Practice Exam 1
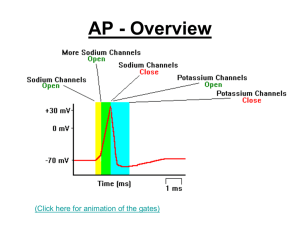
... 10) True or False? In figure 1, if the permeability of Na+ is changed, its equilibrium potential will also change. A) True. B) False. 11) The cerebellum… A) acts as a relay station, filtering all sensory information before it reaches higher brain areas. B) is mainly responsible for processing smell ...
... 10) True or False? In figure 1, if the permeability of Na+ is changed, its equilibrium potential will also change. A) True. B) False. 11) The cerebellum… A) acts as a relay station, filtering all sensory information before it reaches higher brain areas. B) is mainly responsible for processing smell ...
to find the lecture notes for lecture 6 nervous tissue click here
... the breakdown of ACh and raise the level that can activate the still present receptors ...
... the breakdown of ACh and raise the level that can activate the still present receptors ...
Chapter 11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... ______6. A major subdivision of the nervous system that serves as the communication lines, linking all parts of the body to the CNS. 3. This exercise emphasizes the difference between neurons and neuroglia. Indicate which cell type is identified by the following descriptions. A. Neurons B. Neuroglia ...
... ______6. A major subdivision of the nervous system that serves as the communication lines, linking all parts of the body to the CNS. 3. This exercise emphasizes the difference between neurons and neuroglia. Indicate which cell type is identified by the following descriptions. A. Neurons B. Neuroglia ...
Neural Tissue – Chapter 12
... Step Two: At the resting potential, sodium ions are drawn to the outer surface of the cell membrane, attracted by the excess of negative ions on the inside of the membrane. As the cell membrane depolarizes, sodium ions are released from its outer surface. These ions move toward the open channels, re ...
... Step Two: At the resting potential, sodium ions are drawn to the outer surface of the cell membrane, attracted by the excess of negative ions on the inside of the membrane. As the cell membrane depolarizes, sodium ions are released from its outer surface. These ions move toward the open channels, re ...
Nervous System - EMTStudyCenter.com
... 5. All of the following are functions of the nervous system EXCEPT senses changes. analyzes changes. ...
... 5. All of the following are functions of the nervous system EXCEPT senses changes. analyzes changes. ...
AP – All or nothing
... • There is a time after depolarisation where no new AP can start – called the refractory period. – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one ...
... • There is a time after depolarisation where no new AP can start – called the refractory period. – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one ...
Assignment 1 - Gordon State College
... ________________ and __________________. 31. The ___________________ is known as the “brain’s sensory switchboard” because information from all the senses except smell goes through here to be relayed to the appropriate part of the brain. 32. In the limbic system, the _______________________ plays a ...
... ________________ and __________________. 31. The ___________________ is known as the “brain’s sensory switchboard” because information from all the senses except smell goes through here to be relayed to the appropriate part of the brain. 32. In the limbic system, the _______________________ plays a ...
CH 12 shortened for test three nervous tissue A and P 2016
... - the difference in concentrations and the Na/K pump causes a RMP of -70mV - Na/K pump uses 70% of the energy needs of the nervous system diffusion, selective permeability, and ion concentration result in the electrical differences across the membrane which allows for nerve conduction to take place ...
... - the difference in concentrations and the Na/K pump causes a RMP of -70mV - Na/K pump uses 70% of the energy needs of the nervous system diffusion, selective permeability, and ion concentration result in the electrical differences across the membrane which allows for nerve conduction to take place ...
The action potential and the synapses
... The elimination of the neurotransmitter from the inter-synaptic space The correct operation of a chemical synapses, is based on the constant relationship between incoming action potentials and amount of neurotransmitter released in the synaptic cleft. This presupposes the existence of disposal mech ...
... The elimination of the neurotransmitter from the inter-synaptic space The correct operation of a chemical synapses, is based on the constant relationship between incoming action potentials and amount of neurotransmitter released in the synaptic cleft. This presupposes the existence of disposal mech ...
nervous5
... 2. What would be the predicted deficits of a person whose entire thalamus on the right side of the brain was completely ...
... 2. What would be the predicted deficits of a person whose entire thalamus on the right side of the brain was completely ...
