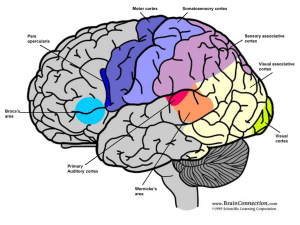
Biology 360: Sensory Systems and Development 1) Describe the
... cells via inhibitory connections. In the case of the olfactory system, the mitral/tufted cells (M/T cells) are connected with adjacent M/T cells through inhibitory synapses made by granule cells (GR). These inhibitory connections modify and sharpen the input information from the olfactory receptor n ...
... cells via inhibitory connections. In the case of the olfactory system, the mitral/tufted cells (M/T cells) are connected with adjacent M/T cells through inhibitory synapses made by granule cells (GR). These inhibitory connections modify and sharpen the input information from the olfactory receptor n ...
Q1 (from chapter 1)
... A. Makes a cell more likely to generate an action potential B. Is called depolarization C. Is called hyperpolarization D. Makes the membrane more permeable for Na+ than K+ ions E. Is called excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) Q3 (from chapter 3) A method that can be used for identification of g ...
... A. Makes a cell more likely to generate an action potential B. Is called depolarization C. Is called hyperpolarization D. Makes the membrane more permeable for Na+ than K+ ions E. Is called excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) Q3 (from chapter 3) A method that can be used for identification of g ...
Ch 49 Pract Test Nervous System
... Tolerance means that decreasing amounts of a drug are needed to be effective. d. A lethal dose is a dose that results in death. ...
... Tolerance means that decreasing amounts of a drug are needed to be effective. d. A lethal dose is a dose that results in death. ...
The Senses
... • Sounds detected as increase in action potentials by the brain ▫ Higher volume = higher amplitude of generated wave ▫ Creates more vigorous vibrations in cochlea = more bending = more action potentials ...
... • Sounds detected as increase in action potentials by the brain ▫ Higher volume = higher amplitude of generated wave ▫ Creates more vigorous vibrations in cochlea = more bending = more action potentials ...
Chapter 32 The Nervous System, Cells of the Nervous System
... [amino acid derivatives]正腎上腺素(Ne) • glycine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid & GABA [amino acids] Neurotransmitters send excitatory &/or inhibitory messages to receptor cells. Drugs can alter neurotransmitter levels. Neurotransmitter imbalance can cause disease. ...
... [amino acid derivatives]正腎上腺素(Ne) • glycine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid & GABA [amino acids] Neurotransmitters send excitatory &/or inhibitory messages to receptor cells. Drugs can alter neurotransmitter levels. Neurotransmitter imbalance can cause disease. ...
Dr. Begay`s Notes from Pharm I
... • Psychoactive drugs: those drugs that alter cognition, behavior, and emotions by changing the functioning of the brain. • Psychopharmacology: the study of the use, mechanisms, and effects of drugs that act on the brain and subsequently ...
... • Psychoactive drugs: those drugs that alter cognition, behavior, and emotions by changing the functioning of the brain. • Psychopharmacology: the study of the use, mechanisms, and effects of drugs that act on the brain and subsequently ...
Document
... - NT binds to receptors and opens ion channels that depolarize the membrane (excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)) or hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane (inhibitory postsynaptic membrane (IPSP). Glial cells remove neurotransmitter from the synaptic cleft ...
... - NT binds to receptors and opens ion channels that depolarize the membrane (excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)) or hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane (inhibitory postsynaptic membrane (IPSP). Glial cells remove neurotransmitter from the synaptic cleft ...
Nervous System
... Nerve impulses reach the axonal terminal of the presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter crosses the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron ...
... Nerve impulses reach the axonal terminal of the presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter crosses the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron ...
Are You suprised ?
... G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest class of molecules involved in signal transduction across membranes, and represent major drug targets in all clinical areas. The serotonin1A receptor is an important neurotransmitter receptor of the GPCR superfamily and is implicated in the generat ...
