Wild-Type Nonneuronal Cells Extend Survival of SOD1 Mutant
... Motor Neurons in ALS Mice A. M. Clement,1,3,4* M. D. Nguyen,5† E. A. Roberts,2,3 M. L. Garcia,1,3,4 S. Boillée,1,3,4 M. Rule,6 A. P. McMahon,6 W. Doucette,7 D. Siwek,8 R. J. Ferrante,8 R. H. Brown Jr.,7 J.-P. Julien,5‡ L. S. B. Goldstein,2,3 D. W. Cleveland1,3,4§ The most common form of amyotrophic ...
... Motor Neurons in ALS Mice A. M. Clement,1,3,4* M. D. Nguyen,5† E. A. Roberts,2,3 M. L. Garcia,1,3,4 S. Boillée,1,3,4 M. Rule,6 A. P. McMahon,6 W. Doucette,7 D. Siwek,8 R. J. Ferrante,8 R. H. Brown Jr.,7 J.-P. Julien,5‡ L. S. B. Goldstein,2,3 D. W. Cleveland1,3,4§ The most common form of amyotrophic ...
Prenatal morphine exposure alters the layer II/III pyramidal neurons
... audio stimulus (Kenny and Turkewitz, 1986; Lewkowicz and Turkewitz, 1981), for example, the newborns’ optimal or preferred amount of stimulation is based on the total amount or intensity of stimulus input (Lawson and Turkewitz, 1980). Additionally, the visual and auditory experience is important not ...
... audio stimulus (Kenny and Turkewitz, 1986; Lewkowicz and Turkewitz, 1981), for example, the newborns’ optimal or preferred amount of stimulation is based on the total amount or intensity of stimulus input (Lawson and Turkewitz, 1980). Additionally, the visual and auditory experience is important not ...
construction of a model demonstrating neural pathways and reflex arcs
... stimuli, even during sleep. For example, as you read this, your nervous system is receiving different types of information gathered by your eyes, such as color, light, texture of the paper, and the words on the paper. This is known as sensory reception. ...
... stimuli, even during sleep. For example, as you read this, your nervous system is receiving different types of information gathered by your eyes, such as color, light, texture of the paper, and the words on the paper. This is known as sensory reception. ...
construction of a model demonstrating neural pathways and reflex arcs
... stimuli, even during sleep. For example, as you read this, your nervous system is receiving different types of information gathered by your eyes, such as color, light, texture of the paper, and the words on the paper. This is known as sensory reception. ...
... stimuli, even during sleep. For example, as you read this, your nervous system is receiving different types of information gathered by your eyes, such as color, light, texture of the paper, and the words on the paper. This is known as sensory reception. ...
All-Optical Interrogation of Neural Circuits
... have proceeded more or less in parallel, and it has proven very difficult to combine readout and manipulation of the same cells, and thus achieve fully “all-optical” interrogation of neural activity. Implementations of simultaneous optical readout and manipulation have faced three main challenges: r ...
... have proceeded more or less in parallel, and it has proven very difficult to combine readout and manipulation of the same cells, and thus achieve fully “all-optical” interrogation of neural activity. Implementations of simultaneous optical readout and manipulation have faced three main challenges: r ...
cortex
... temporal lobe is expansive and is divisible into several regions by sulci that course in an antero-posterior direction. The superior temporal sulcus is a prominent feature, and parallels the lateral fissure for much of its course. The superior temporal gyrus lies between this sulcus and the lateral ...
... temporal lobe is expansive and is divisible into several regions by sulci that course in an antero-posterior direction. The superior temporal sulcus is a prominent feature, and parallels the lateral fissure for much of its course. The superior temporal gyrus lies between this sulcus and the lateral ...
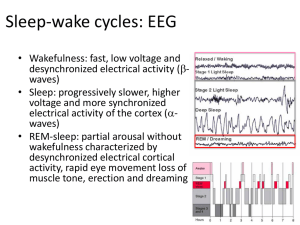
Sleep-wake cycles: EEG
... • Sleep: progressively slower, higher voltage and more synchronized electrical activity of the cortex (awaves) • REM-sleep: partial arousal without wakefulness characterized by ...
... • Sleep: progressively slower, higher voltage and more synchronized electrical activity of the cortex (awaves) • REM-sleep: partial arousal without wakefulness characterized by ...
How the hippocampus preserves order: the role of
... repetition. For example, place cells that initially fire late in a theta cycle have been found to fire at earlier phases of theta as the rodent repeatedly traverses a track or maze. This process, dubbed ‘theta phase precession’, is interpreted as evidence for a prospective code in the hippocampus th ...
... repetition. For example, place cells that initially fire late in a theta cycle have been found to fire at earlier phases of theta as the rodent repeatedly traverses a track or maze. This process, dubbed ‘theta phase precession’, is interpreted as evidence for a prospective code in the hippocampus th ...
A Subjective Distance Between Stimuli: Quantifying the Metric
... definite matrix representing the scalar product. Condition 4 imposes symmetry among the components of the vectors, which means that M must be proportional to the unit matrix. Therefore, out of all the distances that have a scalar product associated with them, the only one that fulfills condition 4 i ...
