Nerves
... • Some innervate muscles of the anterior neck • Phrenic nerve the most important nerve of the cervical plexus ...
... • Some innervate muscles of the anterior neck • Phrenic nerve the most important nerve of the cervical plexus ...
Teacher Guide
... Purpose: Determine the volume of helium gas in an irregularly-shaped Mylar balloon. Background (from “Bridging Physics and Biology Using Resistance and Axons” by Joshua M. Dyer): Neurons are nerve cells that are composed of three major sections, as shown in Fig. 1: the dendrites, the cell body, and ...
... Purpose: Determine the volume of helium gas in an irregularly-shaped Mylar balloon. Background (from “Bridging Physics and Biology Using Resistance and Axons” by Joshua M. Dyer): Neurons are nerve cells that are composed of three major sections, as shown in Fig. 1: the dendrites, the cell body, and ...
Nervous System
... Axons end in axonal terminals Axonal terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters Axonal terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap ...
... Axons end in axonal terminals Axonal terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters Axonal terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap ...
The Nervous System - 1
... *these are graded potentials and as such can be graded in the size of the electrical event will diminish over both space and time travel in all directions across the soma ...
... *these are graded potentials and as such can be graded in the size of the electrical event will diminish over both space and time travel in all directions across the soma ...
Nervous System PPT
... Axons end in axonal terminals Axonal terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters Axonal terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap ...
... Axons end in axonal terminals Axonal terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters Axonal terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap ...
Molecules and mechanisms of dendrite development in Drosophila
... Dendrites – processes of neurons that are primarily specialized for information input – are one of nature’s remarkable architectural feats, and the diverse growth patterns shown by dendritic arbors raise important developmental questions. The particular shapes of dendrites are important in neuronal ...
... Dendrites – processes of neurons that are primarily specialized for information input – are one of nature’s remarkable architectural feats, and the diverse growth patterns shown by dendritic arbors raise important developmental questions. The particular shapes of dendrites are important in neuronal ...
Representing Spatial Information for Limb - Research
... brain? A vector code of movement direction has been described in primary motor cortex Ml (Gcorgopoulos et al., 1982; Schwartz et al., 1988; Caminiti et al., 1990), dorsal premotor cortex PMd (Caminiti et al., 1991; Fu et al., 1993), areas 2 and 5 of the parietal cortex (Kalaska et al., 1983; Cohen e ...
... brain? A vector code of movement direction has been described in primary motor cortex Ml (Gcorgopoulos et al., 1982; Schwartz et al., 1988; Caminiti et al., 1990), dorsal premotor cortex PMd (Caminiti et al., 1991; Fu et al., 1993), areas 2 and 5 of the parietal cortex (Kalaska et al., 1983; Cohen e ...
The effect of fasting on the ultrastructure of the hypothalamic arcuate
... whorls being continuous with the RER and localized near Golgi regions. Similarly, in the arcuate nucleus. Lamperti et al. [10] noticed whorls associated with the RER and Golgi network in mercurytreated female hamsters. Direct comparison of our study with the results of the cited authors does not see ...
... whorls being continuous with the RER and localized near Golgi regions. Similarly, in the arcuate nucleus. Lamperti et al. [10] noticed whorls associated with the RER and Golgi network in mercurytreated female hamsters. Direct comparison of our study with the results of the cited authors does not see ...
Therapeutic Options for Tay-Sachs Disease
... imino sugar and is the N-alkylated derivative of deoxynojirimycin. This compound seems to have several advantages over the PDMP compound as consequently has been studied more extensively (Igdoura et al., 1998). Recent studies have been conducted using NB-DNJ on knockout mouse models of TSD. Knockout ...
... imino sugar and is the N-alkylated derivative of deoxynojirimycin. This compound seems to have several advantages over the PDMP compound as consequently has been studied more extensively (Igdoura et al., 1998). Recent studies have been conducted using NB-DNJ on knockout mouse models of TSD. Knockout ...
UNIVERSIDAD SAN FRANCISCO DE QUITO USFQ Detección y
... The aim of this project was to develop a prototype BCI interface based on LabVIEW capable of acquiring, analyzing, processing and finding appropriate classification parameters related to the brain activity during eyewinks that can be interpreted as simple direction or control commands. A. EEG Emotiv ...
