consciousness
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): When protons (here brain protons) are placed in a magnetic field, they become capable of receiving and then transmitting electromagnetic energy. The strength of the transmitted energy is proportional to the number of protons in the tissue. Signal strength is modifi ...
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): When protons (here brain protons) are placed in a magnetic field, they become capable of receiving and then transmitting electromagnetic energy. The strength of the transmitted energy is proportional to the number of protons in the tissue. Signal strength is modifi ...
MSdoc, 459KB
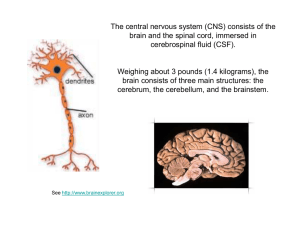
... cranial and spinal nerves and an extensive network of motor and sensory nerve cells – or neurons – interconnecting all parts of the body (see Figure). The brain functions as the main coordinating centre for nervous activity and so controls, directs and integrates all nerve impulses of the human body ...
... cranial and spinal nerves and an extensive network of motor and sensory nerve cells – or neurons – interconnecting all parts of the body (see Figure). The brain functions as the main coordinating centre for nervous activity and so controls, directs and integrates all nerve impulses of the human body ...
Avello_1.4_The_Believer_s_Brain
... The Paradox of Nietzschean Atheism Jason Wakefield, University of Cambridge, England. Review: The Believer's Brain (2014) R.S Donda & K.M Heilman. Psychology Press. Heilman was raised in Brooklyn, New York. He graduated from the University of Virginia School of Medicine in 1963 before studying neuro ...
... The Paradox of Nietzschean Atheism Jason Wakefield, University of Cambridge, England. Review: The Believer's Brain (2014) R.S Donda & K.M Heilman. Psychology Press. Heilman was raised in Brooklyn, New York. He graduated from the University of Virginia School of Medicine in 1963 before studying neuro ...
Chapter 40
... F. Learning involves the storage of information and its retrieval 1. Learning is a long-lasting change in behavior based on experience, and involves both implicit and explicit memory 2. Information processing involves short- and long-term memory a) Short-term memory can hold about 7 pieces of inform ...
... F. Learning involves the storage of information and its retrieval 1. Learning is a long-lasting change in behavior based on experience, and involves both implicit and explicit memory 2. Information processing involves short- and long-term memory a) Short-term memory can hold about 7 pieces of inform ...
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of
... Early investigators of the mammalian brain imagined that the central nervous system (CNS) consisted of a complex interconnected network of neurons that possessed properties essentially identical to those determined by Hodgkin and Huxley for the squid giant axon (i.e., they generated simple action po ...
... Early investigators of the mammalian brain imagined that the central nervous system (CNS) consisted of a complex interconnected network of neurons that possessed properties essentially identical to those determined by Hodgkin and Huxley for the squid giant axon (i.e., they generated simple action po ...
BIOL241NSintro12aJUL2012
... • Synaptic cleft The small gap that separates the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane • Area of terminal containing synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitters ...
... • Synaptic cleft The small gap that separates the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane • Area of terminal containing synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitters ...
Stochastic Modeling the Tripartite Synapse and Applications
... Objective of our current work Recent findings shown that glia cells play an important role in actively supporting and modulating the neuronal information. We focus on a particular element of the neuronal system, the tripartite synapses, extending the concept of synapse to the presence of astrocytes ...
... Objective of our current work Recent findings shown that glia cells play an important role in actively supporting and modulating the neuronal information. We focus on a particular element of the neuronal system, the tripartite synapses, extending the concept of synapse to the presence of astrocytes ...
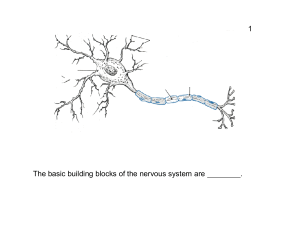
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
Long Term Potentiation
... important in the formation of long term potentiation. Glutamate (also called glutamic acid) is the most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. There are multiple types of glutamate receptors, and glutamate plays a particularly important role in learning and memory. NMDA gl ...
... important in the formation of long term potentiation. Glutamate (also called glutamic acid) is the most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. There are multiple types of glutamate receptors, and glutamate plays a particularly important role in learning and memory. NMDA gl ...
