An Overview on the Physiologic Anatomy of the Autonomic Nervous
... Functions of the ANS 9 The two divisions of the ANS are dominant under different conditions. 9 The sympathetic system is activated during emergency “fight-or-flight” reactions and during exercise. 9 The parasympathetic system is predominant during quiet conditions (“rest and digest”). As such, the ...
... Functions of the ANS 9 The two divisions of the ANS are dominant under different conditions. 9 The sympathetic system is activated during emergency “fight-or-flight” reactions and during exercise. 9 The parasympathetic system is predominant during quiet conditions (“rest and digest”). As such, the ...
Locally evoked potentials in slices of the rat nucleus - UvA-DARE
... suppressive action. Washout of Mg2+ from the superfusion medium reversibly enhanced and prolonged the PSP and this effect was blocked by the NMDA receptor antagonist o(-)-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (D-AP-5). The y-aminobutyric acid antagonist picrotoxin(60 #M) enhanced the PS and induced seco ...
... suppressive action. Washout of Mg2+ from the superfusion medium reversibly enhanced and prolonged the PSP and this effect was blocked by the NMDA receptor antagonist o(-)-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (D-AP-5). The y-aminobutyric acid antagonist picrotoxin(60 #M) enhanced the PS and induced seco ...
28. Nervous Systems
... – Each branch ends in a synaptic terminal – A synapse is a site of communication between a synaptic terminal and another cell ...
... – Each branch ends in a synaptic terminal – A synapse is a site of communication between a synaptic terminal and another cell ...
The Language of the Brain
... Neuroscientists do not fully understand how the brain manages to extract meaningful information from all the signaling that goes on within it. The two of us and others, however, have recently made exciting progress by focusing new attention on how the brain can eiciently use the timing of spikes to ...
... Neuroscientists do not fully understand how the brain manages to extract meaningful information from all the signaling that goes on within it. The two of us and others, however, have recently made exciting progress by focusing new attention on how the brain can eiciently use the timing of spikes to ...
Anatomy of the basal ganglia - Gonda Brain Research Center
... • The striatum (caudate - putamen and the core of nucleus accumbens) • The globus pallidus (GP) (lateral and medial) • The subthalamic nucleus (STN) • Substantia nigra (SN) (pars compacta and pars reticulata) and the ventral tegmental area (VTA) ...
... • The striatum (caudate - putamen and the core of nucleus accumbens) • The globus pallidus (GP) (lateral and medial) • The subthalamic nucleus (STN) • Substantia nigra (SN) (pars compacta and pars reticulata) and the ventral tegmental area (VTA) ...
The Nervous System
... Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Pathway of Flow • CSF is produced by the choroid plexus of each ventricle. • CSF flows through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space via the median and lateral apertures. Some CSF flows through the central canal of the spinal cord. • CSF flows through the subarachn ...
... Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Pathway of Flow • CSF is produced by the choroid plexus of each ventricle. • CSF flows through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space via the median and lateral apertures. Some CSF flows through the central canal of the spinal cord. • CSF flows through the subarachn ...
The Elementary Nervous System Revisited1
... systems in higher organisms, the same molecule, manufactured through the same synthetic pathway, serves as an external chemical signal or pheromone in Dictyostelium. The slime mold cAMP receptor appears to belong to the same molecular family as the /Sadrenergic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors ...
... systems in higher organisms, the same molecule, manufactured through the same synthetic pathway, serves as an external chemical signal or pheromone in Dictyostelium. The slime mold cAMP receptor appears to belong to the same molecular family as the /Sadrenergic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors ...
Exam 3: Friday Oct 20
... – Propagate an electrical current, or action potential, along its sarcolemma – Have a rise in intracellular Ca2+ levels, the final trigger for contraction ...
... – Propagate an electrical current, or action potential, along its sarcolemma – Have a rise in intracellular Ca2+ levels, the final trigger for contraction ...
RH Ettinger - Test Bank 1
... 1. Why does a neuron rest at –70 millivolts inside the cell membrane with respect to outside the cell membrane? 2. What are the differences between action potentials and graded potentials? 3. How does an action potential propagate along an unmyelinated axon? 4. How does myelin affect propagation? Wh ...
... 1. Why does a neuron rest at –70 millivolts inside the cell membrane with respect to outside the cell membrane? 2. What are the differences between action potentials and graded potentials? 3. How does an action potential propagate along an unmyelinated axon? 4. How does myelin affect propagation? Wh ...
Duration
... Lowered pain sensitivity. Possibly due to changes in activity of the 5HT fibers that descend into the spinal cord. Withdrawal. No serious withdrawal symptoms. ...
... Lowered pain sensitivity. Possibly due to changes in activity of the 5HT fibers that descend into the spinal cord. Withdrawal. No serious withdrawal symptoms. ...
How Does the Brain Sense Osmolality?
... the detrimental effects of cell swelling or shrinkage on cellular functions. However, if osmoreceptors displayed volume-regulatory increases or decreases in response to changes in extracellular tonicity, this would not allow for an absolute plasma osmolality around which body fluid homeostasis is ma ...
... the detrimental effects of cell swelling or shrinkage on cellular functions. However, if osmoreceptors displayed volume-regulatory increases or decreases in response to changes in extracellular tonicity, this would not allow for an absolute plasma osmolality around which body fluid homeostasis is ma ...
