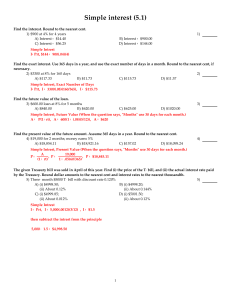
CH. 4 KEY - Allen ISD
... P x R x T=I P- PRINCIPAL R- RATE T- TIME ( IF A FRACTION OF A YEAR EXPRESSED W/ DECIMALS) I- INTEREST EXAMPLE: Calculate the simple interest earned on a savings account in 9 months that begins with a deposit of $2,200 and pays 4 ½ percent interest. $2,200 x .045 x .75 = $74.25 ...
... P x R x T=I P- PRINCIPAL R- RATE T- TIME ( IF A FRACTION OF A YEAR EXPRESSED W/ DECIMALS) I- INTEREST EXAMPLE: Calculate the simple interest earned on a savings account in 9 months that begins with a deposit of $2,200 and pays 4 ½ percent interest. $2,200 x .045 x .75 = $74.25 ...
Chapter 27: Money, Banking, and the Financial Sector
... trades that could not otherwise have taken place and thus have enormous value to society. d. Disagree. The value of an asset depends not only on the quantity but also on its price per unit. The price of land per acre in Japan exceeds that in the United States by so much that the total value of land ...
... trades that could not otherwise have taken place and thus have enormous value to society. d. Disagree. The value of an asset depends not only on the quantity but also on its price per unit. The price of land per acre in Japan exceeds that in the United States by so much that the total value of land ...
PSSA 1.8 Percent and Simple Interest PSSA PREP
... In Chicago the sales tax on clothing is 8%. In Philadelphia there is no sales tax on clothing. How much more would you pay at a store in Chicago for a sweater that costs $79.99? ...
... In Chicago the sales tax on clothing is 8%. In Philadelphia there is no sales tax on clothing. How much more would you pay at a store in Chicago for a sweater that costs $79.99? ...
Phd Economics, Siena - Finance – Final exam (16 April 2014
... Phd Economics, Siena - Finance – Final exam (16 April 2014) ...
... Phd Economics, Siena - Finance – Final exam (16 April 2014) ...
Supplemental Instruction Finance 301: Porter 1o/22/08 A bond that
... 5. What is yield to call? a. The rate of return earned on a bond if it is called before its maturity date. 6. Six years ago a company issued 20 year bonds with a 14% annual coupon rate at their $1000 par value. The bonds had a 9% call premium, with 5 years of call protection. Today, they called the ...
... 5. What is yield to call? a. The rate of return earned on a bond if it is called before its maturity date. 6. Six years ago a company issued 20 year bonds with a 14% annual coupon rate at their $1000 par value. The bonds had a 9% call premium, with 5 years of call protection. Today, they called the ...
Rule of 72
... How many years would it be until his balance doubles, assuming he continues to make no payments? ...
... How many years would it be until his balance doubles, assuming he continues to make no payments? ...
TxLOR - Texas Digital Library
... Finance: Compound Interest and Annuities If interest is compounded a finite number of times per year, then the compound interest calculations can be done with the Finance application on the TI-83/84. TI-83: FINANCE is above the x-1 key. TI-83+/TI-84: FINANCE is accessed using the APPS button The TVM ...
... Finance: Compound Interest and Annuities If interest is compounded a finite number of times per year, then the compound interest calculations can be done with the Finance application on the TI-83/84. TI-83: FINANCE is above the x-1 key. TI-83+/TI-84: FINANCE is accessed using the APPS button The TVM ...
chapter 3 - UniMAP Portal
... • Established when we are indifferent between a future payment, or a series of future payments, and a present sum of money . • Considers the comparison of alternative options, or proposals, by reducing them to an equivalent basis, depending on: – interest rate; – amounts of money involved; – timing ...
... • Established when we are indifferent between a future payment, or a series of future payments, and a present sum of money . • Considers the comparison of alternative options, or proposals, by reducing them to an equivalent basis, depending on: – interest rate; – amounts of money involved; – timing ...
Quiz 3
... ECON 203 – Quiz 3 - Key 1. In symbols, the equation of exchange says MsV = PY 2. High interest rates will stimulate investment, for people will want to consume less. False 3. A budget deficit occurs when government expenditures are greater than tax receipts during a year 4. Assume a relatively small ...
... ECON 203 – Quiz 3 - Key 1. In symbols, the equation of exchange says MsV = PY 2. High interest rates will stimulate investment, for people will want to consume less. False 3. A budget deficit occurs when government expenditures are greater than tax receipts during a year 4. Assume a relatively small ...
Math 1420 Homework 10
... Directions: Show all work for complete credit. The questions are also in your textbook. This test is work a total of 10 points towards your final grade. Section 4.1 1. Problem 54: Use the compound interest formulas: A = P (1 + 1r )nt and A = P ert to solve. Find the accumulated value of an investmen ...
... Directions: Show all work for complete credit. The questions are also in your textbook. This test is work a total of 10 points towards your final grade. Section 4.1 1. Problem 54: Use the compound interest formulas: A = P (1 + 1r )nt and A = P ert to solve. Find the accumulated value of an investmen ...
Lesson Two Exponential and Logarithmic Word
... The half-life of radium is about 1600 years. If 1 kilogram is present now, how much will be present after 800 years? Answer: 707 grams ...
... The half-life of radium is about 1600 years. If 1 kilogram is present now, how much will be present after 800 years? Answer: 707 grams ...
Essay Plan Appreciation of the $A
... an equilibrium amount, without interaction from a third monetary party. In December 1983, the HawkeKeating government initiated one of the most important structural changes within the Australian economy by switching the exchange rate system from a managed peg system to a floating exchange system. Th ...
... an equilibrium amount, without interaction from a third monetary party. In December 1983, the HawkeKeating government initiated one of the most important structural changes within the Australian economy by switching the exchange rate system from a managed peg system to a floating exchange system. Th ...























