Chapter 35 The Nervous System
... 3. dendrites- carries impulses toward the cell body. 4. axon- carries impulses away from the cell body. 5. myelin sheath- covers part of some axons. 6. synapse – at the end of the axon E. Nerve Impulse- an electrical impulse conducted along a nerve fiber. 1. resting potential- the electrical charge ...
... 3. dendrites- carries impulses toward the cell body. 4. axon- carries impulses away from the cell body. 5. myelin sheath- covers part of some axons. 6. synapse – at the end of the axon E. Nerve Impulse- an electrical impulse conducted along a nerve fiber. 1. resting potential- the electrical charge ...
Appendix 4 Mathematical properties of the state-action
... action at as target output. At each time step t of the sequence, the SAANN is updated using the newwinner-take-all rule: a previously unused neuron i is set to the “on” state, while all other neurons are set to the “off” state. The connections from the STM to the winner neuron are updated through t ...
... action at as target output. At each time step t of the sequence, the SAANN is updated using the newwinner-take-all rule: a previously unused neuron i is set to the “on” state, while all other neurons are set to the “off” state. The connections from the STM to the winner neuron are updated through t ...
I. The Nervous System
... 3. dendrites- carries impulses toward the cell body. 4. axon- carries impulses away from the cell body. 5. myelin sheath- covers part of some axons. 6. synapse – at the end of the axon E. Nerve Impulse- an electrical impulse conducted along a nerve fiber. 1. resting potential- the electrical charge ...
... 3. dendrites- carries impulses toward the cell body. 4. axon- carries impulses away from the cell body. 5. myelin sheath- covers part of some axons. 6. synapse – at the end of the axon E. Nerve Impulse- an electrical impulse conducted along a nerve fiber. 1. resting potential- the electrical charge ...
Local Anesthetics
... Local anesthetics work in general by binding to sodium channel receptors inside the cell and thereby inhibiting action potentials in a given axon. They work the best when the axon is firing. The Cell membrane consists of ion pumps, most notably the Na/K pump that create a negative 70mV resting poten ...
... Local anesthetics work in general by binding to sodium channel receptors inside the cell and thereby inhibiting action potentials in a given axon. They work the best when the axon is firing. The Cell membrane consists of ion pumps, most notably the Na/K pump that create a negative 70mV resting poten ...
Option E - OoCities
... sound, pressure of gravity. Example, hair cells in the inner ear send nerve impulses to the brain when sounds make them vibrate. Different hair cells respond to different frequencies of sound. Chemoreceptors - perceives chemical substances such as when nerve cells in the nostrils send impulses to th ...
... sound, pressure of gravity. Example, hair cells in the inner ear send nerve impulses to the brain when sounds make them vibrate. Different hair cells respond to different frequencies of sound. Chemoreceptors - perceives chemical substances such as when nerve cells in the nostrils send impulses to th ...
V036-1 - SignalChem
... and activation of SMAD1, SMAD2 and SMAD3, which form complexes with SMAD4 that accumulate in the nucleus and regulate transcription of target genes. SMAD signaling is negatively regulated by inhibitory SMADs and ubiqui ubiquitinmediated processes and proteasomal degradation of SMADs depend on the di ...
... and activation of SMAD1, SMAD2 and SMAD3, which form complexes with SMAD4 that accumulate in the nucleus and regulate transcription of target genes. SMAD signaling is negatively regulated by inhibitory SMADs and ubiqui ubiquitinmediated processes and proteasomal degradation of SMADs depend on the di ...
Neurology-Movement Disorders
... i. Consists of: caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, substantia nigra (form extra pyramidal system) 1. Involved in involuntary (automatic) movements in terms of posture and tone 2. Most movement disorder are disorders of this tract ii. 2 primary neurotransmitters in the brain are dopamine and ...
... i. Consists of: caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, substantia nigra (form extra pyramidal system) 1. Involved in involuntary (automatic) movements in terms of posture and tone 2. Most movement disorder are disorders of this tract ii. 2 primary neurotransmitters in the brain are dopamine and ...
Pontine Respiratory Center
... then inhibits the apneustic centre thus switching off the inspiration . • This is a protective mechanism preventing excess inflation of the lungs. The threshold for this reflex is tidal volume more than 1.5 litres(T.V.≥1.5l) ...
... then inhibits the apneustic centre thus switching off the inspiration . • This is a protective mechanism preventing excess inflation of the lungs. The threshold for this reflex is tidal volume more than 1.5 litres(T.V.≥1.5l) ...
ascendant cerebral 5-hydroxytryptamine
... Dowdall, R. M. Facino & V. P. Whittaker, unpublished work) that the vesicles contain not more than four main protein components, three in the membrane and the fourth, accounting for over 50 % of the total protein, in the core. After dialysis and freeze-drying, the core protein (vesiculin) is recover ...
... Dowdall, R. M. Facino & V. P. Whittaker, unpublished work) that the vesicles contain not more than four main protein components, three in the membrane and the fourth, accounting for over 50 % of the total protein, in the core. After dialysis and freeze-drying, the core protein (vesiculin) is recover ...
Structural Classification of the Nervous System
... The entry of calcium into the axon terminal causes porelike openings to form, releasing the transmitter ...
... The entry of calcium into the axon terminal causes porelike openings to form, releasing the transmitter ...
