Catalog # 10-1111 Verapamil HCl Clinically useful L
... 5-[N-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenylethyl)methylamino]-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-isopropylvaleronitrile hydrochloride ...
... 5-[N-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenylethyl)methylamino]-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-isopropylvaleronitrile hydrochloride ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... the vestibule and semicircular canals = the vestibular complex contains two saclike, membranous labyrinth parts—the utricle and the saccule - interconnected through a ...
... the vestibule and semicircular canals = the vestibular complex contains two saclike, membranous labyrinth parts—the utricle and the saccule - interconnected through a ...
The Nervous System - Canton Local Schools
... Neuron: a nerve cell. The basic building block of the nervous system Dendrite: The bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward cell body Axon: the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers. Used to pass messages to other neurons or musc ...
... Neuron: a nerve cell. The basic building block of the nervous system Dendrite: The bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward cell body Axon: the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers. Used to pass messages to other neurons or musc ...
LECTURE18.Olfaction&Taste
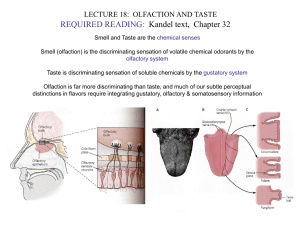
... and are continuously regenerated from basal cells Apical microvilli of taste cells are exposed to saliva through the taste pore Tasty substance is sensed at microvilli by several mechanisms, but always induces depolarization and action potential generation ...
... and are continuously regenerated from basal cells Apical microvilli of taste cells are exposed to saliva through the taste pore Tasty substance is sensed at microvilli by several mechanisms, but always induces depolarization and action potential generation ...
Nervous System - teacherver.com
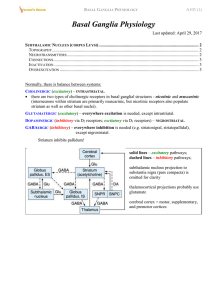
... keeps many neurons from firing controls the preciseness of the signals carried from 1 neuron to the other low level of GABA = anxiety valium increases inhibiting effect of GABA ...
... keeps many neurons from firing controls the preciseness of the signals carried from 1 neuron to the other low level of GABA = anxiety valium increases inhibiting effect of GABA ...
Brain Busters Functions
... This part of the brain receives information from all the senses (except smell) & routes it to the brain regions that deal with vision, ...
... This part of the brain receives information from all the senses (except smell) & routes it to the brain regions that deal with vision, ...
______ 1
... _____________________ 3. The difference in electrical charge across a membrane _____________________ 4. Another name for a receiving neuron _____________________ 5. Another name for a transmitting neuron _____________________ 6. Is generated when a dendrite or cell body is stimulated _______________ ...
... _____________________ 3. The difference in electrical charge across a membrane _____________________ 4. Another name for a receiving neuron _____________________ 5. Another name for a transmitting neuron _____________________ 6. Is generated when a dendrite or cell body is stimulated _______________ ...
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
... The “downtime” following an action potential, when a second action potential cannot be initiated, is called the refractory period and sets a limit on the maximum frequency at which action potentials can be generated. o The refractory period is caused by inactivation of Na+ channels, not by a change ...
... The “downtime” following an action potential, when a second action potential cannot be initiated, is called the refractory period and sets a limit on the maximum frequency at which action potentials can be generated. o The refractory period is caused by inactivation of Na+ channels, not by a change ...
Biosychology_Intro Reading
... known effects, and disorders they are associated with. Acetylcholine: Associated with memory, muscle contractions, and learning. A lack of acetylcholine in the brain is associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Endorphins: Associated with emotions and pain perception. The body releases endorphins in resp ...
... known effects, and disorders they are associated with. Acetylcholine: Associated with memory, muscle contractions, and learning. A lack of acetylcholine in the brain is associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Endorphins: Associated with emotions and pain perception. The body releases endorphins in resp ...
CHAPTER 2 outline
... (b) Enzymatic destruction or breakdown. (5) Each neurotransmitter has a chemically distinct, different shape. For a neurotransmitter to affect a neuron, it must perfectly fit the receptor site. 3. Excitatory and inhibitory messages A neurotransmitter communicates either an excitatory message or an ...
... (b) Enzymatic destruction or breakdown. (5) Each neurotransmitter has a chemically distinct, different shape. For a neurotransmitter to affect a neuron, it must perfectly fit the receptor site. 3. Excitatory and inhibitory messages A neurotransmitter communicates either an excitatory message or an ...
