Types of neurons
... if resting potential rises above threshold an action potential starts to travel from cell body down the axon Figure shows resting axon being approached by an AP ...
... if resting potential rises above threshold an action potential starts to travel from cell body down the axon Figure shows resting axon being approached by an AP ...
No Slide Title
... What is the difference between Excitatory & Inhibitory neurons? Ligands binding with postsynaptic receptors can cause: A _____________ in postsynaptic membrane potential (_________ ~ closer to zero… depolarization) Example: ___ ~ opens Na+ channels An __________ in postsynaptic membrane potential ( ...
... What is the difference between Excitatory & Inhibitory neurons? Ligands binding with postsynaptic receptors can cause: A _____________ in postsynaptic membrane potential (_________ ~ closer to zero… depolarization) Example: ___ ~ opens Na+ channels An __________ in postsynaptic membrane potential ( ...
Histology of Nervous Tissue
... • Chemical synapses (e.g. NMJ) - one way flow & slower – Review components – Synaptic delay about 0.5 msec Synaptic Action • AP arrives at presynaptic region of axon • Voltage-gated Na+ and Ca2+ channels open • Ca2+ moves inward • Ca2+ initiates exocytosis of synaptic vesicles • Neurotransmitter dif ...
... • Chemical synapses (e.g. NMJ) - one way flow & slower – Review components – Synaptic delay about 0.5 msec Synaptic Action • AP arrives at presynaptic region of axon • Voltage-gated Na+ and Ca2+ channels open • Ca2+ moves inward • Ca2+ initiates exocytosis of synaptic vesicles • Neurotransmitter dif ...
Slide 1
... Depolarization of muscle cells (-70 mV ~0 mV) Opening of Ca2+ channels Increased cytosolic Ca2+ Troponin mediated translocation of tropomyosin Response = contraction ...
... Depolarization of muscle cells (-70 mV ~0 mV) Opening of Ca2+ channels Increased cytosolic Ca2+ Troponin mediated translocation of tropomyosin Response = contraction ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses
... Sodium channels open once threshold is reached causing an influx of sodium: depolarization to +50 mv Potassium channels open as the action potential approaches its peak allowing potassium to flow out of the cell: hyperpolarization to -70mv. ...
... Sodium channels open once threshold is reached causing an influx of sodium: depolarization to +50 mv Potassium channels open as the action potential approaches its peak allowing potassium to flow out of the cell: hyperpolarization to -70mv. ...
chapt12-nervous system
... potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. The Synapse Transmission of the nerve impulse from one neuron to another takes place at a synapse when a neurotransmitter molecule is released from a ...
... potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. The Synapse Transmission of the nerve impulse from one neuron to another takes place at a synapse when a neurotransmitter molecule is released from a ...
Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology
... – Acetyl coA (mitochondria) – Choline (dietary) – Catalyzed by choline acetyl transferase (ChAT) ...
... – Acetyl coA (mitochondria) – Choline (dietary) – Catalyzed by choline acetyl transferase (ChAT) ...
D. Vertebrate Nervous Systems
... Gated Na+ channels open Na+ diffuses into the cell the membrane potential becomes less negative. The Action Potential: All or Nothing Depolarization. If graded potentials sum to -55mV a threshold potential is achieved. This triggers an action potential. Axons only. In the resting state ...
... Gated Na+ channels open Na+ diffuses into the cell the membrane potential becomes less negative. The Action Potential: All or Nothing Depolarization. If graded potentials sum to -55mV a threshold potential is achieved. This triggers an action potential. Axons only. In the resting state ...
BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR
... All your behavior begins with actions of your neurons. A neuron gets incoming information from its receptor sites spread around the dendrites. That information is sent to the cell body. Neural impulses are electrical in nature along the neuron. The neuron at rest is more negative inside the cell mem ...
... All your behavior begins with actions of your neurons. A neuron gets incoming information from its receptor sites spread around the dendrites. That information is sent to the cell body. Neural impulses are electrical in nature along the neuron. The neuron at rest is more negative inside the cell mem ...
Open Document - Clinton Community College
... ◦ E.) Terminal Buttons- Axon ends with a cluster of these small knobs secreting chemicals known as neurotransmitters. ◦ F.) Synapse – A “Gap” or junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to another. ...
... ◦ E.) Terminal Buttons- Axon ends with a cluster of these small knobs secreting chemicals known as neurotransmitters. ◦ F.) Synapse – A “Gap” or junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to another. ...
Nerve Notes
... 1. Afferent Division – conducts action potential (AP) from sensory receptors to CNS 2. Efferent Division – AP from CNS to organs a. Somatic Motor Neurons – CNS to skeletal muscle b. Automatic Neurons – CNS to cardiac, smooth muscle ...
... 1. Afferent Division – conducts action potential (AP) from sensory receptors to CNS 2. Efferent Division – AP from CNS to organs a. Somatic Motor Neurons – CNS to skeletal muscle b. Automatic Neurons – CNS to cardiac, smooth muscle ...
The Neuron
... - Inside neuron = mostly negative charge This is how it stays when at resting state When stimulated by incoming message - Cell membrane open and the positive ions rush in when enough has entered to make the inside more positive than the outside. The cell membrane closes again. This opens/close o ...
... - Inside neuron = mostly negative charge This is how it stays when at resting state When stimulated by incoming message - Cell membrane open and the positive ions rush in when enough has entered to make the inside more positive than the outside. The cell membrane closes again. This opens/close o ...
Slide ()
... A. The morphology of peripheral somatic sensory receptors on hairy skin (left) and hairless, or glabrous, skin (right). B. The muscle spindle organ (top inset) is a stretch receptor located within the muscle. It receives an efferent innervation from the spinal cord that maintains receptor sensitivit ...
