section 3 - the nervous system and sensory physiology
... 3. Long ECG elastic band and ECG electrolyte gel 4. Alternatively, Biopac equipment can be used (Biopac lessons 3 and 4). ...
... 3. Long ECG elastic band and ECG electrolyte gel 4. Alternatively, Biopac equipment can be used (Biopac lessons 3 and 4). ...
Lewy Body Diseases
... synaptic protein, found at presynaptic terminal sits in cytosol, transiently binds to cell memb and other synaptic proteins role in synaptic transport, synaptic change, learning aggregation may cause neuronal dysfunction potential disease marker lewy body distribution can occur in - subs ...
... synaptic protein, found at presynaptic terminal sits in cytosol, transiently binds to cell memb and other synaptic proteins role in synaptic transport, synaptic change, learning aggregation may cause neuronal dysfunction potential disease marker lewy body distribution can occur in - subs ...
ph16neuro lectures
... concentrations inside and outside of the cell. The equation says that when a membrane is permeable to several different ions, the resting membrane potential depends on permeability, charge, and concentrations of all of the ions. So, the resting potential is not at the equilibrium potential for any s ...
... concentrations inside and outside of the cell. The equation says that when a membrane is permeable to several different ions, the resting membrane potential depends on permeability, charge, and concentrations of all of the ions. So, the resting potential is not at the equilibrium potential for any s ...
is here
... On November 3, 1906, Alois Alzheimer gave a lecture to the Meeting of the Psychiatrists of South West Germany, presenting the neuropathological and clinical description of the features of one of his cases, Auguste D., who had died of a dementing illness at the age of 55, ...
... On November 3, 1906, Alois Alzheimer gave a lecture to the Meeting of the Psychiatrists of South West Germany, presenting the neuropathological and clinical description of the features of one of his cases, Auguste D., who had died of a dementing illness at the age of 55, ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
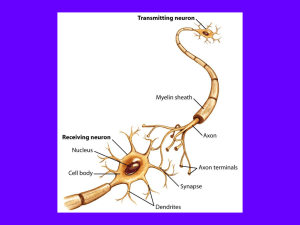
... used to transmit an impulse from the axon of one neuron to the dendrites of the next neuron ...
... used to transmit an impulse from the axon of one neuron to the dendrites of the next neuron ...
Topic 8.1 Neurones and nervous responses File
... _ sodium ___ ions. In addition, they pump in positively charged __ potassium _ ions . Thus there is a high concentration of sodium ions present _ outside _ the neuron, and a high concentration of potassium ions _ inside ___. The neuronal membrane also contains specialized proteins called _ protein c ...
... _ sodium ___ ions. In addition, they pump in positively charged __ potassium _ ions . Thus there is a high concentration of sodium ions present _ outside _ the neuron, and a high concentration of potassium ions _ inside ___. The neuronal membrane also contains specialized proteins called _ protein c ...
Left Brain
... the muscles of its limbs were seen to be so contracted that they seemed to have fallen into tonic convulsions. “ ...
... the muscles of its limbs were seen to be so contracted that they seemed to have fallen into tonic convulsions. “ ...
PD233-Lecture6
... Potential difference leads to flow of current flow when two points with different electric potential are connected with conducting media. ...
... Potential difference leads to flow of current flow when two points with different electric potential are connected with conducting media. ...
The Neuron
... where the package merges with the membrane and it's contents are released outside the cell in a process referred to as exocytosis. The most important type of exocytosis in neural communication occurs in the terminal buttons, often with packages of neurotransmitter that have been created in the Golgi ...
... where the package merges with the membrane and it's contents are released outside the cell in a process referred to as exocytosis. The most important type of exocytosis in neural communication occurs in the terminal buttons, often with packages of neurotransmitter that have been created in the Golgi ...
Nerves and nervous impulses File
... and _ Na+ ___ ions diffuse. After these channels open they become _inactive ___ for a certain time. During this time a voltage change will _ ...
... and _ Na+ ___ ions diffuse. After these channels open they become _inactive ___ for a certain time. During this time a voltage change will _ ...
Chapter 2 Powerpoint - Destiny High School
... • ACETYLCHOLINE: INVOLVED IN AROUSAL, ATTENTION, MEMORY, MOTIVATION, AND MOVEMENT. • CAN LEAD TO ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE • DOPAMINE: VARIETY OF BEHAVIORS AND EMOTIONS, INCLUDING PRESSURE. • IMPLICATED IN SCHIZOPHRENIA AND PARKINSON’S DISEASE • SEROTONIN: REGULATES SLEEP, DREAMING, MOOD, EATING, PAIN, AN ...