Brain Structure and Function
... • Jeff was not really moved around contrary to today’s treatment where patient’s muscles are moved to prevent atrophy • Four months later Jeff awoke and entered into a semi-coma – He was responsive: blinked once for yes, etc. could not talk – Fell in and out of consciousness ...
... • Jeff was not really moved around contrary to today’s treatment where patient’s muscles are moved to prevent atrophy • Four months later Jeff awoke and entered into a semi-coma – He was responsive: blinked once for yes, etc. could not talk – Fell in and out of consciousness ...
Endocrine System—secrete hormones into body fluids
... 1. Steroid-diffuse into cells and direct protein synthesis ...
... 1. Steroid-diffuse into cells and direct protein synthesis ...
Ch. 35 Nervous System ppt - Jamestown Public Schools
... Neurons - cells that transmit impulses Cell Body - largest part of a neuron, contains the nucleus & most of the cytoplasm, where the metabolic activity of the cell takes place ...
... Neurons - cells that transmit impulses Cell Body - largest part of a neuron, contains the nucleus & most of the cytoplasm, where the metabolic activity of the cell takes place ...
BIOL241NSintro12aJUL2012
... • Synaptic cleft The small gap that separates the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane • Area of terminal containing synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitters ...
... • Synaptic cleft The small gap that separates the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane • Area of terminal containing synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitters ...
Recording Action Potentials from Cockroach Mechanoreceptors
... membrane potential of about -70 mv is recorded. As an action potential passes by the point of the recording, the membrane depolarizes to about +50 mv and then about one millisecond later returns to the resting level. Often, however, a neurophysiologist does not need to know the actual changes in the ...
... membrane potential of about -70 mv is recorded. As an action potential passes by the point of the recording, the membrane depolarizes to about +50 mv and then about one millisecond later returns to the resting level. Often, however, a neurophysiologist does not need to know the actual changes in the ...
Optogenetic Technology and Its In Vivo Applications 4 BRIEF SCIENTIFIC REVIEWS
... ChR2 coupled to enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP) (to visualize the cells) in Rohon-Beard and trigeminal neurons of zebrafish, located in the spinal cord. Illumination with 488 nm light (blue), but not with 680 (red) nm light, triggered a robust escape response. Characteristics of the respo ...
... ChR2 coupled to enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP) (to visualize the cells) in Rohon-Beard and trigeminal neurons of zebrafish, located in the spinal cord. Illumination with 488 nm light (blue), but not with 680 (red) nm light, triggered a robust escape response. Characteristics of the respo ...
Objectives * To get an A grade I need to be able to:
... activate the brain's 'reward system', by increasing the release of the chemical dopamine from neurons in key areas of the brain. Dopamine release occurs after pleasurable experiences, for example after food or exercise. Drugs that artificially increase dopamine release in this way may cause craving ...
... activate the brain's 'reward system', by increasing the release of the chemical dopamine from neurons in key areas of the brain. Dopamine release occurs after pleasurable experiences, for example after food or exercise. Drugs that artificially increase dopamine release in this way may cause craving ...
Ch6 - Unit3Biology
... vesicles (on the end of axons only!) • diffuse across the synapse and attach to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane • stimulate another neuron or effector • last for a very short time only (enzymes produced by muscles tissue inactive the substances for example) Example: acetycholine ...
... vesicles (on the end of axons only!) • diffuse across the synapse and attach to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane • stimulate another neuron or effector • last for a very short time only (enzymes produced by muscles tissue inactive the substances for example) Example: acetycholine ...
CHAPTER 39 NEURONS AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS
... a. Synaptic vesicles store neurotransmitters that diffuse across the synapse. b. When the action potential arrives at the presynaptic axon bulb, synaptic vesicles merge with the presynaptic membrane. c. When vesicles merge with the membrane, neurotransmitters are discharged into the synaptic cleft. ...
... a. Synaptic vesicles store neurotransmitters that diffuse across the synapse. b. When the action potential arrives at the presynaptic axon bulb, synaptic vesicles merge with the presynaptic membrane. c. When vesicles merge with the membrane, neurotransmitters are discharged into the synaptic cleft. ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.