2013 Action Potential Modeling in PYTHON
... electrochemical equilibrium, this is called the resting membrane potential of the cell. This membrane potential represents a form of stored energy, and can be used to do work. Excitable cells such as neurons and muscle cells use the membrane potential to help initiate and propagate electrical signal ...
... electrochemical equilibrium, this is called the resting membrane potential of the cell. This membrane potential represents a form of stored energy, and can be used to do work. Excitable cells such as neurons and muscle cells use the membrane potential to help initiate and propagate electrical signal ...
Functions of the Nervous System Functions of the
... The entry of calcium into the axon terminal causes porelike openings to form, releasing the transmitter ...
... The entry of calcium into the axon terminal causes porelike openings to form, releasing the transmitter ...
Snímek 1
... progressive loss of neurons or their systems can result in dementia and severe motor impairment Dementia: memory and cognitive impairment with preserved normal level of consciousness ...
... progressive loss of neurons or their systems can result in dementia and severe motor impairment Dementia: memory and cognitive impairment with preserved normal level of consciousness ...
Initiation of the arousal response
... effects are common. The following analysis is neither exhaustive nor altogether precise, since arcane technical details that would add discriminatory levels of information have been omitted. The brain systems or axes most discussed in this context are those regulating arousal, memory, emotion, moti ...
... effects are common. The following analysis is neither exhaustive nor altogether precise, since arcane technical details that would add discriminatory levels of information have been omitted. The brain systems or axes most discussed in this context are those regulating arousal, memory, emotion, moti ...
Memmler’s The Human Body in Health and Disease 11th edition
... Membrane potential reverses, generates electrical charge (action potential) ...
... Membrane potential reverses, generates electrical charge (action potential) ...
Appendix Basics of the Nervous System
... of a neuron. The additional features of a neuron that are important to note include the dendrites [to glossary], soma [to glossary], axon [to glossary] and terminals [to glossary]. The dendrites receive information from other neurons. Their function will described below when the synapse is discussed ...
... of a neuron. The additional features of a neuron that are important to note include the dendrites [to glossary], soma [to glossary], axon [to glossary] and terminals [to glossary]. The dendrites receive information from other neurons. Their function will described below when the synapse is discussed ...
chapter2
... and white. 1. click on print, when the print dialog box opens look to the lower left, for the menu called "print what". 2. use the mouse to select "handouts" 3. just below that menu is another menu called "Color/grayscale". Use the mouse to select "pure black and white". 4. just to the right of the ...
... and white. 1. click on print, when the print dialog box opens look to the lower left, for the menu called "print what". 2. use the mouse to select "handouts" 3. just below that menu is another menu called "Color/grayscale". Use the mouse to select "pure black and white". 4. just to the right of the ...
The Role of Environmental Estrogens on Human Lung
... environmental estrogens could stimulate cellular proliferation in a similar manner. Treatment of a femalederived adenocarcinoma line, H1793, for 4 days with nanomolar concentrations of cadmium chloride or sodium arsenate induced cellular proliferation similar to that seen for estradiol. Furthermore, ...
... environmental estrogens could stimulate cellular proliferation in a similar manner. Treatment of a femalederived adenocarcinoma line, H1793, for 4 days with nanomolar concentrations of cadmium chloride or sodium arsenate induced cellular proliferation similar to that seen for estradiol. Furthermore, ...
Slide ()
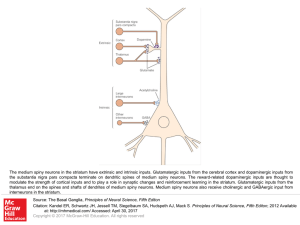
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
Scoring Rubric
... Neurons transmit electrical impulses. The myelination of nerve fibers allows for salutatory conduction. Neurons pump sodium and potassium ions across their membranes to generate a resting potential. An action potential consists of depolarization and repolarization of the neuron. Nerve impulses are a ...
... Neurons transmit electrical impulses. The myelination of nerve fibers allows for salutatory conduction. Neurons pump sodium and potassium ions across their membranes to generate a resting potential. An action potential consists of depolarization and repolarization of the neuron. Nerve impulses are a ...
Dr. Ghassan The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): After studying
... The long postganglionic neurons originating in the ganglion chain then travel outward and terminate on the effector tissues. This divergence of the preganglionic neuron results in coordinated sympathetic stimulation to tissues throughout the body. The concurrent stimulation of many organs and tissue ...
... The long postganglionic neurons originating in the ganglion chain then travel outward and terminate on the effector tissues. This divergence of the preganglionic neuron results in coordinated sympathetic stimulation to tissues throughout the body. The concurrent stimulation of many organs and tissue ...
Uncaging Compunds: - Florida State University
... – Action potentials (Aps) propegate though the axonal arbor and where axons and dendrites overlap in the neuropil a synapse sometimes forms, and synaptic transmission occurs when APs reaches the synapse. – Action potentials invade the presynaptic terminal causing glutamate to be released and then to ...
... – Action potentials (Aps) propegate though the axonal arbor and where axons and dendrites overlap in the neuropil a synapse sometimes forms, and synaptic transmission occurs when APs reaches the synapse. – Action potentials invade the presynaptic terminal causing glutamate to be released and then to ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.