Release of neurotransmitters from glia
... Keywords: neurotransmitter release, synaptic transmission, synaptic vesicle, LTP, astrocytes, tripartite synapse, neuron–glia interactions, calcium, intercellular signaling ...
... Keywords: neurotransmitter release, synaptic transmission, synaptic vesicle, LTP, astrocytes, tripartite synapse, neuron–glia interactions, calcium, intercellular signaling ...
Nerve Impulses and Action Potential
... 4 Propagation of the action potential. Depolarization of the first membrane patch causes permeability changes in the adjacent membrane, and the events described in step 2 are repeated. Thus, the action potential propagates rapidly along the entire length of the membrane. ...
... 4 Propagation of the action potential. Depolarization of the first membrane patch causes permeability changes in the adjacent membrane, and the events described in step 2 are repeated. Thus, the action potential propagates rapidly along the entire length of the membrane. ...
The nervous system
... increase dopamine signalling may produce euphoric effects. Many recreational drugs, such as cocaine and amphetamines, alter the functionality of the dopamine transporter (DAT), the protein responsible for removing dopamine from the neural synapse. These changes can strengthen drug craving and alter ...
... increase dopamine signalling may produce euphoric effects. Many recreational drugs, such as cocaine and amphetamines, alter the functionality of the dopamine transporter (DAT), the protein responsible for removing dopamine from the neural synapse. These changes can strengthen drug craving and alter ...
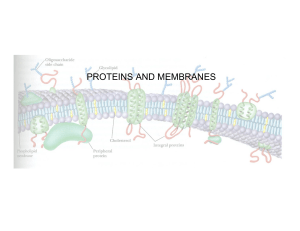
PROTEINS AND MEMBRANES
... version were more likely to have lower pain thresholds. It was as if the normal subjects had taken an ibuprofen, but the subjects with the rare SNP hadn't. ...
... version were more likely to have lower pain thresholds. It was as if the normal subjects had taken an ibuprofen, but the subjects with the rare SNP hadn't. ...
Anatomy of the Sensory organs
... – Free nerve endings are the simplest type: they are the dendrites of sensory neurons – Complex receptors (eyes) are housed in organs – Some receptors respond to only one kind of stimulus ...
... – Free nerve endings are the simplest type: they are the dendrites of sensory neurons – Complex receptors (eyes) are housed in organs – Some receptors respond to only one kind of stimulus ...
lecture notes #4 membrane potentials
... In large fibers, the influx of sodium causes the positive rise to overshoot the zero level In some smaller fibers, as well as in many central nervous system neurons, the potential merely approaches the zero level and does not overshoot to the positive state Repolarization Stage Sodium channels b ...
... In large fibers, the influx of sodium causes the positive rise to overshoot the zero level In some smaller fibers, as well as in many central nervous system neurons, the potential merely approaches the zero level and does not overshoot to the positive state Repolarization Stage Sodium channels b ...
State Dependant Synaptic Plasticity in Purkinje Cells
... One of the popular theories of cerebellar function assumes that the cerebellum stores memory traces at the parallel fibers (pf) synapse. According to this theory, the climbing fibers (cf) control the learning process by inducing long-term depression (LTD) of the simultaneously activated pf synapses. ...
... One of the popular theories of cerebellar function assumes that the cerebellum stores memory traces at the parallel fibers (pf) synapse. According to this theory, the climbing fibers (cf) control the learning process by inducing long-term depression (LTD) of the simultaneously activated pf synapses. ...
neurons
... All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
Document
... b. The choline is then taken up by the axon terminal and used to make more ACh 2. What happens in postsynaptic cell? a. Binding to receptor initiates release of a “second messenger” into the cytoplasm of the postsynaptic cell. This is most often Ca ion, cyclic AMP (= cAMP), or cyclic GMP (= cGMP). b ...
... b. The choline is then taken up by the axon terminal and used to make more ACh 2. What happens in postsynaptic cell? a. Binding to receptor initiates release of a “second messenger” into the cytoplasm of the postsynaptic cell. This is most often Ca ion, cyclic AMP (= cAMP), or cyclic GMP (= cGMP). b ...
test - Scioly.org
... 18. Axoplasm is the a. Blood plasma that nourishes a nerve b. Fluid external to the axon but inside the myelin sheath c. Cytoplasm of the dendrite d. Cytoplasm ofthe axon a constant membrane 19. When the axon is conducting an impulse, the oscilloscope records potential, equal to about -65mV. a. True ...
... 18. Axoplasm is the a. Blood plasma that nourishes a nerve b. Fluid external to the axon but inside the myelin sheath c. Cytoplasm of the dendrite d. Cytoplasm ofthe axon a constant membrane 19. When the axon is conducting an impulse, the oscilloscope records potential, equal to about -65mV. a. True ...
HALLUCINATIONS NATURAL VS. DRUG
... agents work by an agonist effect at the 5HT2 receptor • LSD not only has affinities for 5-HT receptors but also for receptors of histamine, ACh, dopamine, and the catecholines: epinephrine and norepinephrine ...
