Chapter 13
... describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram describes an experiment, make sure you understand the experiment by being able to describe it in your own words. It is often helpful to look in other chapters of the book to gai ...
... describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram describes an experiment, make sure you understand the experiment by being able to describe it in your own words. It is often helpful to look in other chapters of the book to gai ...
Nervous System Cells
... • Somatic Sensory Division – carries feedback information to somatic integration centers in the CNS ...
... • Somatic Sensory Division – carries feedback information to somatic integration centers in the CNS ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Topic iQuiz
... Which of the following structures of a reflex arc transmits impulses toward the central nervous system? Receptor ...
... Which of the following structures of a reflex arc transmits impulses toward the central nervous system? Receptor ...
210_Lecture6_motor
... Treatments include medications that suppress the immune system or inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) ...
... Treatments include medications that suppress the immune system or inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) ...
Class
... c. parasympathetic division d. sympathetic division 18. Which part of the neuron has the responsibility for receiving information from other neurons? a. the cell body b. the axon c. the soma d. the dendrites 19. Internal functions such as heartbeat, breathing, and stomach contractions are controlled ...
... c. parasympathetic division d. sympathetic division 18. Which part of the neuron has the responsibility for receiving information from other neurons? a. the cell body b. the axon c. the soma d. the dendrites 19. Internal functions such as heartbeat, breathing, and stomach contractions are controlled ...
Basal Ganglia
... cerebral cortex. They receive information from the frontal cortex about behavior that is being planned for a particular situation. In turn, the basal ganglia affect activity in the frontal cortex through a series of neural projections that ultimately go back up to the same cortical areas from which ...
... cerebral cortex. They receive information from the frontal cortex about behavior that is being planned for a particular situation. In turn, the basal ganglia affect activity in the frontal cortex through a series of neural projections that ultimately go back up to the same cortical areas from which ...
The Nervous System
... synapses, which totals 50 trillion synapses in the infant brain. By the age of 1, this number increases to 15,000 synapses per neuron for a total of 1,000 trillion synapses. Synaptogenesis is the formation of new synapses. When synapses are created to a high degree through new experiences, they allo ...
... synapses, which totals 50 trillion synapses in the infant brain. By the age of 1, this number increases to 15,000 synapses per neuron for a total of 1,000 trillion synapses. Synaptogenesis is the formation of new synapses. When synapses are created to a high degree through new experiences, they allo ...
Lecture 2
... “As the entomologist chasing butterflies of bright colors, my attention was seeking in the garden of gray matter, those cells of delicate and elegant forms, the mysterious butterflies of the soul, whose ...
... “As the entomologist chasing butterflies of bright colors, my attention was seeking in the garden of gray matter, those cells of delicate and elegant forms, the mysterious butterflies of the soul, whose ...
Chapter 11-自律神經及體運動神經系統檔案
... Curare 劍毒 is an extract of a plant (Chondrodendron tomentosum) found in South America When an animal was struck by a curare-laced arrow or dart, it would become paralyzed and eventually die from respiratory failure 呼吸衰竭 The effective component of curare is a compound called tubocurarine, which ...
... Curare 劍毒 is an extract of a plant (Chondrodendron tomentosum) found in South America When an animal was struck by a curare-laced arrow or dart, it would become paralyzed and eventually die from respiratory failure 呼吸衰竭 The effective component of curare is a compound called tubocurarine, which ...
Chapter 11-自律神經及體運動神經系統檔案
... Curare 劍毒 is an extract of a plant (Chondrodendron tomentosum) found in South America When an animal was struck by a curare-laced arrow or dart, it would become paralyzed and eventually die from respiratory failure 呼吸衰竭 ...
... Curare 劍毒 is an extract of a plant (Chondrodendron tomentosum) found in South America When an animal was struck by a curare-laced arrow or dart, it would become paralyzed and eventually die from respiratory failure 呼吸衰竭 ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... • B) Enriched-environment rats showed more stress and aggression. • C) Enriched-environment rats were able to ...
... • B) Enriched-environment rats showed more stress and aggression. • C) Enriched-environment rats were able to ...
Slide ()
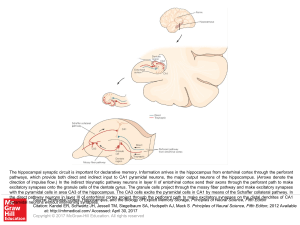
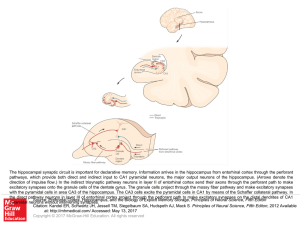
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
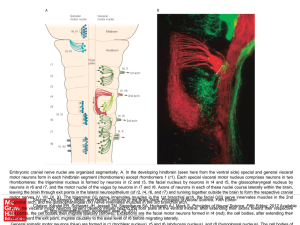
... motor nerves (V, VII, IX, X). The trigeminal (V) nerve innervates muscles in the 1st branchial arch, the facial (VII) nerve innervates muscles in the 2nd Source: The Sensory, Motor, and Reflex Functions of the Brain Stem, Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon branchial arch, and the glossophary ...