Jan 7, 2015. PASSIVE ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF MEMBRANES
... From example trace given in class; Measure time constant Measure change in membrane potential resulting from a given injection of current Calculate input resistance Calculate total capacitance of cell membrane Estimate diameter of the cell ...
... From example trace given in class; Measure time constant Measure change in membrane potential resulting from a given injection of current Calculate input resistance Calculate total capacitance of cell membrane Estimate diameter of the cell ...
Analyzed by Symptoms and history Diagnosis 1. Walking down a
... 22. Dana is taking Prozac to help control her depression. Prozac works by blocking the reuptake of what neurotransmitter? Is Prozac an agonist or antagonist? ...
... 22. Dana is taking Prozac to help control her depression. Prozac works by blocking the reuptake of what neurotransmitter? Is Prozac an agonist or antagonist? ...
What are the biological mechanisms associated with taste?
... • Discuss important issues that • Does non-western medicine affect health care and society place a greater emphasis on preventative medicine? • Apply the social determinants of health • Could genetic testing help in preventing diseases such as • Meet students from different high blood pressure or di ...
... • Discuss important issues that • Does non-western medicine affect health care and society place a greater emphasis on preventative medicine? • Apply the social determinants of health • Could genetic testing help in preventing diseases such as • Meet students from different high blood pressure or di ...
The Nervous System Notes
... Sensory (Afferent) Division- nerve fibers that carry impulses to the CNS from sensory receptors located throughout body – 2 types 1. somatic sensory fibers- delivering impulses from the skin, skeletal muscles, & joints 2. visceral sensory fibers- transmitting impulses from the visceral organs Motor ...
... Sensory (Afferent) Division- nerve fibers that carry impulses to the CNS from sensory receptors located throughout body – 2 types 1. somatic sensory fibers- delivering impulses from the skin, skeletal muscles, & joints 2. visceral sensory fibers- transmitting impulses from the visceral organs Motor ...
Theoretical Neuroscience: From Single Neuron to Network Dynamics
... – Insert such rules in networks, and study how inputs with prescribed statistics shape network attractor landscape – Study maximal storage capacity of the network, with different types of attractors – Learning rules that are able to reach maximal capacity? ...
... – Insert such rules in networks, and study how inputs with prescribed statistics shape network attractor landscape – Study maximal storage capacity of the network, with different types of attractors – Learning rules that are able to reach maximal capacity? ...
Spinal cord worksheet
... 2.A simple, automatic response that involved few neurons__________________ 3.A chemical that carries an impulse across a synapse__________________ 4.A term that describes the parasympathetic portion of the autonomic nervous system, based on where it originates_____________________ 5.A term that mean ...
... 2.A simple, automatic response that involved few neurons__________________ 3.A chemical that carries an impulse across a synapse__________________ 4.A term that describes the parasympathetic portion of the autonomic nervous system, based on where it originates_____________________ 5.A term that mean ...
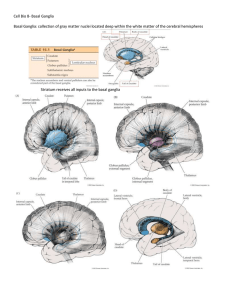
Cell Bio 8- Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia: collection of gray matter
... Patients with basal ganglia lesions can have either hypokinetic or hyperkinetic movement disorders Parkinson’s disease (hypokinetic): rigidity, slowness, and marked difficulty initiating movements Huntington’s disease (hyperkinetic): uncontrolled involuntary movements produce a random pattern of jer ...
... Patients with basal ganglia lesions can have either hypokinetic or hyperkinetic movement disorders Parkinson’s disease (hypokinetic): rigidity, slowness, and marked difficulty initiating movements Huntington’s disease (hyperkinetic): uncontrolled involuntary movements produce a random pattern of jer ...
Drosophila GABA, short neuropeptide F and their receptors
... cells express receptors to neuropeptide F (NPF) and were demonstrated to be under control of NPF (Krashes et al., 2007). 1.1.3. Other neurons and circuits of interest Gustatory and olfactory inputs signal about presence if food and about food quality. However, in order to monitor nutritional needs a ...
... cells express receptors to neuropeptide F (NPF) and were demonstrated to be under control of NPF (Krashes et al., 2007). 1.1.3. Other neurons and circuits of interest Gustatory and olfactory inputs signal about presence if food and about food quality. However, in order to monitor nutritional needs a ...
Loss of orexin/NARP neurons in human narcolepsy
... mRNA, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of ORX are often reduced in patients with cataplexy. Mice and dogs lacking ORX or ORX receptors display narcolepsy-like symptoms similar to those observed in people. Further, mice and rats with an engineered loss of ORX neurons have a nearly identical narcolepsy ...
... mRNA, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of ORX are often reduced in patients with cataplexy. Mice and dogs lacking ORX or ORX receptors display narcolepsy-like symptoms similar to those observed in people. Further, mice and rats with an engineered loss of ORX neurons have a nearly identical narcolepsy ...
Team 1
... According to the University of Maryland Medicine (UMM) Parkinson’s disease (PD) belongs to a group of conditions called motor system disorders which are the result of the loss of dopamine producing brain cells. It is a slowly progressing degenerative disease that is usually associated with the follo ...
... According to the University of Maryland Medicine (UMM) Parkinson’s disease (PD) belongs to a group of conditions called motor system disorders which are the result of the loss of dopamine producing brain cells. It is a slowly progressing degenerative disease that is usually associated with the follo ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.