Brain Gas
... different species. The research in my lab focuses on three different facets of odor memory formation: 1) how learning about odors changes the way animals behave, 2) the brain chemicals involved in learning odors and 3) how the brain’s electrical signals are modified once a new odor has been learned. ...
... different species. The research in my lab focuses on three different facets of odor memory formation: 1) how learning about odors changes the way animals behave, 2) the brain chemicals involved in learning odors and 3) how the brain’s electrical signals are modified once a new odor has been learned. ...
Sample
... 2. Node of Ranvier: space between beads of myelin 3. One oligodendrocyte produces up to 50 myelin segments c. Microglia 1. Phagocytes 2. Protect brain from invading organisms – immune system function 2. Schwann Cells – peripheral nervous system a. Produce myelin in the PNS (Figure 2.8, text p. 26) 1 ...
... 2. Node of Ranvier: space between beads of myelin 3. One oligodendrocyte produces up to 50 myelin segments c. Microglia 1. Phagocytes 2. Protect brain from invading organisms – immune system function 2. Schwann Cells – peripheral nervous system a. Produce myelin in the PNS (Figure 2.8, text p. 26) 1 ...
Orcokinin peptides in developing and adult crustacean
... the central pattern-generating networks that control rhythmic movements of the foregut (Harris-Warrick et al., 1992). One of the most remarkable features of this nervous system is the richness and diversity of its neuromodulatory control systems. Specifically, although the stomatogastric ganglion (S ...
... the central pattern-generating networks that control rhythmic movements of the foregut (Harris-Warrick et al., 1992). One of the most remarkable features of this nervous system is the richness and diversity of its neuromodulatory control systems. Specifically, although the stomatogastric ganglion (S ...
Retinal target cells of the centrifugal projection from the isthmo
... the receptive field size of the IO neurons (Holden and Powell, 1972; Miles, 1972a; Uchiyama et al., 1998). Electrical stimulation of the ION enhances visual responses of the retinal ganglion cells (Miles, 1972b; Uchiyama and Barlow, 1994), whereas cooling of the ION does the opposite (Miles, 1972c; P ...
... the receptive field size of the IO neurons (Holden and Powell, 1972; Miles, 1972a; Uchiyama et al., 1998). Electrical stimulation of the ION enhances visual responses of the retinal ganglion cells (Miles, 1972b; Uchiyama and Barlow, 1994), whereas cooling of the ION does the opposite (Miles, 1972c; P ...
Exam 5 Study Guide
... nervous system, including somatic and autonomic systems. Explain the structure of an idealized neuron, including the functions of all the parts: cell body, dendrites, dendritic spines, axon hillock, axon, axon collateral, myelin sheath, neurofibril node (node of Ranvier), axon terminal, synaptic kno ...
... nervous system, including somatic and autonomic systems. Explain the structure of an idealized neuron, including the functions of all the parts: cell body, dendrites, dendritic spines, axon hillock, axon, axon collateral, myelin sheath, neurofibril node (node of Ranvier), axon terminal, synaptic kno ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology II
... List the functions of the plasma membrane and the structural features that enable it to perform those functions. Describe the organelles of a typical cell, and indicate the specific functions of each. Explain the functions of the cell nucleus and discuss the nature and importance of the genetic code ...
... List the functions of the plasma membrane and the structural features that enable it to perform those functions. Describe the organelles of a typical cell, and indicate the specific functions of each. Explain the functions of the cell nucleus and discuss the nature and importance of the genetic code ...
6419982_1441921514
... rough endoplasmic reticulum known as Nissl bodies that are not found in the dendrites or axon. The cell bodies within the CNS are frequently clustered into groups called nuclei (not to be confused with the nucleus of a cell). Cell bodies in the PNS usually occur in clusters called ganglia (table 7.1 ...
... rough endoplasmic reticulum known as Nissl bodies that are not found in the dendrites or axon. The cell bodies within the CNS are frequently clustered into groups called nuclei (not to be confused with the nucleus of a cell). Cell bodies in the PNS usually occur in clusters called ganglia (table 7.1 ...