... A. The morphology of peripheral somatic sensory receptors on hairy skin (left) and hairless, or glabrous, skin (right). B. The muscle spindle organ (top inset) is a stretch receptor located within the muscle. It receives an efferent innervation from the spinal cord that maintains receptor sensitivit ...
Slide ()
... Neurogenic and myopathic diseases have different effects on the motor unit. A. A motor unit potential is recorded by inserting a needle electrode into the muscle. The muscle fibers innervated by a single motor neuron are not usually adjacent to one another, yet the highly effective transmission at t ...
... Neurogenic and myopathic diseases have different effects on the motor unit. A. A motor unit potential is recorded by inserting a needle electrode into the muscle. The muscle fibers innervated by a single motor neuron are not usually adjacent to one another, yet the highly effective transmission at t ...
Slide ()
... Neurogenic and myopathic diseases have different effects on the motor unit. A. A motor unit potential is recorded by inserting a needle electrode into the muscle. The muscle fibers innervated by a single motor neuron are not usually adjacent to one another, yet the highly effective transmission at t ...
... Neurogenic and myopathic diseases have different effects on the motor unit. A. A motor unit potential is recorded by inserting a needle electrode into the muscle. The muscle fibers innervated by a single motor neuron are not usually adjacent to one another, yet the highly effective transmission at t ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... muscle and other neurons. The chemical substances, however, influence the activity of heart muscle cells in different ways. Loewi placed two hearts in separate chambers. The chambers, however, were connected, allowing the saline solutions of the two containers to mix. He stimulated the vagus nerve o ...
... muscle and other neurons. The chemical substances, however, influence the activity of heart muscle cells in different ways. Loewi placed two hearts in separate chambers. The chambers, however, were connected, allowing the saline solutions of the two containers to mix. He stimulated the vagus nerve o ...
20-NervousSystem
... The Na+ channels remain closed until the membrane potential normalizes (-70 mV), keeping the action potential from moving backward The ion balance across the membrane is restored by the action of the sodium-potassium pump ...
... The Na+ channels remain closed until the membrane potential normalizes (-70 mV), keeping the action potential from moving backward The ion balance across the membrane is restored by the action of the sodium-potassium pump ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... Neuronal glutamate (Glu) is synthesized de novo from glucose (not shown) and from glutamine (Gln) supplied by glial cells. Glutamate is then packaged into synaptic vesicles by vesicular glutamate transporters (vGluTs). SNARE complex proteins mediate the interaction and fusion of vesicles with the pr ...
... Neuronal glutamate (Glu) is synthesized de novo from glucose (not shown) and from glutamine (Gln) supplied by glial cells. Glutamate is then packaged into synaptic vesicles by vesicular glutamate transporters (vGluTs). SNARE complex proteins mediate the interaction and fusion of vesicles with the pr ...
Practice Exam 3 ANSWERS
... a. is propagated by the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels b. occurs whenever a pre-synaptic nerve fires a charge to a post synaptic nerve c. is carried out only whenever half of the neural threshold is reached d. moves bidirectionally away from the cell body 4. Saltatory conduction is made po ...
... a. is propagated by the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels b. occurs whenever a pre-synaptic nerve fires a charge to a post synaptic nerve c. is carried out only whenever half of the neural threshold is reached d. moves bidirectionally away from the cell body 4. Saltatory conduction is made po ...
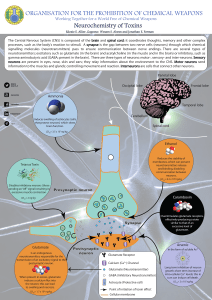
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
File
... same postsynaptic neuron add together. The combination of EPSPs through spatial and temporal summation can trigger an action potential. • Through summation, an IPSP can counter the effect of an EPSP. The summed effect of EPSPs and IPSPs determines whether an axon hillock will reach threshold and gen ...
... same postsynaptic neuron add together. The combination of EPSPs through spatial and temporal summation can trigger an action potential. • Through summation, an IPSP can counter the effect of an EPSP. The summed effect of EPSPs and IPSPs determines whether an axon hillock will reach threshold and gen ...
The Nervous System - Ridgewood High School
... ensues, depolarizing the cell and causing the VM to increase. This is the rising phase of an AP. • Eventually, the Na+ channel will have inactivated and the K+ channels will be open. Now, K+ effluxes and repolarization occurs. This is the falling phase. – K+ channels are slow to open and slow to clo ...
... ensues, depolarizing the cell and causing the VM to increase. This is the rising phase of an AP. • Eventually, the Na+ channel will have inactivated and the K+ channels will be open. Now, K+ effluxes and repolarization occurs. This is the falling phase. – K+ channels are slow to open and slow to clo ...
AP – All or nothing
... an unmyelinated axon? • How does an action potential pass along a myelinated axon? • What factors affect the speed of conductance of an action potential? • What is the refractory period? • What is meant by the “all or nothing” ...
... an unmyelinated axon? • How does an action potential pass along a myelinated axon? • What factors affect the speed of conductance of an action potential? • What is the refractory period? • What is meant by the “all or nothing” ...
Nervous System Structure and Function Pt 1
... • At the leading edge of an impulse, sodium channels open allowing sodium ions to flow into the cell. • This flow of positive ions causes a temporary change in the charges on the cell membrane. • The inside of the membrane gains a positive charge and the outside of the membrane gains a negative char ...
... • At the leading edge of an impulse, sodium channels open allowing sodium ions to flow into the cell. • This flow of positive ions causes a temporary change in the charges on the cell membrane. • The inside of the membrane gains a positive charge and the outside of the membrane gains a negative char ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.