A zebrafish model exemplifies the long preclinical period of motor
... the long preclinical period of motor neuron disease To the Editor, The article ‘Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a long preclinical period?’’ is an interesting and thoughtprovoking review.1 We commend the authors for raising the profile of early embryonic and preclinical stages that are currently poorl ...
... the long preclinical period of motor neuron disease To the Editor, The article ‘Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a long preclinical period?’’ is an interesting and thoughtprovoking review.1 We commend the authors for raising the profile of early embryonic and preclinical stages that are currently poorl ...
Neuropathology Review
... proliferate when there’s ependymal cell damage (i.e. meningitis), forming granulation to protect. Stenosis of the aqueduct: Caused by cellular proliferation. Damage after meningitis, causing aqueduct stenosis ----> hydrocephalus. Mesenchymal components of the CNS: Microglia, Monocytes, Macrophag ...
... proliferate when there’s ependymal cell damage (i.e. meningitis), forming granulation to protect. Stenosis of the aqueduct: Caused by cellular proliferation. Damage after meningitis, causing aqueduct stenosis ----> hydrocephalus. Mesenchymal components of the CNS: Microglia, Monocytes, Macrophag ...
ben_slides2
... emergence of novel perceptual qualities that were not present in each individual odorant ...
... emergence of novel perceptual qualities that were not present in each individual odorant ...
Document
... Model synapse. The synaptic current Isyn = gsyns(V - Esyn), where gsyn is the maximal synaptic conductance and Esyn is the reversal potential. Typically, we set gsyn = 0.1 mS/cm2 and Esyn = -75 mV (inhibitory). ...
... Model synapse. The synaptic current Isyn = gsyns(V - Esyn), where gsyn is the maximal synaptic conductance and Esyn is the reversal potential. Typically, we set gsyn = 0.1 mS/cm2 and Esyn = -75 mV (inhibitory). ...
Updating a Research Agenda for Cerebral Palsy Drs. Laura
... Restoring Excitatory Neuronal Input Kanold (University of Maryland )is studying GABAergic transmission for enhancing maturation of thalomo-cortical and inhibitory circuits in model with ablated subplate neurons ...
... Restoring Excitatory Neuronal Input Kanold (University of Maryland )is studying GABAergic transmission for enhancing maturation of thalomo-cortical and inhibitory circuits in model with ablated subplate neurons ...
Unit 7 Regulation and Body Systems
... consequences, including changes in behavior, loss of body functions and even death. Knowledge and understanding of the structures and functions of the nervous system are needed to understand this coordination. The features of an animal’s nervous system are evolutionarily conserved, with the basic ce ...
... consequences, including changes in behavior, loss of body functions and even death. Knowledge and understanding of the structures and functions of the nervous system are needed to understand this coordination. The features of an animal’s nervous system are evolutionarily conserved, with the basic ce ...
[pdf]
... additive or multiplicative change of neural responses within a voxel. However, a tuning change at the voxel-level could be mediated by selective response gain operating differentially on subpopulations of neurons contained in a voxel. For example, consider a voxel composed of a large subpopulation o ...
... additive or multiplicative change of neural responses within a voxel. However, a tuning change at the voxel-level could be mediated by selective response gain operating differentially on subpopulations of neurons contained in a voxel. For example, consider a voxel composed of a large subpopulation o ...
Neuroscience Course Conference
... c. What might be the side effects of such a drug? 3. Although gNa increases as a graded function of membrane depolarization (Fig. 9-6 of textbook), the action potential has a discrete voltage threshold. Why? 4. During epileptic seizures, massive synchronous bursts of activity in cortical neurons cau ...
... c. What might be the side effects of such a drug? 3. Although gNa increases as a graded function of membrane depolarization (Fig. 9-6 of textbook), the action potential has a discrete voltage threshold. Why? 4. During epileptic seizures, massive synchronous bursts of activity in cortical neurons cau ...
Brain: The Inside Story Educator`s Guide
... breathing, heartbeat, movement, and other bodily functions. The limbic system in the brains of mammals supports more complex behavior and social relations, as well as emotions like fear, rage, and desire. Primates (including humans) recognize facial expressions, communicate, and maintain complex soc ...
... breathing, heartbeat, movement, and other bodily functions. The limbic system in the brains of mammals supports more complex behavior and social relations, as well as emotions like fear, rage, and desire. Primates (including humans) recognize facial expressions, communicate, and maintain complex soc ...
MD0006 11-1 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human
... another. An interneuron "connects" two other neurons. (4) Others. There are other, more specialized types, for example, in the CNS. 11-7. NEURON "CONNECTIONS" A neuron may "connect" either with another neuron or with a muscle fiber. A phrase used to describe such "connections" is "continuity without ...
... another. An interneuron "connects" two other neurons. (4) Others. There are other, more specialized types, for example, in the CNS. 11-7. NEURON "CONNECTIONS" A neuron may "connect" either with another neuron or with a muscle fiber. A phrase used to describe such "connections" is "continuity without ...
the organization of the arthropod central nervous system
... final motor fibers, are present in all animals. Because the delay times involved are the shortest possible, monosynaptic reflexes are common in quick withdrawal movements, which generally have priority over all other responses. However it is quite incorrect to picture such a reflex as an event invol ...