Models of retinotopic development - damtp
... SC, where ephrin-A levels are lowest. Nasal RGCs have low levels of EphA and terminate in posterior SC, where ephrin-A levels are highest. By contrast, the EphB system is attractive, such that ventral retina (with high levels of EphB) projects to medial SC (with high levels of ephrin-B). Cross-talk ...
... SC, where ephrin-A levels are lowest. Nasal RGCs have low levels of EphA and terminate in posterior SC, where ephrin-A levels are highest. By contrast, the EphB system is attractive, such that ventral retina (with high levels of EphB) projects to medial SC (with high levels of ephrin-B). Cross-talk ...
Autonomic nervous system
... The Autonomic nervous system is the portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body It is primarily concerned with the regulation of visceral or vegetative functions of the body, so it is called vegetative or involuntary nervous system This system helps to control art ...
... The Autonomic nervous system is the portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body It is primarily concerned with the regulation of visceral or vegetative functions of the body, so it is called vegetative or involuntary nervous system This system helps to control art ...
Axons break in animals lacking β-spectrin
... integrity when axons or dendrites are placed under strain. In the vertebrate peripheral nervous system, axons are exposed to strains generated by length changes during movement (Phillips et al., 2004). Strain has also been proposed to assist in wiring the central nervous system (Van Essen, 1997) and ...
... integrity when axons or dendrites are placed under strain. In the vertebrate peripheral nervous system, axons are exposed to strains generated by length changes during movement (Phillips et al., 2004). Strain has also been proposed to assist in wiring the central nervous system (Van Essen, 1997) and ...
chapt08_lecture
... 3) This cycle repeats every 90 minutes, and most people go through five per night. 4) If allowed to awaken naturally, people usually do so during REM sleep. 5) Slow-wave is prominent in the first part of sleep, while REM is prominent in the second half ...
... 3) This cycle repeats every 90 minutes, and most people go through five per night. 4) If allowed to awaken naturally, people usually do so during REM sleep. 5) Slow-wave is prominent in the first part of sleep, while REM is prominent in the second half ...
DNA, Human Memory, and the Storage
... environment also plays a significant role in determining which genes are expressed in a given cell during a given phase of development of the organism.13,14 The bottom line is that the information stored in chromosomes, like a giant software package, has many subroutines that can be invoked under va ...
... environment also plays a significant role in determining which genes are expressed in a given cell during a given phase of development of the organism.13,14 The bottom line is that the information stored in chromosomes, like a giant software package, has many subroutines that can be invoked under va ...
Nervous System Chapter 11 Answers
... 1. Propagation of impulse to the axon terminal of the pre-synaptic neuron results in calcium channels opening and calcium ions binding to neurotransmitter vesicles 2. The calcium addition to the neurotransmitter vesicles causes them to fuse to the pre-synaptic neuron and release the neurotransmitter ...
... 1. Propagation of impulse to the axon terminal of the pre-synaptic neuron results in calcium channels opening and calcium ions binding to neurotransmitter vesicles 2. The calcium addition to the neurotransmitter vesicles causes them to fuse to the pre-synaptic neuron and release the neurotransmitter ...
How Neurons Talk to Each Other
... the synaptic cleft separating the transmitting and receiving neurons and the membrane of the receiving (postsynaptic) neuron. ...
... the synaptic cleft separating the transmitting and receiving neurons and the membrane of the receiving (postsynaptic) neuron. ...
Neuroplasticity
... – Associativity: LTP only induced at weak input when associated with activity in strong input – Input specificity: Unstimulated weak pathway not facilitated after tetanus of strong pathway ...
... – Associativity: LTP only induced at weak input when associated with activity in strong input – Input specificity: Unstimulated weak pathway not facilitated after tetanus of strong pathway ...
The Central Nervous System
... Three broad columns run length of brain stem Has far-flung axonal connections with hypothalamus, thalamus, cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and spinal cord can govern brain arousal ...
... Three broad columns run length of brain stem Has far-flung axonal connections with hypothalamus, thalamus, cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and spinal cord can govern brain arousal ...
The Nervous System
... function of the systems in the human body. The course will trace the different levels of organization of cells, tissues, organs, systems and ultimately the integrated organism, the human. The class material will be organized into five major units- the body as a whole, movement and support, coordinat ...
