Lecture nerve
... 9. neuron is hyperpolarized – no new AP can be generated with a normal stimulus 10. all voltage-gated channels closed, Na/K pump “resets” ion distribution to resting situation ...
... 9. neuron is hyperpolarized – no new AP can be generated with a normal stimulus 10. all voltage-gated channels closed, Na/K pump “resets” ion distribution to resting situation ...
chapter_12 - The Anatomy Academy
... membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses for short distance inside membrane producing a change in voltage called a local potential ...
... membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses for short distance inside membrane producing a change in voltage called a local potential ...
Nervous System Neuron: nerve cell, functional unit of nervous
... Purpose of the refractory period is to make the stimulus reach the end because of the potassium. Parts of axon not covered by myelin the action potential jumps Nodes of Ranvier which have voltage gated channels. This is known as the refractory period. Cell begins to Reset Once refectory, +40 mV is r ...
... Purpose of the refractory period is to make the stimulus reach the end because of the potassium. Parts of axon not covered by myelin the action potential jumps Nodes of Ranvier which have voltage gated channels. This is known as the refractory period. Cell begins to Reset Once refectory, +40 mV is r ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
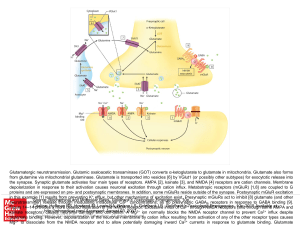
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
the nervous system
... Describe the structural and functional organization of the nervous system into Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System (Afferent and Efferent Divisions). b. Describe the functional organization of the Efferent Division of the Peripheral Nervous System into Autonomic Nervous System and S ...
... Describe the structural and functional organization of the nervous system into Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System (Afferent and Efferent Divisions). b. Describe the functional organization of the Efferent Division of the Peripheral Nervous System into Autonomic Nervous System and S ...
Concepts of Neurobiology
... CNS: neurons, composed of: Cell body, contains nucleus Axon, transmits message to next cell Dendrites, receives messages from cells Three classes of neurons in CNS Afferent (sensory) Efferent (motor) Interneurons in CNS ...
... CNS: neurons, composed of: Cell body, contains nucleus Axon, transmits message to next cell Dendrites, receives messages from cells Three classes of neurons in CNS Afferent (sensory) Efferent (motor) Interneurons in CNS ...
Ch 8 Neurons and Network properties part-1
... Now let’s try to think about a living excitable cell… ...
... Now let’s try to think about a living excitable cell… ...
File
... Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. ...
... Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. ...
How do neurotransmitters generate electrochemical signals in
... 2. triggers the synthesis of a second messenger which: (a) binds to a ligand-activated ion channel, causing the channel to open or close, or (b) diffuses through the cytoplasm where it influences the activities of the neuron (Figure B). ...
... 2. triggers the synthesis of a second messenger which: (a) binds to a ligand-activated ion channel, causing the channel to open or close, or (b) diffuses through the cytoplasm where it influences the activities of the neuron (Figure B). ...
A- A- A- K+ A - How Your Brain Works
... • In addition to the resting (K+ leakage) channels, neurons can have a large variety of gated ion channels which will open transiently in the presence of certain stimuli or chemical signals. These gated channels may be permeable to Na+, Cl- or Ca++. • When these gated channels open, the voltage acro ...
... • In addition to the resting (K+ leakage) channels, neurons can have a large variety of gated ion channels which will open transiently in the presence of certain stimuli or chemical signals. These gated channels may be permeable to Na+, Cl- or Ca++. • When these gated channels open, the voltage acro ...
K - Cloudfront.net
... What happens at the end of the axon? Impulse has to jump the synapse! – junction between neurons – has to jump quickly from one cell to next How does the wave jump the gap? ...
... What happens at the end of the axon? Impulse has to jump the synapse! – junction between neurons – has to jump quickly from one cell to next How does the wave jump the gap? ...
ActionPotentialWebquestCompleteGarrettIan
... 4. After sodium ions have flooded into the cell and the sodium gates close, what happens to the potassium ions? 5. How does an action potential conduct along an axon? 6. Describe and draw an action potential. Part 3 – Ions Control Membrane Potential Go to http://www.bristol.ac.uk/synaptic/basics/bas ...
... 4. After sodium ions have flooded into the cell and the sodium gates close, what happens to the potassium ions? 5. How does an action potential conduct along an axon? 6. Describe and draw an action potential. Part 3 – Ions Control Membrane Potential Go to http://www.bristol.ac.uk/synaptic/basics/bas ...
