impulse triggers release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft (via exocytosis) – Neurotransmitters diffuse across gap & bind to receptors on the adjacent neuron – Cause the impulse to continue (i ...
... • The terminals contain tiny sacs (vesicles) that contain neurotransmitters chemical signals • Impulse triggers release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft (via exocytosis) – Neurotransmitters diffuse across gap & bind to receptors on the adjacent neuron – Cause the impulse to continue (i ...
Chapter 48 - cloudfront.net
... the postsynaptic membrane potential. If the neurotransmitters cause the K+ and Na+ ion channels to open and depolarization takes place then they’re called excitatory postsynaptic potentials(EPSPs) because the inside of the cell will be more positive which will bring the membrane potential closer tow ...
... the postsynaptic membrane potential. If the neurotransmitters cause the K+ and Na+ ion channels to open and depolarization takes place then they’re called excitatory postsynaptic potentials(EPSPs) because the inside of the cell will be more positive which will bring the membrane potential closer tow ...
The Nervous System
... • Bipolar: only two fibers—one dendrite and one axon • Unipolar: single fiber from the cell body which splits into dendrite and axon • Multipolar: many dendrites; one axon ...
... • Bipolar: only two fibers—one dendrite and one axon • Unipolar: single fiber from the cell body which splits into dendrite and axon • Multipolar: many dendrites; one axon ...
Module 9: Synaptic Transmission
... Steps to Synaptic Transmission 1. Action Potential causes synaptic vesicle to open 2. Neurotransmitter (NT) released into synapse 3. NT locks onto receptor molecule in postsynaptic membrane (on receiving dendrite) 4. Receptor site opens and allows positive sodium ions to enter the dendrite trigger ...
... Steps to Synaptic Transmission 1. Action Potential causes synaptic vesicle to open 2. Neurotransmitter (NT) released into synapse 3. NT locks onto receptor molecule in postsynaptic membrane (on receiving dendrite) 4. Receptor site opens and allows positive sodium ions to enter the dendrite trigger ...
29 - IWS2.collin.edu
... Neurotransmitter must be released, diffuse across the synapse, and bind to receptors Synaptic delay – time needed to do this Synaptic delay is the rate-limiting step of neural transmission ...
... Neurotransmitter must be released, diffuse across the synapse, and bind to receptors Synaptic delay – time needed to do this Synaptic delay is the rate-limiting step of neural transmission ...
A5: Neuropharamcology (student) - Ms De Souza`s Super Awesome
... Instead of acting on a single post-synaptic neuron, they diffuse into the surrounding fluid and act on groups of neurons. ...
... Instead of acting on a single post-synaptic neuron, they diffuse into the surrounding fluid and act on groups of neurons. ...
My Reaction Test Score = Neural Transmission
... axon. This wave of changing electrical charge flows down the axon until it reaches the terminal button. At the end (terminal button) of the axon the signal causes small sacks (vesicles) of chemicals to be released into the space between the end of the axon and the dendrite of the next neuron. These ...
... axon. This wave of changing electrical charge flows down the axon until it reaches the terminal button. At the end (terminal button) of the axon the signal causes small sacks (vesicles) of chemicals to be released into the space between the end of the axon and the dendrite of the next neuron. These ...
Chapter 3
... – Presynaptic neuron releases NT into cleft; NT binds receptor on post-synaptic neuron – Binding of NT produces graded (postsynaptic) potential • Repeated binding eventually produces a.p. ...
... – Presynaptic neuron releases NT into cleft; NT binds receptor on post-synaptic neuron – Binding of NT produces graded (postsynaptic) potential • Repeated binding eventually produces a.p. ...
Lect5
... 1. At rest only K+ leak channels open, PK>>PNa 2. With stimulus, voltage-gated Na channels open, PNa>>PK Na+ flows into the cell carrying positive charge ...
... 1. At rest only K+ leak channels open, PK>>PNa 2. With stimulus, voltage-gated Na channels open, PNa>>PK Na+ flows into the cell carrying positive charge ...
Packet 6- The neuron
... A. There is a high concentration of Na+ in the ECF (thanks to what molecule??) B. There is also a higher concentration of Cl- in the ECF 2. The ICF has a slightly negative net charge A. There is a high concentration of K+ in the ICF (thanks to what molecule??) B. There is also a higher concentr ...
... A. There is a high concentration of Na+ in the ECF (thanks to what molecule??) B. There is also a higher concentration of Cl- in the ECF 2. The ICF has a slightly negative net charge A. There is a high concentration of K+ in the ICF (thanks to what molecule??) B. There is also a higher concentr ...
Lecture #19 - Suraj @ LUMS
... • The plasma membrane of neurons, has an unequal distribution of ions and electrical charges between the two sides of the membrane. • The outside of the membrane has a (+), inside has is (-). • This charge difference is a resting potential and is measured in millivolts. • Passage of ions across the ...
... • The plasma membrane of neurons, has an unequal distribution of ions and electrical charges between the two sides of the membrane. • The outside of the membrane has a (+), inside has is (-). • This charge difference is a resting potential and is measured in millivolts. • Passage of ions across the ...
Synaptic Transmission - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... •How a neuron communicates with another neuron and the effects of drugs on this process. •Types of Neurotransmitters ...
... •How a neuron communicates with another neuron and the effects of drugs on this process. •Types of Neurotransmitters ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... C. Termination & reabsorption of neurotransmitters 1. The neurotransmitter will continue to __________________ the receptors as long as they are __________________. The neurotransmitters must be __________________ in one of three ways. a. Chemical breakdown (__________________ [AChE]) b. ___________ ...
... C. Termination & reabsorption of neurotransmitters 1. The neurotransmitter will continue to __________________ the receptors as long as they are __________________. The neurotransmitters must be __________________ in one of three ways. a. Chemical breakdown (__________________ [AChE]) b. ___________ ...
nervous system
... • Narrow gap, synaptic cleft, between cells • More common than electrical in vertebrates and most invertebrates • Require neurotransmitters (chemical intercellular messengers) ...
... • Narrow gap, synaptic cleft, between cells • More common than electrical in vertebrates and most invertebrates • Require neurotransmitters (chemical intercellular messengers) ...
Neurotransmitters
... • Much of human behavior is mediated by the action of neurotransmitters in the brain. Researchers are also demonstrating that behavioral pathology is largely due to imbalances in one or more neurotransmitter systems. Physical diseases may also be due to specific neurotransmitter pathway disturbances ...
... • Much of human behavior is mediated by the action of neurotransmitters in the brain. Researchers are also demonstrating that behavioral pathology is largely due to imbalances in one or more neurotransmitter systems. Physical diseases may also be due to specific neurotransmitter pathway disturbances ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses
... Figure 2.16 The sodium and potassium gradients for a resting membrane Sodium ions are more concentrated outside the neuron; potassium ions are more concentrated inside. However, because the body has far more sodium than potassium, the total number of positive charges is greater outside the cell tha ...
... Figure 2.16 The sodium and potassium gradients for a resting membrane Sodium ions are more concentrated outside the neuron; potassium ions are more concentrated inside. However, because the body has far more sodium than potassium, the total number of positive charges is greater outside the cell tha ...
Heart
... glykokalyx … protective cover of some cells formed of oligosacharides, … there are receptors, glykoproteins and other proteoglikans … protects against chemical and mechanical damage ...
... glykokalyx … protective cover of some cells formed of oligosacharides, … there are receptors, glykoproteins and other proteoglikans … protects against chemical and mechanical damage ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.