... function of the systems in the human body. The course will trace the different levels of organization of cells, tissues, organs, systems and ultimately the integrated organism, the human. The class material will be organized into five major units- the body as a whole, movement and support, coordinat ...
Study guide (Word Document)
... 3. cerebrospinal fluid is comprised of water, ions, glucose, proteins and other substances 4. spina bifida is caused by malformation of the spinal cord and/or vertebrae; it can be treated by surgery and by draining excessive cerebrospinal fluid Lab 16 p. 99 1. Your sense of touch includes your sense ...
... 3. cerebrospinal fluid is comprised of water, ions, glucose, proteins and other substances 4. spina bifida is caused by malformation of the spinal cord and/or vertebrae; it can be treated by surgery and by draining excessive cerebrospinal fluid Lab 16 p. 99 1. Your sense of touch includes your sense ...
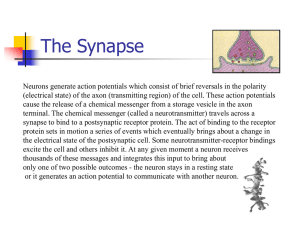
The Synapse
... Neurons generate action potentials which consist of brief reversals in the polarity (electrical state) of the axon (transmitting region) of the cell. These action potentials cause the release of a chemical messenger from a storage vesicle in the axon terminal. The chemical messenger (called a neurot ...
... Neurons generate action potentials which consist of brief reversals in the polarity (electrical state) of the axon (transmitting region) of the cell. These action potentials cause the release of a chemical messenger from a storage vesicle in the axon terminal. The chemical messenger (called a neurot ...
Auditory: Stimulus Auditory
... cochlea by the tectorial membrane • Afferent Signals: unevenly distributed to allow most signals for range of human speech • Pathway: contralateral to primary auditory cortex • CNS Areas: Primary in superior temporal lobe; Wernicke’s, Broca’s, and right hemisphere specializations • Perception: C ...
... cochlea by the tectorial membrane • Afferent Signals: unevenly distributed to allow most signals for range of human speech • Pathway: contralateral to primary auditory cortex • CNS Areas: Primary in superior temporal lobe; Wernicke’s, Broca’s, and right hemisphere specializations • Perception: C ...
The Nervous System
... illions of people suffer from conditions affecting the brain and nervous system, such as Lou Gehrig’s disease, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s. Some of these diseases harm the brain but leave the rest of the body alone. Others, as in Hawking’s case, weaken or deform the body but leave the parts of the ...
... illions of people suffer from conditions affecting the brain and nervous system, such as Lou Gehrig’s disease, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s. Some of these diseases harm the brain but leave the rest of the body alone. Others, as in Hawking’s case, weaken or deform the body but leave the parts of the ...
Neural Manipulation 1 Preparation
... a. frontal bone, petrouss part of temporal bone, occiput b. occiput, parietal, temporal, bones, anterior and posterior clinoid processes of sphenoid bone c. occiput, parietal and temporal bones, maxilla ...
... a. frontal bone, petrouss part of temporal bone, occiput b. occiput, parietal, temporal, bones, anterior and posterior clinoid processes of sphenoid bone c. occiput, parietal and temporal bones, maxilla ...
Chapter 13 - PNS
... – Receptor membranes become less responsive – Receptor potentials decline in frequency or stop ...
... – Receptor membranes become less responsive – Receptor potentials decline in frequency or stop ...
chapter_1_powerpoint_hagerty - YISS-Anatomy2010-11
... - most abundant substance in body - required for metabolic processes - required for transport of substances - regulates body temperature ...
... - most abundant substance in body - required for metabolic processes - required for transport of substances - regulates body temperature ...
Is there a correlation between the use of cannabis and the
... THC effectively acts as a dopamine agonist, thus blocking the reuptake of dopamine and L-DOPA (which stimulates the synthesis of dopamine) ...
... THC effectively acts as a dopamine agonist, thus blocking the reuptake of dopamine and L-DOPA (which stimulates the synthesis of dopamine) ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.