The First Open International Symposium
... found that insulin/PI 3-kinase pathway is essential for causing starvation-dependent behavioral switching, and it acts in the sensory neuron. Recent findings on the molecular mechanisms of the regulation of the insulin pathway will be briefly described. ...
... found that insulin/PI 3-kinase pathway is essential for causing starvation-dependent behavioral switching, and it acts in the sensory neuron. Recent findings on the molecular mechanisms of the regulation of the insulin pathway will be briefly described. ...
Data/hora: 28/03/2017 12:03:40 Provedor de dados: 17 País: United
... comparison, electrical devices use either digital or analog signals for communication or processing, and the mathematics behind these subjects is well understood. However, in regards to pulse frequency processing devices, there has not yet been a clear and persuasive mathematical model to describe t ...
... comparison, electrical devices use either digital or analog signals for communication or processing, and the mathematics behind these subjects is well understood. However, in regards to pulse frequency processing devices, there has not yet been a clear and persuasive mathematical model to describe t ...
Sympathetic - Perkins Science
... α1– causes vasoconstriction by increasing Ca2+ α2 – they are activated by norepi, but then cause a negative feedback reduction in epi levels (p. 254) clonidine (drug) - α2 receptors in the brain lowers sympathoadrenal system β(beta) -adrenergic receptors stimulate the production of cAMP in the tar ...
... α1– causes vasoconstriction by increasing Ca2+ α2 – they are activated by norepi, but then cause a negative feedback reduction in epi levels (p. 254) clonidine (drug) - α2 receptors in the brain lowers sympathoadrenal system β(beta) -adrenergic receptors stimulate the production of cAMP in the tar ...
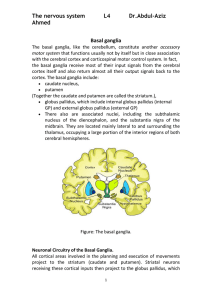
1.In the direct pathway
... 1.the substantia nigra, send Dopamine secreting neuron into the striatum. Dopamine has an excitatory effect upon cells in the striatum that are part of the Direct Pathway. This is via D1 receptors. Dopamine ...
... 1.the substantia nigra, send Dopamine secreting neuron into the striatum. Dopamine has an excitatory effect upon cells in the striatum that are part of the Direct Pathway. This is via D1 receptors. Dopamine ...
review glutamate and gaba receptor signalling in - lópez
... both ionotropic (ligand-gated ion channels) and metabotropic (G protein-coupled) receptors, and are generally associated with neuronal communication in the mature brain. However, before the emergence of their role in neurotransmission in adulthood, they also act to influence earlier developmental ev ...
... both ionotropic (ligand-gated ion channels) and metabotropic (G protein-coupled) receptors, and are generally associated with neuronal communication in the mature brain. However, before the emergence of their role in neurotransmission in adulthood, they also act to influence earlier developmental ev ...
HUMAN ANATOMY
... • Neuroglia comprises nervous system, which consists of 2 departments: • Central Nervous System (CNS) & • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) (p.440, fig.12.1). CNS is presented by 2 subdivisions: • BRAIN, located within the cranium, & • SPINAL CORD (located within vertebral channel) ...
... • Neuroglia comprises nervous system, which consists of 2 departments: • Central Nervous System (CNS) & • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) (p.440, fig.12.1). CNS is presented by 2 subdivisions: • BRAIN, located within the cranium, & • SPINAL CORD (located within vertebral channel) ...
The Nervous System
... • Function of system – Processes information sent by the PNS – Brain- largest organ in nervous system –mission control • cerebrum- stores memories, controls voluntary movement, detects touch, light, sound, sight, odors, taste; judgment • cerebellum- controls body position and movement • medulla- con ...
... • Function of system – Processes information sent by the PNS – Brain- largest organ in nervous system –mission control • cerebrum- stores memories, controls voluntary movement, detects touch, light, sound, sight, odors, taste; judgment • cerebellum- controls body position and movement • medulla- con ...
Nervous System WS (handed out after section exam)
... f. What part of the neuron is usually wrapped in myelin sheath? The myelin sheath is responsible for saltatory conduction / transmission. This is where the electrical impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next node. This increases the speed of the nerve impulse. The speed increases becau ...
... f. What part of the neuron is usually wrapped in myelin sheath? The myelin sheath is responsible for saltatory conduction / transmission. This is where the electrical impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next node. This increases the speed of the nerve impulse. The speed increases becau ...