... motor nerves (V, VII, IX, X). The trigeminal (V) nerve innervates muscles in the 1st branchial arch, the facial (VII) nerve innervates muscles in the 2nd Source: The Sensory, Motor, and Reflex Functions of the Brain Stem, Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon branchial arch, and the glossophary ...
nervous system physiology 1
... volume control, volume transmission K+ and H+ uptake vs. spatial buffering; Ca waves… ...
... volume control, volume transmission K+ and H+ uptake vs. spatial buffering; Ca waves… ...
Vertebrate Zoology BIOL 322/Nervous System Ch 33 and Brain
... Know parts of reflex arc: (Fig. 33.11, p. 321) receptor --> afferent (= sensory) neuron (goes toward central nervous system) --> central nervous system (where synaptic connections are made between the sensory neurons and the interneurons) --> efferent (= motor) neuron --> effector (e.g., muscles, gl ...
... Know parts of reflex arc: (Fig. 33.11, p. 321) receptor --> afferent (= sensory) neuron (goes toward central nervous system) --> central nervous system (where synaptic connections are made between the sensory neurons and the interneurons) --> efferent (= motor) neuron --> effector (e.g., muscles, gl ...
ATP-Sensitive K+ Channels in the Brain: Sensors of
... energy-demanding seizure during metabolic stress, the ATPsensitive K+ (KATP) channel, the molecule that controls membrane potentials by sensing intracellular ATP levels, may play a pivotal role. In this brief review, recent progress in accord with this hypothesis is discussed, together with other vi ...
... energy-demanding seizure during metabolic stress, the ATPsensitive K+ (KATP) channel, the molecule that controls membrane potentials by sensing intracellular ATP levels, may play a pivotal role. In this brief review, recent progress in accord with this hypothesis is discussed, together with other vi ...
Interneurons and triadic circuitry of the thalamus
... F2 terminal and a relay X-cell appendage, and the F2 terminal contacts the same appendage; thus, three synapses are involved. In other thalamic relays, the main input (e.g. medial lemniscal input to the ventral posterior nucleus or inferior collicular input to the medial geniculate nucleus) replaces ...
... F2 terminal and a relay X-cell appendage, and the F2 terminal contacts the same appendage; thus, three synapses are involved. In other thalamic relays, the main input (e.g. medial lemniscal input to the ventral posterior nucleus or inferior collicular input to the medial geniculate nucleus) replaces ...
Chapter 12
... Nerve impulses carried by VIII cranial nerve (vestibulocochlear nerve) to auditory area in the temporal lobe of the brain ...
... Nerve impulses carried by VIII cranial nerve (vestibulocochlear nerve) to auditory area in the temporal lobe of the brain ...
The Nervous System
... receiving impulses from most of the sensory neurons and directing these impulses to the part of the brain where each will be interpreted. -Screens out less significant stimuli (prevents sensory overload) ...
... receiving impulses from most of the sensory neurons and directing these impulses to the part of the brain where each will be interpreted. -Screens out less significant stimuli (prevents sensory overload) ...
Axia College Material Appendix C Brain Response of Behavior Part I
... commonly referred to as the “little brain”. The brains “relay station” for information is the thalamus. Located beneath the thalamus is the hypothalamus. This is the area of the brain which has immense impact on an individuals’ motivation and emotional responses. Desire for food, drink, and even se ...
... commonly referred to as the “little brain”. The brains “relay station” for information is the thalamus. Located beneath the thalamus is the hypothalamus. This is the area of the brain which has immense impact on an individuals’ motivation and emotional responses. Desire for food, drink, and even se ...
Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium (II) The Nervous System
... It affects nerve cells surrounding brain and spinal cord. The myelin becomes inflamed or damaged and disrupts impulses. Some symptoms are: blurred or double vision, slurred speech, loss of coordination, muscle weakness, tingling or numbness in arms and legs, and seizures. MS attacks occur in episode ...
... It affects nerve cells surrounding brain and spinal cord. The myelin becomes inflamed or damaged and disrupts impulses. Some symptoms are: blurred or double vision, slurred speech, loss of coordination, muscle weakness, tingling or numbness in arms and legs, and seizures. MS attacks occur in episode ...
Vision + Desensitization
... recognizes the activated conformation of the receptor. Activated GRKs phosphorylate (P) intracellular domains of the receptor and are then released. The agonist-activated, GRKphosphorylated receptor binds tightly to an arrestin protein, which desensitizes further G protein activation and couples the ...
... recognizes the activated conformation of the receptor. Activated GRKs phosphorylate (P) intracellular domains of the receptor and are then released. The agonist-activated, GRKphosphorylated receptor binds tightly to an arrestin protein, which desensitizes further G protein activation and couples the ...
Class Notes
... The diencephalon lies above the brain stem and contains the thalamus and hypothalamus. Other portions of the diencephalon are the optic tracts and optic chiasma, the infundibulum (attachment for the pituitary), the posterior pituitary, mammillary bodies, and the pineal gland. The thalamus functions ...
... The diencephalon lies above the brain stem and contains the thalamus and hypothalamus. Other portions of the diencephalon are the optic tracts and optic chiasma, the infundibulum (attachment for the pituitary), the posterior pituitary, mammillary bodies, and the pineal gland. The thalamus functions ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.