A. What is a neuron? 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and
... (an agonist) of a neurotransmitter. B. Drugs can influence synaptic activity in many ways including altering synthesis of the neurotransmitter, disrupting the vesicles, increasing release, decreasing reuptake, blocking its breakdown into inactive chemical, or directly simulating or blocking postsyna ...
... (an agonist) of a neurotransmitter. B. Drugs can influence synaptic activity in many ways including altering synthesis of the neurotransmitter, disrupting the vesicles, increasing release, decreasing reuptake, blocking its breakdown into inactive chemical, or directly simulating or blocking postsyna ...
Types of neurons
... Repolarization leads to a voltage below the resting potential, called hyperpolarization Now neuron cannot produce a new action potential This is the refractory period ...
... Repolarization leads to a voltage below the resting potential, called hyperpolarization Now neuron cannot produce a new action potential This is the refractory period ...
Biology 3201
... This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside (this is helped by the (-)’ly charged proteins, etc. on the inside) The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This furthe ...
... This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside (this is helped by the (-)’ly charged proteins, etc. on the inside) The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This furthe ...
Neuroanatomy
... neurotransmitter has been released, the next neuron will react differently. Since nerve cells are connected to the brain, muscles, glands, etc., the entire human body reacts different depending upon what type of neurotransmitter has been released. ...
... neurotransmitter has been released, the next neuron will react differently. Since nerve cells are connected to the brain, muscles, glands, etc., the entire human body reacts different depending upon what type of neurotransmitter has been released. ...
Slide 1
... neurotransmitter has been released, the next neuron will react differently. Since nerve cells are connected to the brain, muscles, glands, etc., the entire human body reacts different depending upon what type of neurotransmitter has been released. ...
... neurotransmitter has been released, the next neuron will react differently. Since nerve cells are connected to the brain, muscles, glands, etc., the entire human body reacts different depending upon what type of neurotransmitter has been released. ...
6.5 Neurons and Synapses - Mr Cartlidge`s Saigon Science Blog
... Neurons transmit electrical impulses. The myelination of nerve fibres allows for saltatory conduction. Neurons pump sodium and potassium ions across their membranes to generate a resting potential. An action potential consists of depolarization and repolarization of the neuron. Nerve impulses are ac ...
... Neurons transmit electrical impulses. The myelination of nerve fibres allows for saltatory conduction. Neurons pump sodium and potassium ions across their membranes to generate a resting potential. An action potential consists of depolarization and repolarization of the neuron. Nerve impulses are ac ...
Chapter 12
... 32. Define the anatomic, chemical, enzymatic, and receptor components of a chemical synapse. 33. Go through the sequence of events that allow an action potential on an axon to be transmitted into a graded potential on a postsynaptic membrane. Excitatory and Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials 34. Ind ...
... 32. Define the anatomic, chemical, enzymatic, and receptor components of a chemical synapse. 33. Go through the sequence of events that allow an action potential on an axon to be transmitted into a graded potential on a postsynaptic membrane. Excitatory and Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials 34. Ind ...
Mod 07-Lecture - Phoenix Military Academy
... the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites in the dendrites of the receiving neuron, influencing its action potential. The sending neuron then reabsorbs excess NT molecules in a process called reuptake. NTs will only fit into particular receptor sites, like keys that only fit certain locks. NTs hav ...
... the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites in the dendrites of the receiving neuron, influencing its action potential. The sending neuron then reabsorbs excess NT molecules in a process called reuptake. NTs will only fit into particular receptor sites, like keys that only fit certain locks. NTs hav ...
Chapter 3
... • Results from unequal distribution of ions btwn ECF & ICF – buildup of negative ions in cytosol (PO4-3, amino acids) – buildup of positive ions outside membrane (Na+) • Separation of charges represents a form of potential energy – the greater the charge difference across membrane, the greater the p ...
... • Results from unequal distribution of ions btwn ECF & ICF – buildup of negative ions in cytosol (PO4-3, amino acids) – buildup of positive ions outside membrane (Na+) • Separation of charges represents a form of potential energy – the greater the charge difference across membrane, the greater the p ...
Neurology - Porterville College
... Excitatory Neurotransmitters • Dopamine – Gross subconscious movement – Fine motor skills – Emotional responses ...
... Excitatory Neurotransmitters • Dopamine – Gross subconscious movement – Fine motor skills – Emotional responses ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.