Biology of the Mind Powerpoint
... All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
Biology of Mind
... All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
Term - k20 learn
... Occurs when sodium ions rush into the cell during an action potential, raising the membrane potential from a very negative value to be more positive. For a short time, the charges on either side of the cell membrane switch, making the inside of the cell membrane positive relative to the outside. ...
... Occurs when sodium ions rush into the cell during an action potential, raising the membrane potential from a very negative value to be more positive. For a short time, the charges on either side of the cell membrane switch, making the inside of the cell membrane positive relative to the outside. ...
abstract - ELSC at
... over the past decade have established circuit models in which dynamical properties can be comprehensively analyzed taking account of each and every AP. In this presentation, I will use such models to examine the relationship of single neuron AP initiation dynamics and a fundamental feature of inform ...
... over the past decade have established circuit models in which dynamical properties can be comprehensively analyzed taking account of each and every AP. In this presentation, I will use such models to examine the relationship of single neuron AP initiation dynamics and a fundamental feature of inform ...
Neuronal Signaling
... - Decreases time to charge the nearby membrane, increasing conduction velocity - Myelin increases the passive conduction distance (remember that larger Rm increases the length constant, lambda) - Myelin decreases the time to charge the membrane by decreasing Cm ...
... - Decreases time to charge the nearby membrane, increasing conduction velocity - Myelin increases the passive conduction distance (remember that larger Rm increases the length constant, lambda) - Myelin decreases the time to charge the membrane by decreasing Cm ...
Nervous System - wondersofscience
... • carries information from the various parts of the body to the brain. It is also the reflex center. – A reflex is a rapid and involuntary reaction to a stimulus – A reflex arc is the path taken by a nerve impulse during a reflex ...
... • carries information from the various parts of the body to the brain. It is also the reflex center. – A reflex is a rapid and involuntary reaction to a stimulus – A reflex arc is the path taken by a nerve impulse during a reflex ...
Unit 3 Notes
... Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Motor neurons: neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands. Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate i ...
... Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Motor neurons: neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands. Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate i ...
File
... m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List the following in order: A. K+ channels open and K+ floods out of cell B. Membrane is polarized (resting potential) C. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles into synaptic cleft D. Na+ channels open and Na+ ...
... m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List the following in order: A. K+ channels open and K+ floods out of cell B. Membrane is polarized (resting potential) C. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles into synaptic cleft D. Na+ channels open and Na+ ...
Androgen Receptor Localization in the Haplochromis burtoni
... eggs. This will let us observe if the yolk (IgY) antibody has a greater (more selective) binding affinity than the serum primary Ab that we have been using thus far. Let’s keep our fingers crossed…… ...
... eggs. This will let us observe if the yolk (IgY) antibody has a greater (more selective) binding affinity than the serum primary Ab that we have been using thus far. Let’s keep our fingers crossed…… ...
Vertebrate Zoology BIOL 322/Nervous System and Brain Complete
... Know parts of reflex arc: (Fig.33.11) receptor --> afferent (= sensory) neuron (goes toward central nervous system) --> central nervous system (where synaptic connections are made between the sensory neurons and the interneurons) --> efferent (= motor) neuron --> effector (e.g., muscles, glands, etc ...
... Know parts of reflex arc: (Fig.33.11) receptor --> afferent (= sensory) neuron (goes toward central nervous system) --> central nervous system (where synaptic connections are made between the sensory neurons and the interneurons) --> efferent (= motor) neuron --> effector (e.g., muscles, glands, etc ...
Chapter 12
... Action potential is an electrical impulse produced by a graded potential that spreads along the surface of an axon to synapse. Synaptic activity releases neurotransmitters at presynaptic membrane and produces graded potentials in postsynaptic membrane Information processing is the response (integrat ...
... Action potential is an electrical impulse produced by a graded potential that spreads along the surface of an axon to synapse. Synaptic activity releases neurotransmitters at presynaptic membrane and produces graded potentials in postsynaptic membrane Information processing is the response (integrat ...
CHAPTER 46 NEURONS AND NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Neurotransmitter Molecules 1. At least 25 different neurotransmitters have been identified. 2. Acetylcholine (Ach) and norepinephrine (NE) are two well-known neurotransmitters. 3. Once a neurotransmitter is released into a synaptic cleft, it initiates a response and is then removed from the cleft. 4 ...
... Neurotransmitter Molecules 1. At least 25 different neurotransmitters have been identified. 2. Acetylcholine (Ach) and norepinephrine (NE) are two well-known neurotransmitters. 3. Once a neurotransmitter is released into a synaptic cleft, it initiates a response and is then removed from the cleft. 4 ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. ...
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.