... definite matrix representing the scalar product. Condition 4 imposes symmetry among the components of the vectors, which means that M must be proportional to the unit matrix. Therefore, out of all the distances that have a scalar product associated with them, the only one that fulfills condition 4 i ...
microcircuits in the striatum striatal cell types and their
... “down” state near –80 mV and a relatively depolarized “up” state near –50 mV (e.g. Figure 2). The neurons never fire from the down state, which is characterized by the relative absence of inputs, and may or may not fire during the up state, creating an extremely phasic or episodic bursty pattern of ...
... “down” state near –80 mV and a relatively depolarized “up” state near –50 mV (e.g. Figure 2). The neurons never fire from the down state, which is characterized by the relative absence of inputs, and may or may not fire during the up state, creating an extremely phasic or episodic bursty pattern of ...
THE BRAIN`S CONCEPTS: THE ROLE OF THE SENSORY
... looks like for someone to grasp and what a graspable object looks like). Although we won’t discuss them here, there are other modalities involved as ...
... looks like for someone to grasp and what a graspable object looks like). Although we won’t discuss them here, there are other modalities involved as ...
Rhythms for Cognition: Communication through
... indistinguishable from human behavior, and detailed to the point of atomistic resolution. This hypothetical model would be an invaluable tool in place of imperfect experimental recordings from living subjects by providing complete downloads from the model. However, those downloaded data would requir ...
... indistinguishable from human behavior, and detailed to the point of atomistic resolution. This hypothetical model would be an invaluable tool in place of imperfect experimental recordings from living subjects by providing complete downloads from the model. However, those downloaded data would requir ...
M1 Corticospinal Mirror Neurons and Their Role in
... Changes in firing rate were sustained at lower levels during the hold period. Similar patterns were found in M43. For facilitation mirror neurons (F-F type, n = 18), discharge during execution was 60% of the maximum modulation above baseline versus 44% for observation. Suppression mirror neurons (S- ...
... Changes in firing rate were sustained at lower levels during the hold period. Similar patterns were found in M43. For facilitation mirror neurons (F-F type, n = 18), discharge during execution was 60% of the maximum modulation above baseline versus 44% for observation. Suppression mirror neurons (S- ...
Visual Responses of Pulvinar and Collicular Neurons During Eye
... required that eye position be maintained within 2’ of the desired location. In all conditions, the monkey’s task was to detect the dimming of a target light. The following conditions were used to assess the response characteristics of cells in relation to several types of stimulus movement. All test ...
... required that eye position be maintained within 2’ of the desired location. In all conditions, the monkey’s task was to detect the dimming of a target light. The following conditions were used to assess the response characteristics of cells in relation to several types of stimulus movement. All test ...
Horvitz, J.C. Stimulus-response and response
... expression [23,102,125] via DA modulation of real-time glutamate transmission at cortico- and limbic-striatal synapses [64], the focus here is on models of DA-mediated striatal plasticity and learning. 2. DA and striatal plasticity Corticostriatal synapses can express both long-term potentiation (LT ...
... expression [23,102,125] via DA modulation of real-time glutamate transmission at cortico- and limbic-striatal synapses [64], the focus here is on models of DA-mediated striatal plasticity and learning. 2. DA and striatal plasticity Corticostriatal synapses can express both long-term potentiation (LT ...
Hasselmo M.E. (2007) Arc length coding by interference of
... Many memory models focus on encoding of sequences by excitatory recurrent synapses in region CA3 of the hippocampus. However, data and modeling suggest an alternate mechanism for encoding of sequences in which interference between theta frequency oscillations encodes the position within a sequence b ...
... Many memory models focus on encoding of sequences by excitatory recurrent synapses in region CA3 of the hippocampus. However, data and modeling suggest an alternate mechanism for encoding of sequences in which interference between theta frequency oscillations encodes the position within a sequence b ...
14132.full - Explore Bristol Research
... Neural substrates that underlie requisite alterations in autonomic functions (e.g., cardiorespiratory adjustments) and sensory processing (e.g., modulation of pain processing) that accompany defense are well understood (Lovick and Bandler, 2005); however, little is known of the neural circuits that ...
... Neural substrates that underlie requisite alterations in autonomic functions (e.g., cardiorespiratory adjustments) and sensory processing (e.g., modulation of pain processing) that accompany defense are well understood (Lovick and Bandler, 2005); however, little is known of the neural circuits that ...
Goal-direction and top-down control
... information with a ‘cache’ system that only learns the most rewarding alternative at each decision point (i.e. what is the best branch to take at each state, considered in isolation, without integrating higher order decisions). The BG cache system is computationally simple (and therefore fast) but i ...
... information with a ‘cache’ system that only learns the most rewarding alternative at each decision point (i.e. what is the best branch to take at each state, considered in isolation, without integrating higher order decisions). The BG cache system is computationally simple (and therefore fast) but i ...
Selectivity and Tolerance - Penn Arts and Sciences
... real-time eye tracking. Stimuli, reward, and data acquisition were controlled using customized software. Stimuli were presented on a cathode ray tube monitor with an 85 Hz refresh rate positioned 49 cm away such that it subtended 44 ! 33°. All images were presented at the center of gaze, in a circul ...
... real-time eye tracking. Stimuli, reward, and data acquisition were controlled using customized software. Stimuli were presented on a cathode ray tube monitor with an 85 Hz refresh rate positioned 49 cm away such that it subtended 44 ! 33°. All images were presented at the center of gaze, in a circul ...