... G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest class of molecules involved in signal transduction across membranes, and represent major drug targets in all clinical areas. The serotonin1A receptor is an important neurotransmitter receptor of the GPCR superfamily and is implicated in the generat ...
2014 nervous system ppt
... B. Opens voltage-gated channels that result in rapid outflow of Na+ ions C. Is the depolarization that is need to generate an action potential D. Is a graded potential that is proportional to the strength of a stimulus ...
... B. Opens voltage-gated channels that result in rapid outflow of Na+ ions C. Is the depolarization that is need to generate an action potential D. Is a graded potential that is proportional to the strength of a stimulus ...
MS Word Version
... 37. (Page 12.) Glutamate is the most common and most potent excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Glutamate acts directly on ion channels that permit passage of both _______ and _______, producing fast excitatory postsynaptic potentials. a. sodium, potassium b. chloride 38. (Pag ...
... 37. (Page 12.) Glutamate is the most common and most potent excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Glutamate acts directly on ion channels that permit passage of both _______ and _______, producing fast excitatory postsynaptic potentials. a. sodium, potassium b. chloride 38. (Pag ...
The Nervous System : communication
... Strychnine poisoning can be fatal to humans and animals and can occur by inhalation, swallowing or absorption through eyes or mouth Strychnine is a neurotoxin which acts as an antagonist of acetylcholine receptors. It primarily affects the motor nerves in the spinal cord which control muscle contrac ...
... Strychnine poisoning can be fatal to humans and animals and can occur by inhalation, swallowing or absorption through eyes or mouth Strychnine is a neurotoxin which acts as an antagonist of acetylcholine receptors. It primarily affects the motor nerves in the spinal cord which control muscle contrac ...
Ch 09 Nervous System
... Strychnine poisoning can be fatal to humans and animals and can occur by inhalation, swallowing or absorption through eyes or mouth Strychnine is a neurotoxin which acts as an antagonist of acetylcholine receptors. It primarily affects the motor nerves in the spinal cord which control muscle contrac ...
... Strychnine poisoning can be fatal to humans and animals and can occur by inhalation, swallowing or absorption through eyes or mouth Strychnine is a neurotoxin which acts as an antagonist of acetylcholine receptors. It primarily affects the motor nerves in the spinal cord which control muscle contrac ...
Nervous System Exam Review
... Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classification and functional classification. Explain how an impulse travels and the ions involved. Terms: action potential resting membrane potential repolarization depolarization sodium-pot ...
... Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classification and functional classification. Explain how an impulse travels and the ions involved. Terms: action potential resting membrane potential repolarization depolarization sodium-pot ...
K - Cloudfront.net
... 3. A salt is an organic compound found in the body in the form of minerals – Calcium and phosphorus, found in teeth and bones – Dissolved minerals found in urine – Sodium and potassium ions used for nerve impulses in the brain – Iron, found in hemoglobin, in the blood cells (this is what makes it re ...
... 3. A salt is an organic compound found in the body in the form of minerals – Calcium and phosphorus, found in teeth and bones – Dissolved minerals found in urine – Sodium and potassium ions used for nerve impulses in the brain – Iron, found in hemoglobin, in the blood cells (this is what makes it re ...
Part1
... CVt = -gCa m(V) (V-ECa) - gKn(V-EK) - gL(V-EL) + Iapp nt = (n(V) - n) / n(V) m(V) = .5(1+tanh((v-v1)/v2) n(V) = .5(1+tanh((v-v3)/v4) n(V) = 1/cosh((v-v3)/2v4) We will write this system as: V’ = f(V,n) + Iapp n’ = g(V,n) ...
... CVt = -gCa m(V) (V-ECa) - gKn(V-EK) - gL(V-EL) + Iapp nt = (n(V) - n) / n(V) m(V) = .5(1+tanh((v-v1)/v2) n(V) = .5(1+tanh((v-v3)/v4) n(V) = 1/cosh((v-v3)/2v4) We will write this system as: V’ = f(V,n) + Iapp n’ = g(V,n) ...
