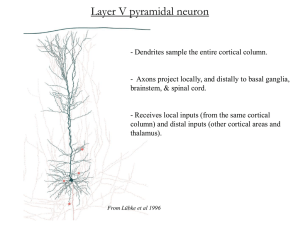
Chapters 13, and 14
... The action potential occurs in each successive portion of an axon. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. The Synapse Transmission of the nerve ...
... The action potential occurs in each successive portion of an axon. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. The Synapse Transmission of the nerve ...
Nervous System
... 50. What term is given to functionally related bundles of axons in the white matter? 51. Are tracts distinguishable in the brain or spinal cord with routine processing? 52. What is neuropil? 53. What is the location of white matter in the spinal cord? 54. What term applies to groups of nerve cell b ...
... 50. What term is given to functionally related bundles of axons in the white matter? 51. Are tracts distinguishable in the brain or spinal cord with routine processing? 52. What is neuropil? 53. What is the location of white matter in the spinal cord? 54. What term applies to groups of nerve cell b ...
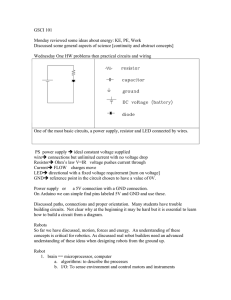
slides - Purdue Math
... Previous work done by many researchers had suggested this muscle is a relatively simple system that uses voltage dependent Ca2+ and K+ channels that do not inactivate under current stimulation. Also evidence for Ca2+ dependent K+ channels. ...
... Previous work done by many researchers had suggested this muscle is a relatively simple system that uses voltage dependent Ca2+ and K+ channels that do not inactivate under current stimulation. Also evidence for Ca2+ dependent K+ channels. ...
Diseases and Disorders of the Nervous System
... that accumulate outside neurons and appear to trigger death of neighboring neurons • PIB: chemical that accumulates in regions of amyloid deposits; may help in early detection/ identifying treatments for AD ...
... that accumulate outside neurons and appear to trigger death of neighboring neurons • PIB: chemical that accumulates in regions of amyloid deposits; may help in early detection/ identifying treatments for AD ...
PET (positron emission tomography): measures the different levels
... Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory ...
... Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory ...
Biology 4 Study Guide
... There are 3 functions of the nervous system: 1) It collects __________ input which is information about the internal & external ____________ and is gathered by ____________ receptors; 2) ________________ is the __________________ of that sensory input gathered by the receptors; and 3) It provides a ...
... There are 3 functions of the nervous system: 1) It collects __________ input which is information about the internal & external ____________ and is gathered by ____________ receptors; 2) ________________ is the __________________ of that sensory input gathered by the receptors; and 3) It provides a ...
Neuron Notes Neuron- Cells that carry messages throughout the
... 4. myelin sheath: (lipids) insulating membrane around axon. There are small gaps in the myelin sheath along an axon called _nodes_____ Schwann Cells – individual cells of the myelin sheath 5. Axon Terminal- the ending of the nerve cell where the synapse is located. Nerve Impulses • Messages carried ...
... 4. myelin sheath: (lipids) insulating membrane around axon. There are small gaps in the myelin sheath along an axon called _nodes_____ Schwann Cells – individual cells of the myelin sheath 5. Axon Terminal- the ending of the nerve cell where the synapse is located. Nerve Impulses • Messages carried ...
MCB 32 Introductory Human Physiology
... When an action potential arrives at the synaptic bulb, a series of events is initiated that ultimately result in movement of these vesicles to the cell membrane. There the vesicles fuse with the cell membrane, releasing their contents into the space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic cells; t ...
... When an action potential arrives at the synaptic bulb, a series of events is initiated that ultimately result in movement of these vesicles to the cell membrane. There the vesicles fuse with the cell membrane, releasing their contents into the space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic cells; t ...
Chapter 48 Learning Objectives: Nervous Systems - STHS-AP-Bio
... 1. Compare and contrast the nervous systems of the following animals and explain how variations in design and complexity relate to their phylogeny, natural history, and habitat: hydra, sea star, planarian, insect, squid, and vertebrate. 2. Name the three stages in the processing of information by ne ...
... 1. Compare and contrast the nervous systems of the following animals and explain how variations in design and complexity relate to their phylogeny, natural history, and habitat: hydra, sea star, planarian, insect, squid, and vertebrate. 2. Name the three stages in the processing of information by ne ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. • They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. • A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron. Synapses can be electrical or chemical. Ions carry information in electrical synapses. In chemical synap ...
... • Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. • They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. • A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron. Synapses can be electrical or chemical. Ions carry information in electrical synapses. In chemical synap ...
Monoammonium glutamate
... Monoammonium glutamate is the ammonium acid salt of glutamic acid, which is a natural essential amino acid. It is the most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and is present in all complete proteins. Monoammonium glutamate has the ability to make bland and tasteless foods taste wonderful ...