Nervous System - Uplift Education
... 2. Ca+ gates open, allowing Ca+ into the axon. 3. The Ca+ causes vesicles containing neurotransmitters to empty into the synapse ...
... 2. Ca+ gates open, allowing Ca+ into the axon. 3. The Ca+ causes vesicles containing neurotransmitters to empty into the synapse ...
File
... Impulse: electrochemical message carried by nerve cell Receptor: structure that detects stimuli Effector: muscle or gland that responds or reacts to the ...
... Impulse: electrochemical message carried by nerve cell Receptor: structure that detects stimuli Effector: muscle or gland that responds or reacts to the ...
The Nervous System
... • There have been at least 25 different neurotransmitters that have been identified. • Two very well-known ones are acetylcholine (Ach) and norepinephrine (NE). • Once a neurotransmitter has been released into a synaptic cleft and has initiated a response, it is removed from the cleft. • The short e ...
... • There have been at least 25 different neurotransmitters that have been identified. • Two very well-known ones are acetylcholine (Ach) and norepinephrine (NE). • Once a neurotransmitter has been released into a synaptic cleft and has initiated a response, it is removed from the cleft. • The short e ...
CHAPTER 21 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM and SENSES
... The Tactile Corpuscles of Meissner are grouped on the skin of the fingertips, lips, and orifices of the body and the nipples. Only stimulated when touched, meissner corpuscles tells the brain the shape and feel of an object in the hand. They adjust constantly to the environment, which is why the br ...
... The Tactile Corpuscles of Meissner are grouped on the skin of the fingertips, lips, and orifices of the body and the nipples. Only stimulated when touched, meissner corpuscles tells the brain the shape and feel of an object in the hand. They adjust constantly to the environment, which is why the br ...
Too little
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up ...
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up ...
The Nervous System (Chapter 7)
... 22. Outline the steps of the generation of a nerve impulse along unmyelinated fibers using the reading on pages 202 and 203 and also the Figure 7.9 on page 203. ...
... 22. Outline the steps of the generation of a nerve impulse along unmyelinated fibers using the reading on pages 202 and 203 and also the Figure 7.9 on page 203. ...
The Brain and Nervous System
... All or none principle of nerve cells. What we feel is dependent on the amount of neurons that fire. ...
... All or none principle of nerve cells. What we feel is dependent on the amount of neurons that fire. ...
CHAPTER 2 –OUTLINE I. Introduction: Neuroscience and Behavior
... 3. The axon is a single, elongated tube that extends from the cell body and carries information from the neuron to other neurons, glands, and muscles. Axons vary in length from a few thousandths of an inch to about four feet. a. Many axons are surrounded by a myelin sheath, a white, fatty covering t ...
... 3. The axon is a single, elongated tube that extends from the cell body and carries information from the neuron to other neurons, glands, and muscles. Axons vary in length from a few thousandths of an inch to about four feet. a. Many axons are surrounded by a myelin sheath, a white, fatty covering t ...
AP Ch. 9 Nervous System Part 1 Worksheets
... 10. The ______________________ function of the nervous system refers to information being interpreted so that the brain can make decisions. 11. The junction between two communicating neurons is called the ____________________________ 12. Acetylcholine, serotonin and endorphins are all forms of _____ ...
... 10. The ______________________ function of the nervous system refers to information being interpreted so that the brain can make decisions. 11. The junction between two communicating neurons is called the ____________________________ 12. Acetylcholine, serotonin and endorphins are all forms of _____ ...
Exam 3 suggested answers
... autoradiography to visualize the zones, or electrophysiological recording to determine the OD of many neurons. The autoradiography would show an increase in areas receiving input from the non-deprived eye; more cells would be driven by only the non-deprived eye in the electrophys. measurements. (5) ...
... autoradiography to visualize the zones, or electrophysiological recording to determine the OD of many neurons. The autoradiography would show an increase in areas receiving input from the non-deprived eye; more cells would be driven by only the non-deprived eye in the electrophys. measurements. (5) ...
Chapter 17:
... This sudden rise in Ca2+ causes synaptic vesicles to move and merge with the presynaptic membrane, releasing their neurotransmitter molecules into the synapse The binding of the neurotransmitter to receptors in the postsynaptic membrane causes either excitation or inhibition. ...
... This sudden rise in Ca2+ causes synaptic vesicles to move and merge with the presynaptic membrane, releasing their neurotransmitter molecules into the synapse The binding of the neurotransmitter to receptors in the postsynaptic membrane causes either excitation or inhibition. ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.