Document
... -Neurotransmitter is released by exocytosis -Diffuses to other side of cleft and binds to chemical- or ligand-gated receptor proteins -Neurotransmitter action is terminated by enzymatic cleavage or cellular uptake 10 ...
... -Neurotransmitter is released by exocytosis -Diffuses to other side of cleft and binds to chemical- or ligand-gated receptor proteins -Neurotransmitter action is terminated by enzymatic cleavage or cellular uptake 10 ...
Nervous System Notes
... 1. Unequal distribution of ions across the plasma membrane. (ECF is rich in Na+ and Cl- ions the cytoplasm is high in K+) 2. Relative permeability of the plasma membrane to Na+ and K+. - In a resting neuron or muscle fiber, the permeability of the plasma membrane is 50 to 100 times greater to K+ tha ...
... 1. Unequal distribution of ions across the plasma membrane. (ECF is rich in Na+ and Cl- ions the cytoplasm is high in K+) 2. Relative permeability of the plasma membrane to Na+ and K+. - In a resting neuron or muscle fiber, the permeability of the plasma membrane is 50 to 100 times greater to K+ tha ...
Neuroscience Course Conference
... 8. A dominant mutation in the gene that encodes the -subunit of the voltage gated Na+ channel in skeletal muscle has been shown to cause the mutant channels to have defective inactivation gates. In a heterozygote, approximately half of the channels are normal and the other half are in the mutant fo ...
... 8. A dominant mutation in the gene that encodes the -subunit of the voltage gated Na+ channel in skeletal muscle has been shown to cause the mutant channels to have defective inactivation gates. In a heterozygote, approximately half of the channels are normal and the other half are in the mutant fo ...
The Nervous System - Ridgewood High School
... ensues, depolarizing the cell and causing the VM to increase. This is the rising phase of an AP. • Eventually, the Na+ channel will have inactivated and the K+ channels will be open. Now, K+ effluxes and repolarization occurs. This is the falling phase. – K+ channels are slow to open and slow to clo ...
... ensues, depolarizing the cell and causing the VM to increase. This is the rising phase of an AP. • Eventually, the Na+ channel will have inactivated and the K+ channels will be open. Now, K+ effluxes and repolarization occurs. This is the falling phase. – K+ channels are slow to open and slow to clo ...
The Brain and the Neuron (1)
... • Communication goes directly from interneurons in spinal cord to motor neurons to move (reflexively) at the same time the info is going to the brain to be perceived ...
... • Communication goes directly from interneurons in spinal cord to motor neurons to move (reflexively) at the same time the info is going to the brain to be perceived ...
Abstract View A HYBRID ELECTRO-DIFFUSION MODEL FOR NEURAL SIGNALING. ;
... A new method is introduced for modeling the three-dimensional movement of ions in neurons. Using the Nernst-Planck equation, concentration gradients and electric fields were evaluated using a weighted moving least-squares algorithm. We incorporate this method into MCell, a Monte-Carlo cell simulator ...
... A new method is introduced for modeling the three-dimensional movement of ions in neurons. Using the Nernst-Planck equation, concentration gradients and electric fields were evaluated using a weighted moving least-squares algorithm. We incorporate this method into MCell, a Monte-Carlo cell simulator ...
Differential Permeability of the Membrane
... called the presynaptic membrane. The presynaptic membrane is separated from the other neuron by what is called the synaptic cleft. ...
... called the presynaptic membrane. The presynaptic membrane is separated from the other neuron by what is called the synaptic cleft. ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... B. axon sends neural impulse to axon terminal C. a neurotransmitter (NT) is release and makes contact with another neuron (synapse) ...
... B. axon sends neural impulse to axon terminal C. a neurotransmitter (NT) is release and makes contact with another neuron (synapse) ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.