... The aim of this project was to develop a prototype BCI interface based on LabVIEW capable of acquiring, analyzing, processing and finding appropriate classification parameters related to the brain activity during eyewinks that can be interpreted as simple direction or control commands. A. EEG Emotiv ...
Chapter 17-Pathways and Integrative Functions
... • Communication of CNS with body structures through pathways • Tracts = groups or bundles of axons that travel together in CNS • Nucleus = collection of neuron cell bodies within CNS • Somatotropy = correspondence between body area of receptors and functional areas in cerebral cortex ...
... • Communication of CNS with body structures through pathways • Tracts = groups or bundles of axons that travel together in CNS • Nucleus = collection of neuron cell bodies within CNS • Somatotropy = correspondence between body area of receptors and functional areas in cerebral cortex ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 32.1 Eye movements that stabilize
... the caudate nucleus (CN) and substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNpr) provides inhibitory control over activity in the superior colliculus. These descending control signals are then converted into motor commands by circuits involving regions such as the reticular formation (RF), pontine nuclei (PN), ...
... the caudate nucleus (CN) and substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNpr) provides inhibitory control over activity in the superior colliculus. These descending control signals are then converted into motor commands by circuits involving regions such as the reticular formation (RF), pontine nuclei (PN), ...
Creativity and emotion: Reformulating the Romantic theory of art
... Freeman (2000) echoes LeDoux (1996) when he says: “it is neither necessary nor feasible to separate the expression of autonomic states and one's perceptions [or interpretations] or them, whether conscious or not, in the intentional loop. They evolve as an organic whole” (pp. 215). Through a variety ...
... Freeman (2000) echoes LeDoux (1996) when he says: “it is neither necessary nor feasible to separate the expression of autonomic states and one's perceptions [or interpretations] or them, whether conscious or not, in the intentional loop. They evolve as an organic whole” (pp. 215). Through a variety ...
Introduction to the Pharmacology of CNS Drugs: Introduction Drugs
... be discovered by primitive humans and are still the most widely used group of pharmacologic agents. In addition to their use in therapy, many drugs acting on the CNS are used without prescription to increase one's sense of well-being. The mechanisms by which various drugs act in the CNS have not alw ...
... be discovered by primitive humans and are still the most widely used group of pharmacologic agents. In addition to their use in therapy, many drugs acting on the CNS are used without prescription to increase one's sense of well-being. The mechanisms by which various drugs act in the CNS have not alw ...
The Human Body: An Orientation - dr
... Organs are made up of different types of tissues. 6 Organismal level The human organism is made up of many organ systems. ...
... Organs are made up of different types of tissues. 6 Organismal level The human organism is made up of many organ systems. ...
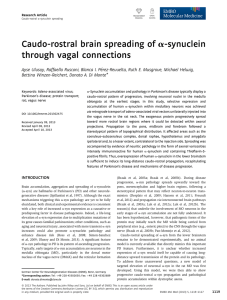
Caudo‐rostral brain spreading of α‐synuclein through vagal
... a-Synuclein accumulation and pathology in Parkinson’s disease typically display a caudo-rostral pattern of progression, involving neuronal nuclei in the medulla oblongata at the earliest stages. In this study, selective expression and accumulation of human a-synuclein within medullary neurons was ac ...
... a-Synuclein accumulation and pathology in Parkinson’s disease typically display a caudo-rostral pattern of progression, involving neuronal nuclei in the medulla oblongata at the earliest stages. In this study, selective expression and accumulation of human a-synuclein within medullary neurons was ac ...
The mirror neuron system and the consequences of its
... - the activation of the core-circuit for imitation (slide 7) is delayed in patients with autism - autistic children showed reduced MNS activity during observation and imitation of emotional facial expressions ...
... - the activation of the core-circuit for imitation (slide 7) is delayed in patients with autism - autistic children showed reduced MNS activity during observation and imitation of emotional facial expressions ...
