Review (10/25/16) updated
... neurons are gated by • Cyclic nucleotides (cAMP) • There are also Ca activated chloride channels. ...
... neurons are gated by • Cyclic nucleotides (cAMP) • There are also Ca activated chloride channels. ...
Chapter 28
... slight delay, causing K+ to flow out of the cell • this makes the interior of the neuron more negative, causing the voltage-gated Na+ channels to close. ...
... slight delay, causing K+ to flow out of the cell • this makes the interior of the neuron more negative, causing the voltage-gated Na+ channels to close. ...
Neuron is the basic working unit of the nervous system, specialized
... ACTION POTENTIAL ‐ An electrical charge that travels along the axon to the neuron’s terminal, where it triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. This occurs when a neuron is activated and temporarily reverses the electrical state of its interior membrane from negative to positive. ACETYLCHOLIN ...
... ACTION POTENTIAL ‐ An electrical charge that travels along the axon to the neuron’s terminal, where it triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. This occurs when a neuron is activated and temporarily reverses the electrical state of its interior membrane from negative to positive. ACETYLCHOLIN ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... generating and propagating ACTION POTENTIALS (AP). Only cells with excitable membranes (like muscle cells and neurons) can generate APs. ...
... generating and propagating ACTION POTENTIALS (AP). Only cells with excitable membranes (like muscle cells and neurons) can generate APs. ...
Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
... Resting state: Voltage-gated Na and K channels are closed; resting potential is maintained by ungated channels (not shown). ...
... Resting state: Voltage-gated Na and K channels are closed; resting potential is maintained by ungated channels (not shown). ...
PNS Study Guide
... 5. What structures of the body make up the CNS and PNS? 6. What are the two functional classifications of the PNS? Describe the function of each (flow chart). 7. What are the 2 types of motor nerves? How are they different? 8. What are the 2 types of autonomic nerves? Make sure you know when they ar ...
... 5. What structures of the body make up the CNS and PNS? 6. What are the two functional classifications of the PNS? Describe the function of each (flow chart). 7. What are the 2 types of motor nerves? How are they different? 8. What are the 2 types of autonomic nerves? Make sure you know when they ar ...
The Neuron
... – Keeps out some substances – Allows others in only under certain circumstances – Protein channels: open and close to let molecules in when neuron is active ...
... – Keeps out some substances – Allows others in only under certain circumstances – Protein channels: open and close to let molecules in when neuron is active ...
Pt2Localization - MemoryAndCognition
... Members of groups rarely have exactly the same damage (location or extent) No record of processing or brain organization before the damage Difficult to assess all possible types of functional ...
... Members of groups rarely have exactly the same damage (location or extent) No record of processing or brain organization before the damage Difficult to assess all possible types of functional ...
Biology 232
... Sensory and Motor Pathways sensation – conscious or subconscious awareness of internal or external stimuli perception – conscious awareness and interpretation of sensations (occurs in thalamus and cerebral cortex) Basic Sensory Pathway 1) sensory receptor – specialized cell or dendrites that detect ...
... Sensory and Motor Pathways sensation – conscious or subconscious awareness of internal or external stimuli perception – conscious awareness and interpretation of sensations (occurs in thalamus and cerebral cortex) Basic Sensory Pathway 1) sensory receptor – specialized cell or dendrites that detect ...
proposal2000a.doc
... binding of the GABA agonist muscimol, which selectively binds to GABAA receptors, is reduced in the deprived barrels. This effect was observed in both neonatally and adult deprived rats, and was still present even after allowing the rats to grow their whiskers for ten additional weeks after the tri ...
... binding of the GABA agonist muscimol, which selectively binds to GABAA receptors, is reduced in the deprived barrels. This effect was observed in both neonatally and adult deprived rats, and was still present even after allowing the rats to grow their whiskers for ten additional weeks after the tri ...
Slide ()
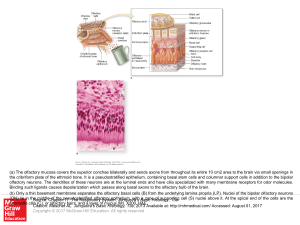
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
Chapter 2 Notes Packet (Part 1)
... _________________________________Period: After a neuron fires, for the next thousandth of a second it will not fire again regardless of the strength of the incoming message's Relative Refractory Period: during the resting state of a cell the neuron will only fire if the incoming message is consi ...
... _________________________________Period: After a neuron fires, for the next thousandth of a second it will not fire again regardless of the strength of the incoming message's Relative Refractory Period: during the resting state of a cell the neuron will only fire if the incoming message is consi ...
Neurons – A whistle-stop Tour
... At synapses, the ends of axons (called axon terminals) nearly, but not actually touch the next neuron. Axon terminals contain many synaptic vesicules loaded with 2000 molecules of a specialised compound called a neurotransmitter. An electrical impulse called a ‘spike’ sends electrical impulses down ...
