Theories of Personality 5th Edition
... obstacles to a scientific study of human behavior • Therapist molds desirable behavior by reinforcing slightly improved changes in behavior • Behavior therapists play an active role in the treatment process, using behavior modification techniques and pointing out the positive consequences of some be ...
... obstacles to a scientific study of human behavior • Therapist molds desirable behavior by reinforcing slightly improved changes in behavior • Behavior therapists play an active role in the treatment process, using behavior modification techniques and pointing out the positive consequences of some be ...
Applied Behavior Analysis Vocabulary Antecedent stimulus
... following a response, which increases the future rate and/or probability of the response Punisher – a consequent stimulus that decreases the future rate and/or probability of the behavior Reinforcer – a consequent stimulus that increases or maintains the future rate and/or probability of occurrence ...
... following a response, which increases the future rate and/or probability of the response Punisher – a consequent stimulus that decreases the future rate and/or probability of the behavior Reinforcer – a consequent stimulus that increases or maintains the future rate and/or probability of occurrence ...
Behavior The way an organism responds to stimuli in its
... Other behaviors keyed to tidal, lunar, and other external cycles Biological Clock - an internal time-keeper that governs cycling of behavior many behaviors are repeated with a regular cycle even when deprived of external cues but they drift from the external cycle clock cycle can be reset by exposur ...
... Other behaviors keyed to tidal, lunar, and other external cycles Biological Clock - an internal time-keeper that governs cycling of behavior many behaviors are repeated with a regular cycle even when deprived of external cues but they drift from the external cycle clock cycle can be reset by exposur ...
Behavior The way an organism responds to stimuli in its
... Other behaviors keyed to tidal, lunar, and other external cycles Biological Clock - an internal time-keeper that governs cycling of behavior many behaviors are repeated with a regular cycle even when deprived of external cues but they drift from the external cycle clock cycle can be reset by exposur ...
... Other behaviors keyed to tidal, lunar, and other external cycles Biological Clock - an internal time-keeper that governs cycling of behavior many behaviors are repeated with a regular cycle even when deprived of external cues but they drift from the external cycle clock cycle can be reset by exposur ...
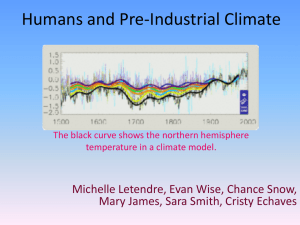
Humans and Preindustrial Climate
... This may be more complicated than we think… Hominins lived in many different environments (woodlands, grasslands, river margins) This leads to a different Hypothesis… The The Variability Selection Hypothesis: Rapid evolution occurred because rapidly changing climate put new demands on our ancestors ...
... This may be more complicated than we think… Hominins lived in many different environments (woodlands, grasslands, river margins) This leads to a different Hypothesis… The The Variability Selection Hypothesis: Rapid evolution occurred because rapidly changing climate put new demands on our ancestors ...
Human Complex Trait Genetics in the 21st Century
... possible to take bone samples from a number of individuals who lived 100, 200, ... 10,000 years ago and infer recent natural selection as if it was in real time by tracking changes in allele frequencies of variants that are known (from modern day studies) to be associated with complex traits and fitn ...
... possible to take bone samples from a number of individuals who lived 100, 200, ... 10,000 years ago and infer recent natural selection as if it was in real time by tracking changes in allele frequencies of variants that are known (from modern day studies) to be associated with complex traits and fitn ...
History of Life - CHS
... • Homo erectus 1.8 million – 300K yrs ago “upright human” hunting & fire? • Homo antecessor 780 K yrs ago (1977) earliest European hominid ...
... • Homo erectus 1.8 million – 300K yrs ago “upright human” hunting & fire? • Homo antecessor 780 K yrs ago (1977) earliest European hominid ...
Still Evolving After All These Years
... [12] We are used to thinking about evolution as a process of “good” genes replacing “bad” ones, but the most recent phase of human adaptation is a testament to the power of randomness in evolution. Beneficial mutations do not automatically persist. It all depends on timing and population size. I fir ...
