Review Book Topic D: Evolution - wfs
... more difficult than gathering pant foods, so natural selection may have favored hominids with larger brains and greater intelligence. 20. The large brains of Homo sapiens and other species of Homo allow much to be learned in childhood and adulthood. 21. Many kinds of behavior are passed on from one ...
... more difficult than gathering pant foods, so natural selection may have favored hominids with larger brains and greater intelligence. 20. The large brains of Homo sapiens and other species of Homo allow much to be learned in childhood and adulthood. 21. Many kinds of behavior are passed on from one ...
Unit 1: Motivation, Emotion and Stress - Ms. Anderson
... Specific need or desire, such as hunger, thirst, or achievement, that prompts goal-directed behavior ...
... Specific need or desire, such as hunger, thirst, or achievement, that prompts goal-directed behavior ...
Chapter 1
... Cognitive Psychology – Experimental research on mental processes or cognition Modern Perspective and the Eclectic Approach ...
... Cognitive Psychology – Experimental research on mental processes or cognition Modern Perspective and the Eclectic Approach ...
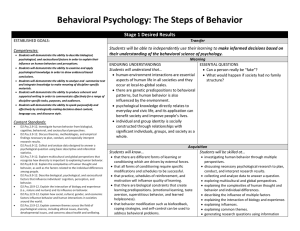
BEHAVIORAL PSYCH The Steps of Behavior
... • human-environment interactions are essential • What would happen if society had no family aspects of human life in all societies and they structure? occur at local-to-global scales. • there are genetic predispositions to behavioral patterns, but human behavior is also influenced by the environment ...
... • human-environment interactions are essential • What would happen if society had no family aspects of human life in all societies and they structure? occur at local-to-global scales. • there are genetic predispositions to behavioral patterns, but human behavior is also influenced by the environment ...
Learning
... Variable-ratio: after random number of responses Fixed-interval: Fixed interval: after a set time interval Variable-interval: after random time intervals ...
... Variable-ratio: after random number of responses Fixed-interval: Fixed interval: after a set time interval Variable-interval: after random time intervals ...
Learning
... - parent gives an order - child does not comply - parent spend much time arguing and explaining - child is receiving extra attention ...
... - parent gives an order - child does not comply - parent spend much time arguing and explaining - child is receiving extra attention ...
Psychology 155: Personality Study Guide 2 Chapter 5: Biological
... 4. Biological Determinism: The belief that an individual's personality is completely determined by biological factors (and especially by genetic factors). 5. Drugs: tranquilizers, sleeping pills, antidepressants, cocaine can have both short and long term effects on personality; Psychopharmacology Tr ...
... 4. Biological Determinism: The belief that an individual's personality is completely determined by biological factors (and especially by genetic factors). 5. Drugs: tranquilizers, sleeping pills, antidepressants, cocaine can have both short and long term effects on personality; Psychopharmacology Tr ...
A Short History of Psychology
... Origins Continued… • During Renaissance people began to experiment and observe results • Rene Descartes first to pose dualismidea that a link existed between the mind and body – Nativism- is the view that certain skills or abilities are 'native' or hard wired into the brain at birth. ...
... Origins Continued… • During Renaissance people began to experiment and observe results • Rene Descartes first to pose dualismidea that a link existed between the mind and body – Nativism- is the view that certain skills or abilities are 'native' or hard wired into the brain at birth. ...
Behavioral
... Behavioral: Dennis Rodman’s father and grandfather were both cross dressers and frequently dyed their hair. Dennis observed this throughout his life and is now imitating the same behavior. Cognitive: Dennis Rodman interprets his role in the NBA as needing to create attention for his team. As a resul ...
... Behavioral: Dennis Rodman’s father and grandfather were both cross dressers and frequently dyed their hair. Dennis observed this throughout his life and is now imitating the same behavior. Cognitive: Dennis Rodman interprets his role in the NBA as needing to create attention for his team. As a resul ...
Sample text for translation quality evaluation
... observe. The human development approach tends to focus on functionings rather than abilities because of its major concern with assessing progress, since functionings can be observed and measured. It is much more difficult to measure capabilities, although there have been a number of attempts, both t ...
... observe. The human development approach tends to focus on functionings rather than abilities because of its major concern with assessing progress, since functionings can be observed and measured. It is much more difficult to measure capabilities, although there have been a number of attempts, both t ...
Behavioral modernity

Behavioral modernity is a suite of behavioral and cognitive traits that distinguishes current Homo sapiens from anatomically modern humans, hominins, and other primates. Although often debated, most scholars agree that modern human behavior can be characterized by abstract thinking, planning depth, symbolic behavior (e.g. art, ornamentation, music), exploitation of large game, blade technology, among others. Underlying these behaviors and technological innovations are cognitive and cultural foundations that have been documented experimentally and ethnographically. Some of these human universal patterns are cumulative cultural adaptation, social norms, language, cooperative breeding, and extensive help and cooperation beyond close kin. These traits have been viewed as largely responsible for the human replacement of Neanderthals in Western Europe, along with the climatic conditions of the Last Glacial Maximum, and the peopling of the rest of the world.Arising from differences in the archaeological record, a debate continues as to whether anatomically modern humans were behaviorally modern as well. There are many theories on the evolution of behavioral modernity. These generally fall into two camps: gradualist and cognitive approaches. The Later Upper Paleolithic Model refers to the idea that modern human behavior arose through cognitive, genetic changes abruptly around 40–50,000 years ago. Other models focus on how modern human behavior may have arisen through gradual steps; the archaeological signatures of such behavior only appearing through demographic or subsistence-based changes.