... At synapses, the ends of axons (called axon terminals) nearly, but not actually touch the next neuron. Axon terminals contain many synaptic vesicules loaded with 2000 molecules of a specialised compound called a neurotransmitter. An electrical impulse called a ‘spike’ sends electrical impulses down ...
Chapter 4
... Dendrites: of neuron that receives inputs from other neurons Axon: part of neuron that transmits electrical signals to other neurons Synapses: point where connections between neurons are made http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c UGuWh2UeMk ...
... Dendrites: of neuron that receives inputs from other neurons Axon: part of neuron that transmits electrical signals to other neurons Synapses: point where connections between neurons are made http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c UGuWh2UeMk ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... “Bath salts” are synthetic powders that contain synthetic amphetamine-like chemicals and inhibit the reuptake of several neurotransmitters, producing a euphoric sensation. 17.7 Disorders of the Nervous System A myriad of abnormal conditions can affect the nervous system. Disorders of the Brain Alzhe ...
... “Bath salts” are synthetic powders that contain synthetic amphetamine-like chemicals and inhibit the reuptake of several neurotransmitters, producing a euphoric sensation. 17.7 Disorders of the Nervous System A myriad of abnormal conditions can affect the nervous system. Disorders of the Brain Alzhe ...
Topic: Neurons Student learning outcome: Explain how neurons
... that the Hershey Kisses are neurotransmitters (perhaps acetylcholine, responsible for muscle movement). Begin by suggesting that you are the terminal branch of a nearby neuron and toss Hershey Kisses (neurotransmitters) in the direction of the dendrites and cell body (that is, into the synapse). The ...
... that the Hershey Kisses are neurotransmitters (perhaps acetylcholine, responsible for muscle movement). Begin by suggesting that you are the terminal branch of a nearby neuron and toss Hershey Kisses (neurotransmitters) in the direction of the dendrites and cell body (that is, into the synapse). The ...
Heart
... Material transport across the cytoplasmic membrane Pasive transport Difusion - free transport of small non-polar molecules across membrane Membrane channel - transmembrane protein - transport is possible without additional energy - cell can regulate whether it is open or not (deactivated) - channel ...
... Material transport across the cytoplasmic membrane Pasive transport Difusion - free transport of small non-polar molecules across membrane Membrane channel - transmembrane protein - transport is possible without additional energy - cell can regulate whether it is open or not (deactivated) - channel ...
Lecture-24-2012-Bi
... with drug taken from that point. 1. Circuit-based: Cell-selective upregulation of α4β2 nicotinic receptors (pharmacological deep brain stimulation) 2. Presynaptic: Selective upregulation in nerve terminals of dopaminergic neurons 3. Cell-delimited: Pharmacological chaperoning of intracellular recept ...
... with drug taken from that point. 1. Circuit-based: Cell-selective upregulation of α4β2 nicotinic receptors (pharmacological deep brain stimulation) 2. Presynaptic: Selective upregulation in nerve terminals of dopaminergic neurons 3. Cell-delimited: Pharmacological chaperoning of intracellular recept ...
neuron
... cell body down the axon – Threshold - Each neuron receives excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity (threshold) the neuron fires an action potential. ...
... cell body down the axon – Threshold - Each neuron receives excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity (threshold) the neuron fires an action potential. ...
Opioids General - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... Opioid receptors are part of a large superfamily of membrane-bound receptors that are coupled to G proteins. Each opioid receptor has a unique distribution in the brain, spinal cord, and periphery. Opioids combine reversibly with these receptors and alter the transmission and perception of pain. Oth ...
... Opioid receptors are part of a large superfamily of membrane-bound receptors that are coupled to G proteins. Each opioid receptor has a unique distribution in the brain, spinal cord, and periphery. Opioids combine reversibly with these receptors and alter the transmission and perception of pain. Oth ...
File
... 5. List the four types of Neuroglial cells and their function: a. Astrocytes-their functions include the following: 1) Producing neurotransmitters 2) Maintaining potassium levels in the CNS-this aids in the production of nerve impulses. 3) These help to form the blood-brain barrier which regulates ...
... 5. List the four types of Neuroglial cells and their function: a. Astrocytes-their functions include the following: 1) Producing neurotransmitters 2) Maintaining potassium levels in the CNS-this aids in the production of nerve impulses. 3) These help to form the blood-brain barrier which regulates ...
bio 342 human physiology
... d) Axons of second order neurons travel in the medial lemniscus. e) Axons of first order neurons ascend in the dorsal columns and synapse onto second order neurons in the dorsal column nuclei. ...
... d) Axons of second order neurons travel in the medial lemniscus. e) Axons of first order neurons ascend in the dorsal columns and synapse onto second order neurons in the dorsal column nuclei. ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.