... [12] We are used to thinking about evolution as a process of “good” genes replacing “bad” ones, but the most recent phase of human adaptation is a testament to the power of randomness in evolution. Beneficial mutations do not automatically persist. It all depends on timing and population size. I fir ...
Theory and Practice of Counseling and Psychotherapy
... Technical eclecticism—borrow techniques from other therapy system The BASIC I.D. (Behavior, Affective responses, Sensations, Images, Cognitions, Interpersonal relationship, Drug, biological functions, nutrition, and exercise ...
... Technical eclecticism—borrow techniques from other therapy system The BASIC I.D. (Behavior, Affective responses, Sensations, Images, Cognitions, Interpersonal relationship, Drug, biological functions, nutrition, and exercise ...
Learning
... shoe…causes you pain…removing the stone, relieves the pain. Putting on sunscreen before going to the beach. ...
... shoe…causes you pain…removing the stone, relieves the pain. Putting on sunscreen before going to the beach. ...
LT2Ch10
... Blisspoint is established by looking at behavior before a contingency is established. The established contingency must take blisspoint into account or it may not increase desired behavior. ...
... Blisspoint is established by looking at behavior before a contingency is established. The established contingency must take blisspoint into account or it may not increase desired behavior. ...
Human Variation - Department of Anthropology
... Office Hours (Fall Semester): Wednesday 1-4 P.M, or by appointment Course Description: This is a course in physical anthropology that describes variation in living humans, and identifies the random or adaptive evolutionary processes responsible for this variation. It deals with genetic, anatomical, ...
... Office Hours (Fall Semester): Wednesday 1-4 P.M, or by appointment Course Description: This is a course in physical anthropology that describes variation in living humans, and identifies the random or adaptive evolutionary processes responsible for this variation. It deals with genetic, anatomical, ...
Survival of the Adaptable - Smithsonian`s Human Origins
... they can stay aware of predators and may gang up to scare them away. Many primates have warning calls as well; some are specific to attacks from birds, snakes, and leopards. Social and vocal behaviors like these may have made it reasonably safe for our ancestors to venture away from the trees in the ...
... they can stay aware of predators and may gang up to scare them away. Many primates have warning calls as well; some are specific to attacks from birds, snakes, and leopards. Social and vocal behaviors like these may have made it reasonably safe for our ancestors to venture away from the trees in the ...
introduction to psychology and key people
... Types of Psychology Basic research- conduct studies with a long-term goal to find out more about human and animal behavior Applied psychology- discovering ways to use what we already know about people to benefit others. ...
... Types of Psychology Basic research- conduct studies with a long-term goal to find out more about human and animal behavior Applied psychology- discovering ways to use what we already know about people to benefit others. ...
Behavioral modernity

Behavioral modernity is a suite of behavioral and cognitive traits that distinguishes current Homo sapiens from anatomically modern humans, hominins, and other primates. Although often debated, most scholars agree that modern human behavior can be characterized by abstract thinking, planning depth, symbolic behavior (e.g. art, ornamentation, music), exploitation of large game, blade technology, among others. Underlying these behaviors and technological innovations are cognitive and cultural foundations that have been documented experimentally and ethnographically. Some of these human universal patterns are cumulative cultural adaptation, social norms, language, cooperative breeding, and extensive help and cooperation beyond close kin. These traits have been viewed as largely responsible for the human replacement of Neanderthals in Western Europe, along with the climatic conditions of the Last Glacial Maximum, and the peopling of the rest of the world.Arising from differences in the archaeological record, a debate continues as to whether anatomically modern humans were behaviorally modern as well. There are many theories on the evolution of behavioral modernity. These generally fall into two camps: gradualist and cognitive approaches. The Later Upper Paleolithic Model refers to the idea that modern human behavior arose through cognitive, genetic changes abruptly around 40–50,000 years ago. Other models focus on how modern human behavior may have arisen through gradual steps; the archaeological signatures of such behavior only appearing through demographic or subsistence-based changes.