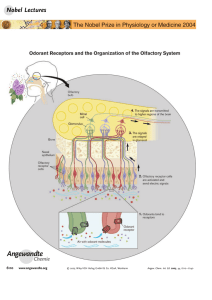
Scents and Sensibility: A Molecular Logic of Olfactory Perception
... own laboratory in 1974, Michael Wigler, my first graduate student along with Sol Silverstein, a Professor at Columbia, developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transformation of mammalian cells. Michael, even at this very early stage in his career, was conceptually and technically master ...
... own laboratory in 1974, Michael Wigler, my first graduate student along with Sol Silverstein, a Professor at Columbia, developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transformation of mammalian cells. Michael, even at this very early stage in his career, was conceptually and technically master ...
Embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cell
... mouse, and termed epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs) to distinguish them from the more primitive mES cells [26, 27]. Reflecting the developmentally more restricted stage of their origin, EpiSCs demonstrated a poor ability to contribute to chimeras and were germline incompetent [27, 28]. Interestingly, the ...
... mouse, and termed epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs) to distinguish them from the more primitive mES cells [26, 27]. Reflecting the developmentally more restricted stage of their origin, EpiSCs demonstrated a poor ability to contribute to chimeras and were germline incompetent [27, 28]. Interestingly, the ...
Chapter 2 The Neural Bases of Learning and Memory
... The hindbrain is the most primitive brain region. It controls many of the cranial nerves and nuclei that send impulses to and from the spinal cord and cranial nerves. Some of the most basic behaviors, like respiration, sleep and wakefulness, circulation, heart activity, and fine coordination of mov ...
... The hindbrain is the most primitive brain region. It controls many of the cranial nerves and nuclei that send impulses to and from the spinal cord and cranial nerves. Some of the most basic behaviors, like respiration, sleep and wakefulness, circulation, heart activity, and fine coordination of mov ...
A Biologically Plausible Spiking Neuron Model of Fear Conditioning
... The single neuron model used in the fear conditioning circuit presented here is the Leaky Integrate-and-Fire (LIF) neuron. While the NEF can support a wide variety of neural models, there are advantages to choosing LIF neurons: they capture a sufficient level of biological detail, and at the same ti ...
... The single neuron model used in the fear conditioning circuit presented here is the Leaky Integrate-and-Fire (LIF) neuron. While the NEF can support a wide variety of neural models, there are advantages to choosing LIF neurons: they capture a sufficient level of biological detail, and at the same ti ...
Chapter 9
... nerve fibers arising from their cell bodies and are commonly found in the brain and spinal cord. Sensory neurons (afferent neurons) conduct impulses from peripheral receptors to the CNS and are usually unipolar, although some are bipolar neurons. ...
... nerve fibers arising from their cell bodies and are commonly found in the brain and spinal cord. Sensory neurons (afferent neurons) conduct impulses from peripheral receptors to the CNS and are usually unipolar, although some are bipolar neurons. ...
Review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The following outline will advise you on what you need to know for your final exam in Human Biology. Along with the biological information you learned you also need to be prepared to discuss the ethical and emotional side of issues and topics we covered like organ donation, anorexia and bulimia, smo ...
... The following outline will advise you on what you need to know for your final exam in Human Biology. Along with the biological information you learned you also need to be prepared to discuss the ethical and emotional side of issues and topics we covered like organ donation, anorexia and bulimia, smo ...
Chapter 9- Nervous System Lecture 9.1
... nerve fibers arising from their cell bodies and are commonly found in the brain and spinal cord. Sensory neurons (afferent neurons) conduct impulses from peripheral receptors to the CNS and are usually unipolar, although some are bipolar neurons. ...
... nerve fibers arising from their cell bodies and are commonly found in the brain and spinal cord. Sensory neurons (afferent neurons) conduct impulses from peripheral receptors to the CNS and are usually unipolar, although some are bipolar neurons. ...
Document
... – A central nervous system (CNS) where integration takes place; this includes the brain and a nerve cord – A peripheral nervous system (PNS), which carries information into and out of the CNS – The neurons of the PNS, when bundled together, form nerves ...
... – A central nervous system (CNS) where integration takes place; this includes the brain and a nerve cord – A peripheral nervous system (PNS), which carries information into and out of the CNS – The neurons of the PNS, when bundled together, form nerves ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.