... Monoammonium glutamate is the ammonium acid salt of glutamic acid, which is a natural essential amino acid. It is the most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and is present in all complete proteins. Monoammonium glutamate has the ability to make bland and tasteless foods taste wonderful ...
04-21-06
... – Electrical current flows directly from one cell to another via a gap junction (tail flick escape response in lobster uses electrical connection because it must be as fast as possible). ...
... – Electrical current flows directly from one cell to another via a gap junction (tail flick escape response in lobster uses electrical connection because it must be as fast as possible). ...
Nerve tissue for stu..
... Nissl substance – basophilic (rER); protein-producing cell (membrane, neurotransmitters, enzymes) Golgi apparatus mitochondria lysosomes transport vesicles lipofuscin (pigment of age), melanin (pigments) cytoskeleton – keep the shape of cell; transport LM: neurofibrils (argyrophilic, brown or black ...
... Nissl substance – basophilic (rER); protein-producing cell (membrane, neurotransmitters, enzymes) Golgi apparatus mitochondria lysosomes transport vesicles lipofuscin (pigment of age), melanin (pigments) cytoskeleton – keep the shape of cell; transport LM: neurofibrils (argyrophilic, brown or black ...
Neuroscience - HuskiesScience
... quickly regains its composure (hyperpolarize) • Active process in which sodium is removed from the cell • Sodium is exchanged for potassium • Requires metabolic activity • Returns charge inside cell to -70 mV • Refractory period-neuron cannot fire ...
... quickly regains its composure (hyperpolarize) • Active process in which sodium is removed from the cell • Sodium is exchanged for potassium • Requires metabolic activity • Returns charge inside cell to -70 mV • Refractory period-neuron cannot fire ...
Chapter 12 - Membrane Transport . PPT - A
... presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter crosses the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron Postsynaptic membrane permeability changes due to opening of ion channels, causing an excitatory ...
... presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter crosses the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron Postsynaptic membrane permeability changes due to opening of ion channels, causing an excitatory ...
Types of neurons
... Na-K pump moves Na and K against their net electrochemical gradients! At rest – net flow of passive Na+ and K+ matched by Na-K pump! – Driven by ATP! – One ATP pumps 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in! – Restores battery - but battery discharges only slowly ...
... Na-K pump moves Na and K against their net electrochemical gradients! At rest – net flow of passive Na+ and K+ matched by Na-K pump! – Driven by ATP! – One ATP pumps 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in! – Restores battery - but battery discharges only slowly ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... b. an electrical charge travels from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron. c. a neuron fires more rapidly than usual. d. dendrites transmit more electrical signals to axons. e. positively charged ions are pumped back outside a neural membrane. 4. Mandy came home late. As she reached to turn on the kit ...
... b. an electrical charge travels from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron. c. a neuron fires more rapidly than usual. d. dendrites transmit more electrical signals to axons. e. positively charged ions are pumped back outside a neural membrane. 4. Mandy came home late. As she reached to turn on the kit ...
BehNeuro11#2 (2) - Biology Courses Server
... d) The arcuate N. cells shown above release NPY & AgRP. What roles do the arcuate neurons that contain MSH & CART play (how does their activity influence the PV and lateral hypothalamic areas?). Use a diagram like the one shown above. ...
... d) The arcuate N. cells shown above release NPY & AgRP. What roles do the arcuate neurons that contain MSH & CART play (how does their activity influence the PV and lateral hypothalamic areas?). Use a diagram like the one shown above. ...
Topic: Nervous system Reading: Chapter 38 Main concepts
... • There may be over 1000 different olfactory receptor proteins in in the receptors cells. • Pain • Damage to skin, blood vessels, and small nerves cause the release of potassium ions, stimulating pain receptors. • Other chemicals are involved in this response, some of which are blocked by pain medic ...
... • There may be over 1000 different olfactory receptor proteins in in the receptors cells. • Pain • Damage to skin, blood vessels, and small nerves cause the release of potassium ions, stimulating pain receptors. • Other chemicals are involved in this response, some of which are blocked by pain medic ...
301 Definitions – Revised Shannon Benson
... definitions is a person who is taking an introductory level psychology class. Three types of definitions will be given for the term “neuron” from one of my core disciplines, psychology. The first of these is a parenthetical definition, which illustrates the meaning of a term by following it with a c ...
... definitions is a person who is taking an introductory level psychology class. Three types of definitions will be given for the term “neuron” from one of my core disciplines, psychology. The first of these is a parenthetical definition, which illustrates the meaning of a term by following it with a c ...
Technical Definitions
... definitions is a person who is taking an introductory level psychology class. Three types of definitions will be given for the term “neuron” from one of my core disciplines, psychology. The first of these is a parenthetical definition, which illustrates the meaning of a term by following it with a c ...
... definitions is a person who is taking an introductory level psychology class. Three types of definitions will be given for the term “neuron” from one of my core disciplines, psychology. The first of these is a parenthetical definition, which illustrates the meaning of a term by following it with a c ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.