... agents work by an agonist effect at the 5HT2 receptor • LSD not only has affinities for 5-HT receptors but also for receptors of histamine, ACh, dopamine, and the catecholines: epinephrine and norepinephrine ...
Autonomic NS
... Draw a simple diagram to show the peripheral efferent neural pathway for the eye pupil response in this acutely stressful situation of encountering a bear. For each synapse along the pathway, name the neurotransmitter released and receptors for the neurotransmitter . CNS Æ ...
... Draw a simple diagram to show the peripheral efferent neural pathway for the eye pupil response in this acutely stressful situation of encountering a bear. For each synapse along the pathway, name the neurotransmitter released and receptors for the neurotransmitter . CNS Æ ...
Milestone
... • Hypothesis is a prediction of a particular outcome. • Always hypothesize a difference. • Hypothesis must be testable. • You should include directionality in the hypothesis • Viewing more TV will increase anxiety. ...
... • Hypothesis is a prediction of a particular outcome. • Always hypothesize a difference. • Hypothesis must be testable. • You should include directionality in the hypothesis • Viewing more TV will increase anxiety. ...
nervous system worksheet
... ..................................... 10. The sense organ or cells that receive stimuli from within and outside the body. ..................................... 11. The reaction to a stimulus by a muscle or gland. ..................................... 12.The part of the nerve cell containing the nucl ...
... ..................................... 10. The sense organ or cells that receive stimuli from within and outside the body. ..................................... 11. The reaction to a stimulus by a muscle or gland. ..................................... 12.The part of the nerve cell containing the nucl ...
Synapse formation
... through the release of neurotransmitters. In this process, glutamate is released by the presynaptic neurons. • Glutamate is the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain for learning. • When glutamate is released by the presynaptic neuron, it acts on two types of glutamate receptors in the posts ...
... through the release of neurotransmitters. In this process, glutamate is released by the presynaptic neurons. • Glutamate is the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain for learning. • When glutamate is released by the presynaptic neuron, it acts on two types of glutamate receptors in the posts ...
Chapter 48 PowerPoint 2016 - Spring
... • Voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels respond to a change in membrane potential • When a stimulus depolarizes the membrane, Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ to diffuse into the cell • The movement of Na+ into the cell increases the depolarization and causes even more Na+ channels to open • A strong sti ...
... • Voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels respond to a change in membrane potential • When a stimulus depolarizes the membrane, Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ to diffuse into the cell • The movement of Na+ into the cell increases the depolarization and causes even more Na+ channels to open • A strong sti ...
Neurotransmitters Role in Health 2008 PPT
... • Disclaimer: The opinions expressed in this educational activity are those of the faculty and do not reflect the views of Medical Education Collaborative (MEC) and/or Jespersen & Associates. This educational activity may discuss off-label and/or investigational uses and dosages for therapeutic prod ...
... • Disclaimer: The opinions expressed in this educational activity are those of the faculty and do not reflect the views of Medical Education Collaborative (MEC) and/or Jespersen & Associates. This educational activity may discuss off-label and/or investigational uses and dosages for therapeutic prod ...
The nervous system
... increase dopamine signalling may produce euphoric effects. Many recreational drugs, such as cocaine and amphetamines, alter the functionality of the dopamine transporter (DAT), the protein responsible for removing dopamine from the neural synapse. These changes can strengthen drug craving and alter ...
... increase dopamine signalling may produce euphoric effects. Many recreational drugs, such as cocaine and amphetamines, alter the functionality of the dopamine transporter (DAT), the protein responsible for removing dopamine from the neural synapse. These changes can strengthen drug craving and alter ...
First-order neuron
... temperatures between 50-105 degrees F • Warm receptors in the dermis respond to temperatures between 90-118 degrees F • Both adapt rapidly at first, but continue to generate impulses at a low frequency • Pain is produced below 50 and over 118 degrees F. ...
... temperatures between 50-105 degrees F • Warm receptors in the dermis respond to temperatures between 90-118 degrees F • Both adapt rapidly at first, but continue to generate impulses at a low frequency • Pain is produced below 50 and over 118 degrees F. ...
Chapter_03_4E
... neurotransmitters across synapses • Synapses involve a presynaptic axon terminal, neurotransmitters, a postsynaptic receptor, and the synaptic cleft • Once sufficient amounts of neurotransmitter bind to the receptors, depolarization (excitation) or hyperpolarization (inhibition) occurs, depending on ...
... neurotransmitters across synapses • Synapses involve a presynaptic axon terminal, neurotransmitters, a postsynaptic receptor, and the synaptic cleft • Once sufficient amounts of neurotransmitter bind to the receptors, depolarization (excitation) or hyperpolarization (inhibition) occurs, depending on ...
Chapter 3
... Why do drug addictions occur? Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses? ...
... Why do drug addictions occur? Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses? ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... Possibly caused by stimulation from neurons that used to receive signals from the appendage. Possibly from the brain and its sense of body ...
... Possibly caused by stimulation from neurons that used to receive signals from the appendage. Possibly from the brain and its sense of body ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.