MLP and SVM Networks – a Comparative Study
... This paper will summarize and compare these two networks: MLP and SVM. The comparison will be done with respect to the complexity of the structure as well as the accuracy of results for the solution of different learning tasks, including classification, prediction and regression problem. Special emp ...
... This paper will summarize and compare these two networks: MLP and SVM. The comparison will be done with respect to the complexity of the structure as well as the accuracy of results for the solution of different learning tasks, including classification, prediction and regression problem. Special emp ...
On Multi-Class Cost-Sensitive Learning
... The first series of experiments deal with consistent cost matrices while the second series deal with inconsistent ones. Here the consistent matrices are generated as follows: a cdimensional real value vector is randomly generated and regarded as the root of Eq. 9, then a real value is randomly gener ...
... The first series of experiments deal with consistent cost matrices while the second series deal with inconsistent ones. Here the consistent matrices are generated as follows: a cdimensional real value vector is randomly generated and regarded as the root of Eq. 9, then a real value is randomly gener ...
PDF file
... discriminative for classifying a scene type or for recognizing an object, such methods can be used to classify scenes or even for recognizing objects from general backgrounds (Fei-Fei, 2006) [9], Poggio & coworkers [25]). However, we can expect that the performance will depend on how discriminative ...
... discriminative for classifying a scene type or for recognizing an object, such methods can be used to classify scenes or even for recognizing objects from general backgrounds (Fei-Fei, 2006) [9], Poggio & coworkers [25]). However, we can expect that the performance will depend on how discriminative ...
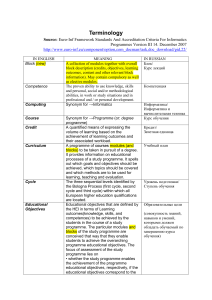
Terminology
... volume of learning based on the achievement of learning outcomes and their associated workload. A programme of courses modules (and blocks) to be taken in pursuit of a degree. It provides information on educational processes of a study programme. It spells out which goals and objectives should be ac ...
... volume of learning based on the achievement of learning outcomes and their associated workload. A programme of courses modules (and blocks) to be taken in pursuit of a degree. It provides information on educational processes of a study programme. It spells out which goals and objectives should be ac ...
Close - IJCAI
... with soft quantifiers. Unlike other SRL frameworks whose atoms are Boolean, atoms in PSL can take continuous values in the interval [0, 1], which facilitates analysis of continuous domains such as user behavior in social media. Indeed, in practice user behavior is not always black-and-white. For exa ...
... with soft quantifiers. Unlike other SRL frameworks whose atoms are Boolean, atoms in PSL can take continuous values in the interval [0, 1], which facilitates analysis of continuous domains such as user behavior in social media. Indeed, in practice user behavior is not always black-and-white. For exa ...
Cognitive Science and Normativity II
... There are plenty of less or more serious arguments against the thesis that human minds work mechanically. However only few (I will try to indicate that all of them are reducible to one in the end) are really meaningful. In particular I do not want to focus on commonly raised arguments on existence o ...
... There are plenty of less or more serious arguments against the thesis that human minds work mechanically. However only few (I will try to indicate that all of them are reducible to one in the end) are really meaningful. In particular I do not want to focus on commonly raised arguments on existence o ...
Simple Algorithmic Theory of Subjective Beauty, Novelty
... of their observations. Since short and simple explanations of the past usually reflect some repetitive regularity that helps to predict the future, every intelligent system interested in achieving future goals should be motivated to compress the history of raw sensory inputs in response to its action ...
... of their observations. Since short and simple explanations of the past usually reflect some repetitive regularity that helps to predict the future, every intelligent system interested in achieving future goals should be motivated to compress the history of raw sensory inputs in response to its action ...
AAAI announces newly-elected Fellows
... distinguished AI scientists for their outstanding contributions to the theory or practice of AI by electing them AAAI Fellows — a lifetime honor. Fellows are honored for providing intellectual leadership and making significant research or service contributions to the field over a period of at least ...
... distinguished AI scientists for their outstanding contributions to the theory or practice of AI by electing them AAAI Fellows — a lifetime honor. Fellows are honored for providing intellectual leadership and making significant research or service contributions to the field over a period of at least ...
The Symbol Grounding Problem
... Grounding – a representation is grounded when the agent can reason about all of the perceivable features of the entity represented and can construct an instantiation of the ...
... Grounding – a representation is grounded when the agent can reason about all of the perceivable features of the entity represented and can construct an instantiation of the ...
Acquiring Visibly Intelligent Behavior with Example
... algorithms it is possible to incorporate phenotypic adaptation back into the genotype via reverse engineering. For example, if an adaptation step is added to the evolutionary life cycle in neuroevolution, any resulting modifications to a network’s weights can be written back to the network’s represe ...
... algorithms it is possible to incorporate phenotypic adaptation back into the genotype via reverse engineering. For example, if an adaptation step is added to the evolutionary life cycle in neuroevolution, any resulting modifications to a network’s weights can be written back to the network’s represe ...
Serre-Poggio_ACM_R2_finalSubmission
... classifier) and will require less training examples to achieve a similar level of performance transformations such as scaling, translation, thus lowering the sample complexity of the classification problem. In the limit, learning in illumination, changes in viewpoint, clutter, as well as panel (B) c ...
