Basal Ganglia and Associated Pathways
... disorders. As output from the basal ganglia goes to the ipsilateral cerebral cortex, movement disorders occur on the contralateral side of the body to the side of basal ganglia damage. Such disorders can usually be differentiated from other motor disorders, such as the irregular uncoordinated moveme ...
... disorders. As output from the basal ganglia goes to the ipsilateral cerebral cortex, movement disorders occur on the contralateral side of the body to the side of basal ganglia damage. Such disorders can usually be differentiated from other motor disorders, such as the irregular uncoordinated moveme ...
Part 1
... Physiology of Smell • Olfactory receptors respond to several different odor-causing chemicals – You can smell about 10,000 smells ...
... Physiology of Smell • Olfactory receptors respond to several different odor-causing chemicals – You can smell about 10,000 smells ...
nitz - UCSD Cognitive Science
... given that different hippocampal neurons bear different place fields, the firing rates of those neurons at any given time can be used to predict the animal’s position in the environment for a set of neurons, the firing rates across the full set describe the ‘pattern’ of activity across the full popu ...
... given that different hippocampal neurons bear different place fields, the firing rates of those neurons at any given time can be used to predict the animal’s position in the environment for a set of neurons, the firing rates across the full set describe the ‘pattern’ of activity across the full popu ...
14.1-NervousMusculo-Skeletal-System
... The gap between the neurons is called the synapse. This is where an electrical signal is passed from an axon of one neuron to a dendrite of another neuron. The signals are passed via neurotransmitters (serotonin, for example), which once released into the synapse, they stimulate a new electrical sig ...
... The gap between the neurons is called the synapse. This is where an electrical signal is passed from an axon of one neuron to a dendrite of another neuron. The signals are passed via neurotransmitters (serotonin, for example), which once released into the synapse, they stimulate a new electrical sig ...
Optical controlling reveals time-dependent roles for adult
... The adult hippocampus continues to give rise to several thousand new dentate granule cells everyday. Studies using global perturbation or ablation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis has revealed deficits in some forms of hippocampal memory. ...
... The adult hippocampus continues to give rise to several thousand new dentate granule cells everyday. Studies using global perturbation or ablation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis has revealed deficits in some forms of hippocampal memory. ...
nervous system
... The brain is one of the few organs that can only use glucose to get ATP as its energy source. Therefore, without some sugar in our bloodstream, the brain will die. That’s one reason why proper nutrition is so important. By the way, geniuses have the same size brain as everyone else; they are just mo ...
... The brain is one of the few organs that can only use glucose to get ATP as its energy source. Therefore, without some sugar in our bloodstream, the brain will die. That’s one reason why proper nutrition is so important. By the way, geniuses have the same size brain as everyone else; they are just mo ...
Anatomical and molecular analyses used to
... functions that are not consciously directed such as digestion and reproduction, and has historically been divided into two main arms, parasympathetic and sympathetic—the first is generally associated with reactions to circumstances, such as instigating the processes involved in the fight-or-flight r ...
... functions that are not consciously directed such as digestion and reproduction, and has historically been divided into two main arms, parasympathetic and sympathetic—the first is generally associated with reactions to circumstances, such as instigating the processes involved in the fight-or-flight r ...
Document
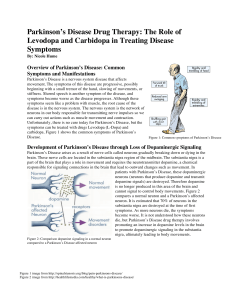
... Only 1-3% of oral L-Dopa reaches the brain before it is metabolized to another substance that is neither a dopamine precursor nor cross the blood-brain barrier, which means that when taking L-Dopa alone, only a small percentage of the drug taken is effectively alleviating symptoms of Parkinson’s Dis ...
... Only 1-3% of oral L-Dopa reaches the brain before it is metabolized to another substance that is neither a dopamine precursor nor cross the blood-brain barrier, which means that when taking L-Dopa alone, only a small percentage of the drug taken is effectively alleviating symptoms of Parkinson’s Dis ...