Lesson 4 Section 9.2 Electrochemical Impulse
... This happens from the axon of one neuron to the dendrite of another Neurons have a rich supply of positive (+) and negative (-) ions both inside and outside the cell Negative ions are too large to pass through the cell membrane The positive ions do have the ability to diffuse in and out of the cell ...
... This happens from the axon of one neuron to the dendrite of another Neurons have a rich supply of positive (+) and negative (-) ions both inside and outside the cell Negative ions are too large to pass through the cell membrane The positive ions do have the ability to diffuse in and out of the cell ...
Ch. 48 - Ltcconline.net
... a. activates a signal transduction pathway involving a second messenger in postsynaptic cell b. slower onset but last longer 2. eg. when norepinephrine binds to its receptor, a G protein is activated, which ultimately opens many channels (review ch. 11) D. Neurotransmitters - each bind to own recept ...
... a. activates a signal transduction pathway involving a second messenger in postsynaptic cell b. slower onset but last longer 2. eg. when norepinephrine binds to its receptor, a G protein is activated, which ultimately opens many channels (review ch. 11) D. Neurotransmitters - each bind to own recept ...
Membrane potential (mV)
... postsynaptic cells are separated by a narrow synaptic cleft. Neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the cleft and bind to receptors in the plasma membrane of the postsynaptic cell. The binding opens channels to ion flow that may generate an impulse in the postsynaptic cell. ...
... postsynaptic cells are separated by a narrow synaptic cleft. Neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the cleft and bind to receptors in the plasma membrane of the postsynaptic cell. The binding opens channels to ion flow that may generate an impulse in the postsynaptic cell. ...
Physiology Lecture 6
... little less negative than the equilibrium potential for K+ . Depolarization of a small region of an axon can be experimentally induced by a pair of stimulating electrodes that act as if they were injecting positive charges into the axon. If the depolarization is below a certain level, it will simply ...
... little less negative than the equilibrium potential for K+ . Depolarization of a small region of an axon can be experimentally induced by a pair of stimulating electrodes that act as if they were injecting positive charges into the axon. If the depolarization is below a certain level, it will simply ...
Action Potentials & Nerve Conduction
... •A graded potential depolarization is called excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP). A graded potential hyperpolarization is called an inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP). •They occur in the cell body and dendrites of the neuron. •The wave of depolarization or hyperpolarization which moves ...
... •A graded potential depolarization is called excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP). A graded potential hyperpolarization is called an inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP). •They occur in the cell body and dendrites of the neuron. •The wave of depolarization or hyperpolarization which moves ...
Summary Sodium pump.
... of the vesicles to move to the end of the axon and discharge their contents into the synaptic cleft. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across the cleft, and bind to receptors on the other cell's membrane, causing ion channels on that cell to open. Some neurotransmitters cause an action potential, o ...
... of the vesicles to move to the end of the axon and discharge their contents into the synaptic cleft. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across the cleft, and bind to receptors on the other cell's membrane, causing ion channels on that cell to open. Some neurotransmitters cause an action potential, o ...
Neurons
... from tissues and organs into the CNS motor = efferent neurons - transmit signals from the CNS to the effector cells ...
... from tissues and organs into the CNS motor = efferent neurons - transmit signals from the CNS to the effector cells ...
PPTX - Bonham Chemistry
... Hormone: A chemical messenger released by an endocrine gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse ...
... Hormone: A chemical messenger released by an endocrine gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse ...
The Neuron: The Basic Unit of Communication Neuron: Basic
... Neuron: Basic building blocks of the nervous system. It is a highly specialized nerve cell that communicate information in electrical and chemical form. ...
... Neuron: Basic building blocks of the nervous system. It is a highly specialized nerve cell that communicate information in electrical and chemical form. ...
The following are Biology 201 terms that will be used in Biology 202
... 201 and since we stress homeostasis in both courses there will be a fair amount of information from biology 201 that is used in 202. The following terms you are expected to know and be able to use in biology 202. Anatomical position Directional terms Body planes and sections Body cavities Homeostasi ...
... 201 and since we stress homeostasis in both courses there will be a fair amount of information from biology 201 that is used in 202. The following terms you are expected to know and be able to use in biology 202. Anatomical position Directional terms Body planes and sections Body cavities Homeostasi ...
Psych 9A. Lec. 05 PP Slides: Brain and Nervous System
... • These cells have many functions, both during development and in supporting the function of the mature nervous system. • They may also constitute a separate, slow signal system. • Oligodendrocytes: produce myelin sheaths for neuron axons (white ...
... • These cells have many functions, both during development and in supporting the function of the mature nervous system. • They may also constitute a separate, slow signal system. • Oligodendrocytes: produce myelin sheaths for neuron axons (white ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.