... • ACETYLCHOLINE: INVOLVED IN AROUSAL, ATTENTION, MEMORY, MOTIVATION, AND MOVEMENT. • CAN LEAD TO ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE • DOPAMINE: VARIETY OF BEHAVIORS AND EMOTIONS, INCLUDING PRESSURE. • IMPLICATED IN SCHIZOPHRENIA AND PARKINSON’S DISEASE • SEROTONIN: REGULATES SLEEP, DREAMING, MOOD, EATING, PAIN, AN ...
16. Taste, smell
... - qualities of smell: current research has discredited former popular theory of seven primary odors; approx. 100 genes coding for specific odorant receptors & approx. 50 specific anosmias (loss of specific odorant sensitivity) have been identified - transduction: chemicals dissolve in mucus and bind ...
... - qualities of smell: current research has discredited former popular theory of seven primary odors; approx. 100 genes coding for specific odorant receptors & approx. 50 specific anosmias (loss of specific odorant sensitivity) have been identified - transduction: chemicals dissolve in mucus and bind ...
Lecture 1 st week
... • 1. Opening specific ion channels through the postsynaptic cell membrane • 2. Activation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) or cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in the neuronal cell • 3. Activation of one or more intracellular enzymes • 4. Activation of gene transcription ...
... • 1. Opening specific ion channels through the postsynaptic cell membrane • 2. Activation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) or cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in the neuronal cell • 3. Activation of one or more intracellular enzymes • 4. Activation of gene transcription ...
The nervous system
... as a response to a sensory input. Many threads of research suggest that motor activity exists well before the maturation of the sensory systems, and senses only influence behavior without dictating it. This has brought the conception of the CNS as an autonomous system. ...
... as a response to a sensory input. Many threads of research suggest that motor activity exists well before the maturation of the sensory systems, and senses only influence behavior without dictating it. This has brought the conception of the CNS as an autonomous system. ...
Nociceptin mediated microvascular inflammation during sepsis
... Expansions of a noncoding GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeat in the C9ORF72 gene are the most common genetic defect found to date in motor neurone disease (MND) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). How these expansions cause disease is not known, but may involve both loss-of-function (C9ORF72 haploinsuffici ...
... Expansions of a noncoding GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeat in the C9ORF72 gene are the most common genetic defect found to date in motor neurone disease (MND) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). How these expansions cause disease is not known, but may involve both loss-of-function (C9ORF72 haploinsuffici ...
Lecture Outline
... The “downtime” following an action potential, when a second action potential cannot be initiated, is called the refractory period and sets a limit on the maximum frequency at which action potentials can be generated. o The refractory period is caused by inactivation of Na+ channels, not by a change ...
... The “downtime” following an action potential, when a second action potential cannot be initiated, is called the refractory period and sets a limit on the maximum frequency at which action potentials can be generated. o The refractory period is caused by inactivation of Na+ channels, not by a change ...
PPT - University of Colorado-MCDB
... peptides, lipids, growth factors, and membrane bound ligands. - hydrophilic signals: can not diffuse into a cell and signal by binding to a cell surface receptor - hydrophobic signals: carried by carrier protein in the blood and enter cells ...
... peptides, lipids, growth factors, and membrane bound ligands. - hydrophilic signals: can not diffuse into a cell and signal by binding to a cell surface receptor - hydrophobic signals: carried by carrier protein in the blood and enter cells ...
Neuron Stations
... 1) Cell body: take one long pipe cleaner and roll it into a ball. Inside the cell body is the nucleus, which is the control center of the cell. Q2: Do you know what DNA is, where is it? 2) Axon: take another long pipe cleaner and attach it to the new "cell body" by pushing it through the ball so the ...
... 1) Cell body: take one long pipe cleaner and roll it into a ball. Inside the cell body is the nucleus, which is the control center of the cell. Q2: Do you know what DNA is, where is it? 2) Axon: take another long pipe cleaner and attach it to the new "cell body" by pushing it through the ball so the ...
Neurotransmitters in the retina
... autoradiography, immunology and molecular biology are developing specific stains for neurochemicals, their synthesizing enzymes or the nucleic acids manufacturing these chemicals, so that cells containing these compounds can be marked. Cells stained with horseradish peroxidase conjugated antibodies ...
... autoradiography, immunology and molecular biology are developing specific stains for neurochemicals, their synthesizing enzymes or the nucleic acids manufacturing these chemicals, so that cells containing these compounds can be marked. Cells stained with horseradish peroxidase conjugated antibodies ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.