投影片 1
... Several feature categories were systematically tested in this study. * First, individual spectral power from 30 scalp electrodes were used as the features, including Fp1, Fp2, F7, F3, Fz, F4, F8, FT7, FC3, FCz, FC4, FT8, T7, C3, Cz, C4, T8, TP7, CP3, CPz, CP4, TP8, P7, P3, Pz, P4, P8, O1, Oz, and O2 ...
... Several feature categories were systematically tested in this study. * First, individual spectral power from 30 scalp electrodes were used as the features, including Fp1, Fp2, F7, F3, Fz, F4, F8, FT7, FC3, FCz, FC4, FT8, T7, C3, Cz, C4, T8, TP7, CP3, CPz, CP4, TP8, P7, P3, Pz, P4, P8, O1, Oz, and O2 ...
Target-cell-specific concentration of a metabotropic glutamate
... TilE probability of synaptic neurotransmitter release from nerve terminals is regulated by presynaptic receptors responding to transmitters released fro m the same nerve terminal or from terminals of other neurons. The release of glutamate, the major excitatory neurotransmitter, is suppressed by pre ...
... TilE probability of synaptic neurotransmitter release from nerve terminals is regulated by presynaptic receptors responding to transmitters released fro m the same nerve terminal or from terminals of other neurons. The release of glutamate, the major excitatory neurotransmitter, is suppressed by pre ...
Chapter Two
... The role of the nervous system in disease and behavior The Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal cord The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Somatic and autonomic branches ...
... The role of the nervous system in disease and behavior The Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal cord The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Somatic and autonomic branches ...
Untitled
... recognition, and how this has evolved from the glutamate-recognition properties of iGluRs. I have investigated IRs LBD structure in silico by comprehensive protein modeling. This analysis combined with evolutionary-guided structure function studies of IR75a and IR75b, activated by one to six carbon ...
... recognition, and how this has evolved from the glutamate-recognition properties of iGluRs. I have investigated IRs LBD structure in silico by comprehensive protein modeling. This analysis combined with evolutionary-guided structure function studies of IR75a and IR75b, activated by one to six carbon ...
Nerves and Special Senses
... – Fewer positive ions are inside the cell than outside the cell • Depolarization – a stimulus depolarizes the neuron’s membrane • A deploarized membrane allows sodium (Na+) to flow inside the membrane • The exchange of ions initiates an action potential in the neuron Figure 7.9a–c ...
... – Fewer positive ions are inside the cell than outside the cell • Depolarization – a stimulus depolarizes the neuron’s membrane • A deploarized membrane allows sodium (Na+) to flow inside the membrane • The exchange of ions initiates an action potential in the neuron Figure 7.9a–c ...
Alterations in Neurons of the Brainstem Due to Administration of
... Abstract: A Quantitative Histopathology study on rats’ brainstem was used to analyze morphological alterations in the neurons and glial cells of rats that received inhaled tetrahydrocanabinol for 4, 8 and 12 weeks. Puffing of smoke was performed with the use of a Hamilton syringe delivering 100ml pu ...
... Abstract: A Quantitative Histopathology study on rats’ brainstem was used to analyze morphological alterations in the neurons and glial cells of rats that received inhaled tetrahydrocanabinol for 4, 8 and 12 weeks. Puffing of smoke was performed with the use of a Hamilton syringe delivering 100ml pu ...
How the Brain Pays Attention
... the next, fundamental question: What controls the synchronous activity in the brain’s visual system? To explore this question, we first used human subjects and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scanners to pinpoint the areas of the brain involved in visual attention and, likewise, where t ...
... the next, fundamental question: What controls the synchronous activity in the brain’s visual system? To explore this question, we first used human subjects and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scanners to pinpoint the areas of the brain involved in visual attention and, likewise, where t ...
Your Body Is Nothing Without A Brain
... When neurons are damaged or destroyed, they may be able to regenerate or repair themselves. Since they generate electrical signals called action potentials that provide all the motor information described above, it is important for every person to reduce the risk of damaging or destroying any portio ...