... classifier) and will require less training examples to achieve a similar level of performance transformations such as scaling, translation, thus lowering the sample complexity of the classification problem. In the limit, learning in illumination, changes in viewpoint, clutter, as well as panel (B) c ...
PDF
... of actions that should take place in all the possible situations. We take benefit of the human capabilities of knowing which action to perform in currently observed situations to efficiently generate knowledge for decision making in a multitask robot. The idea of learning cause-effects is based on P ...
... of actions that should take place in all the possible situations. We take benefit of the human capabilities of knowing which action to perform in currently observed situations to efficiently generate knowledge for decision making in a multitask robot. The idea of learning cause-effects is based on P ...
all publications as Word document
... International Conference on the Synthesis and Simulation of Living Systems (ALIFE XIV). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2014, New York, USA, pp.1-8. Pugh, JK, Soltoggio, A, Stanley, KO (2014) Real-time Hebbian Learning from Autoencoder Features for Control Tasks. In Fourteenth International Conference on ...
... International Conference on the Synthesis and Simulation of Living Systems (ALIFE XIV). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2014, New York, USA, pp.1-8. Pugh, JK, Soltoggio, A, Stanley, KO (2014) Real-time Hebbian Learning from Autoencoder Features for Control Tasks. In Fourteenth International Conference on ...
x - inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... Lazy learning: keep data around and predict from it at test time 2 Examples ...
... Lazy learning: keep data around and predict from it at test time 2 Examples ...
An introduction to graphical models
... Many of the classical multivariate probabalistic systems studied in fields such as statistics, systems engineering, information theory, pattern recognition and statistical mechanics are special cases of the general graphical model formalism – examples include mixture models, factor analysis, hidden ...
... Many of the classical multivariate probabalistic systems studied in fields such as statistics, systems engineering, information theory, pattern recognition and statistical mechanics are special cases of the general graphical model formalism – examples include mixture models, factor analysis, hidden ...
A Framework for Average Case Analysis of Conjunctive Learning
... Therefore, unlike the PAC model, the framework we have developed is not distribution-free. Furthermore, to simplify computations (or reduce the amount of information required by the model) we will make certain independence assumptions (e.g., the probabilities of all irrelevant features occurring in ...
... Therefore, unlike the PAC model, the framework we have developed is not distribution-free. Furthermore, to simplify computations (or reduce the amount of information required by the model) we will make certain independence assumptions (e.g., the probabilities of all irrelevant features occurring in ...
Program Statement - Eden Daycare Mississauga
... Eden Daycare strives to implement flexibility in our programming so that each child can realize their full potential by indulging their capabilities and curiosities. They can try new things and explore new ideas, all while learning and developing at their own pace. Independence and self-reliance: Ou ...
... Eden Daycare strives to implement flexibility in our programming so that each child can realize their full potential by indulging their capabilities and curiosities. They can try new things and explore new ideas, all while learning and developing at their own pace. Independence and self-reliance: Ou ...
Reexamining Behavior-Based Artificial Intelligence
... local to layers of modules [e.g. 4, 28]. Unfortunately, this promising approach was apparently smothered by the attractive simplicity and radicalism of his deemphasis on representation and centralized control. Of the researchers who did not immediately adopt “no representation” as a mantra, most at ...
... local to layers of modules [e.g. 4, 28]. Unfortunately, this promising approach was apparently smothered by the attractive simplicity and radicalism of his deemphasis on representation and centralized control. Of the researchers who did not immediately adopt “no representation” as a mantra, most at ...
ANNs - WordPress.com
... Basic learning mechanisms Unsupervised learning Minimize some given cost/energy function Reinforcement learning Data generated by agent’s interactions with environment Agent observes accumulated costs and adjust actions accordingly ...
... Basic learning mechanisms Unsupervised learning Minimize some given cost/energy function Reinforcement learning Data generated by agent’s interactions with environment Agent observes accumulated costs and adjust actions accordingly ...
Artificial Neural Networks for Data Mining
... artificial neural networks (ANN) Know the similarities and differences between biological and artificial neural networks Learn the different types of neural network ...
... artificial neural networks (ANN) Know the similarities and differences between biological and artificial neural networks Learn the different types of neural network ...
Concepts and Concept
... 1995) represent knowledge procedurally as a series of “IF THEN Rules” which specify a condition and action, or premise and conclusion. Concept mapping, representing knowledge in graphs is a technique developed at Cornell University (Novak, 1977.). (Novak, 1984) suggest that the initial ideas are art ...
... 1995) represent knowledge procedurally as a series of “IF THEN Rules” which specify a condition and action, or premise and conclusion. Concept mapping, representing knowledge in graphs is a technique developed at Cornell University (Novak, 1977.). (Novak, 1984) suggest that the initial ideas are art ...
Synergies Between Symbolic and Sub
... the game of Go used multiple machine learning algorithms for training itself, and also used a sophisticated search procedure while playing the game. Another recent succesful example of integrating symbolic AI (reinforcement learning) and sub-symbolic AI (deep neural networks): Google DeepMind learni ...
... the game of Go used multiple machine learning algorithms for training itself, and also used a sophisticated search procedure while playing the game. Another recent succesful example of integrating symbolic AI (reinforcement learning) and sub-symbolic AI (deep neural networks): Google DeepMind learni ...