... final motor fibers, are present in all animals. Because the delay times involved are the shortest possible, monosynaptic reflexes are common in quick withdrawal movements, which generally have priority over all other responses. However it is quite incorrect to picture such a reflex as an event invol ...
Bio211 Lecture 19
... Upper figure From: Marieb & Hoehn, Human Anatomy & Physiology, 9th ed., Pearson, 2013 ...
... Upper figure From: Marieb & Hoehn, Human Anatomy & Physiology, 9th ed., Pearson, 2013 ...
Session 1 Introduction
... Major landmark is the corpus callosum – the set of fibers that link the two hemispheres. These are the fibers that are cut in split-brain surgery. Underneath is the translucent partition between the lateral ventricles (containing the cerebrospinal fluid within the hemispheres) Cingulate gyrus is the ...
... Major landmark is the corpus callosum – the set of fibers that link the two hemispheres. These are the fibers that are cut in split-brain surgery. Underneath is the translucent partition between the lateral ventricles (containing the cerebrospinal fluid within the hemispheres) Cingulate gyrus is the ...
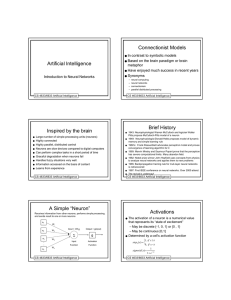
Artificial Intelligence Connectionist Models Inspired by the brain
... Neurons are organized into networks. ● Connections are one or two-way communication links between neurons ● Weights are the strength of connections. A weight wij is a real number than indicates the influence neuron ui has on neuron uj ...
... Neurons are organized into networks. ● Connections are one or two-way communication links between neurons ● Weights are the strength of connections. A weight wij is a real number than indicates the influence neuron ui has on neuron uj ...
DOWN - Ubiquitous Computing Lab
... of contradiction on the second level. Obedience was the Second Law and [the robot] was suffering from two roughly equal and contradictory orders. Robot- block was what the general population called it or, more frequently, roblock for short . . . [or] `mental freeze- out.' No matter how subtle and in ...
... of contradiction on the second level. Obedience was the Second Law and [the robot] was suffering from two roughly equal and contradictory orders. Robot- block was what the general population called it or, more frequently, roblock for short . . . [or] `mental freeze- out.' No matter how subtle and in ...
autonomic nervous system
... center is in lower regions of the brain • Hypothalamus is major control center – input: emotions and visceral sensory information • smell, taste, temperature, osmolarity of blood, etc – output: to nuclei in brainstem and spinal cord – posterior & lateral portions control sympathetic NS ...
... center is in lower regions of the brain • Hypothalamus is major control center – input: emotions and visceral sensory information • smell, taste, temperature, osmolarity of blood, etc – output: to nuclei in brainstem and spinal cord – posterior & lateral portions control sympathetic NS ...
A monument of inefficiency: The presumed course of the recurrent
... anatomical evidence for vocal ability” in non−avian dino− saurs. In the absence of data, the most that can be said is that if sauropods produced or modulated sounds using their la− rynges, those activities were subject to relatively long physi− ological delays. This effect of large body size on nerv ...
... anatomical evidence for vocal ability” in non−avian dino− saurs. In the absence of data, the most that can be said is that if sauropods produced or modulated sounds using their la− rynges, those activities were subject to relatively long physi− ological delays. This effect of large body size on nerv ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... An increase in sympathetic stimulation causes HR to increase whereas an increase in parasympathetic stimulation causes HR to decrease ...
... An increase in sympathetic stimulation causes HR to increase whereas an increase in parasympathetic stimulation causes HR to decrease ...
Nerve 4 ppt - Educypedia
... An increase in sympathetic stimulation causes HR to increase whereas an increase in parasympathetic stimulation causes HR to decrease ...
... An increase in sympathetic stimulation causes HR to increase whereas an increase in parasympathetic stimulation causes HR to decrease ...
Organ System Overview
... components of the cardiovascular system are used to illustrate the various levels of structural organization in a human being. the digestive system includes the esophagus, the stomach, and the small and large intestines (to name a few of its organs). Each organ has its own job to do, and, by working ...
... components of the cardiovascular system are used to illustrate the various levels of structural organization in a human being. the digestive system includes the esophagus, the stomach, and the small and large intestines (to name a few of its organs). Each organ has its own job to do, and, by working ...
Unit 1- Basics of Anatomy Anatomy – (Greek – to cut up)
... 6. Organismal – highest level of structural organization; all systems of body working together ...
... 6. Organismal – highest level of structural organization; all systems of body working together ...
What I Learned Last Week - Chapter 13
... A patient has damage to several spinal nerves. Which of the major divisions of the nervous system has been damaged? a. central nervous system ...
... A patient has damage to several spinal nerves. Which of the major divisions of the nervous system has been damaged? a. central nervous system ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Extension – takes limb away from body (opens penknife) Flexion – brings limb toward body (closes penknife) Muscles can only pull not push so any movement requires coordination Synergists -- muscles that work together ...
... Extension – takes limb away from body (opens penknife) Flexion – brings limb toward body (closes penknife) Muscles can only pull not push so any movement requires coordination Synergists -- muscles that work together ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.






![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008855303_1-42c5934975f83fadb4141440e1a86c3f-300x300.png)