... When neurons are damaged or destroyed, they may be able to regenerate or repair themselves. Since they generate electrical signals called action potentials that provide all the motor information described above, it is important for every person to reduce the risk of damaging or destroying any portio ...
CH 8-9 BS and CH 10 MT
... Conscious: alert Syncope: fainting Lethargy: lowered level of consciousness, listlessness, drowsiness, and apathy Coma : loss of consciousness Delirium: associated with high fever, sudden onset where patient is confused, disoriented, and unable to think clearly Dementia: slow, progressive decline in ...
... Conscious: alert Syncope: fainting Lethargy: lowered level of consciousness, listlessness, drowsiness, and apathy Coma : loss of consciousness Delirium: associated with high fever, sudden onset where patient is confused, disoriented, and unable to think clearly Dementia: slow, progressive decline in ...
Brain lateralisation: a question of spatial frequency?
... When a neuron is activated, current flows from the cell body to the axon terminal To be registered by electrodes on the scalp many neurons would need to fire at the same time, which is unlikely given that action potentials lasts around 1msec No dipole created ...
... When a neuron is activated, current flows from the cell body to the axon terminal To be registered by electrodes on the scalp many neurons would need to fire at the same time, which is unlikely given that action potentials lasts around 1msec No dipole created ...
File
... • Most responses are controlled by the brain. • However, a reflex is controlled by the spinal cord. • A reflex is a rapid, involuntary response to a stimulus. • An example, if you touch a really hot object with your hand. The impulse is sent to the spinal cord immediately. The spinal cord responds b ...
... • Most responses are controlled by the brain. • However, a reflex is controlled by the spinal cord. • A reflex is a rapid, involuntary response to a stimulus. • An example, if you touch a really hot object with your hand. The impulse is sent to the spinal cord immediately. The spinal cord responds b ...
The Nervous System How your body responds to a stimulus
... Each second, your body fires off about five trillion nerve impulses. • Your emotions, decisions, and physical actions all happen through nerve impulses traveling through neurons in your brain, spinal cord and nerves. • A single neuron can have up to ten thousand dendrites connecting to other neurons ...
... Each second, your body fires off about five trillion nerve impulses. • Your emotions, decisions, and physical actions all happen through nerve impulses traveling through neurons in your brain, spinal cord and nerves. • A single neuron can have up to ten thousand dendrites connecting to other neurons ...
Anatomy of Brain Functions
... of the spine beginning at the medulla oblongata of the brain on its superior end and continuing inferiorly to the lumbar region of the spine. Nerves-Extending from the left and right sides of the spinal cord are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. The spinal nerves are mixed nerves that carry both sensory an ...
... of the spine beginning at the medulla oblongata of the brain on its superior end and continuing inferiorly to the lumbar region of the spine. Nerves-Extending from the left and right sides of the spinal cord are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. The spinal nerves are mixed nerves that carry both sensory an ...
NervousSystemPPT
... is absorbed back into the bloodstream, rinsing the metabolic waste from the central nervous system through the blood–brain barrier. This allows for homeostatic regulation of the distribution of neuroendocrine factors, to which slight changes can cause problems or damage to the nervous system. For ex ...
... is absorbed back into the bloodstream, rinsing the metabolic waste from the central nervous system through the blood–brain barrier. This allows for homeostatic regulation of the distribution of neuroendocrine factors, to which slight changes can cause problems or damage to the nervous system. For ex ...
Elements of the nervous system
... chemical compounds released from vesicles transfer the information between them ...
... chemical compounds released from vesicles transfer the information between them ...
In The Name of Allah The Most Beneficent The
... due to movement of ions across the membrane of neurons Mainly due to movement of Na and K ions Inside the cell: more K and less Na Outside the cell: less K and more Na Inside of the cell is negative with respect to outside of the cells due to larger size of the K ions as compared Na ions ...
... due to movement of ions across the membrane of neurons Mainly due to movement of Na and K ions Inside the cell: more K and less Na Outside the cell: less K and more Na Inside of the cell is negative with respect to outside of the cells due to larger size of the K ions as compared Na ions ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.