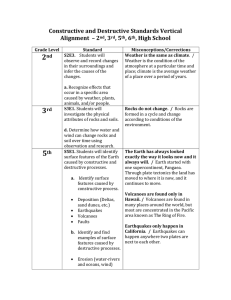
Constructive and Destructive Standards Vertical Alignment – 2 nd , 3
... exactly the way it looks now and it always will. / Earth started with one supercontinent, Pangaea. Through plate tectonics the land has moved to where it is now, and it continues to move. Volcanoes are found only in Hawaii. / Volcanoes are found in many places around the world, but most are concentr ...
... exactly the way it looks now and it always will. / Earth started with one supercontinent, Pangaea. Through plate tectonics the land has moved to where it is now, and it continues to move. Volcanoes are found only in Hawaii. / Volcanoes are found in many places around the world, but most are concentr ...
Geography A2 Revision PLATE TECTONICS AND ASSOCIATED
... >Hot Spot: A point on the surface of the earth located above a plume of rising magma. E.g. Hawaiian Islands. >Plate: Rigid slabs that float on the underlying semi-molten mantle (asthenosphere) and are moved by convection current within it. >Plate Tectonics: A theory that attempts to explain the form ...
... >Hot Spot: A point on the surface of the earth located above a plume of rising magma. E.g. Hawaiian Islands. >Plate: Rigid slabs that float on the underlying semi-molten mantle (asthenosphere) and are moved by convection current within it. >Plate Tectonics: A theory that attempts to explain the form ...
Chapter 5 Key Concepts
... pours out of cracks in the ocean floor. This process gradually builds new mountains. Volcanoes also form along diverging plate boundaries on land. Many volcanoes form near converging plate boundaries where two oceanic plates collide. The resulting volcanoes sometimes create a string of islands calle ...
... pours out of cracks in the ocean floor. This process gradually builds new mountains. Volcanoes also form along diverging plate boundaries on land. Many volcanoes form near converging plate boundaries where two oceanic plates collide. The resulting volcanoes sometimes create a string of islands calle ...
volcanic activity
... Common Parts of a Volcano Within a volcano, there is a portion that fuels the eruptions. This is referred to as the magma chamber. Once the magma chamber is fueled, it erupts through an opening in the crust. This opening is called the vent. Over time, the lava will solidify and accumulate to form a ...
... Common Parts of a Volcano Within a volcano, there is a portion that fuels the eruptions. This is referred to as the magma chamber. Once the magma chamber is fueled, it erupts through an opening in the crust. This opening is called the vent. Over time, the lava will solidify and accumulate to form a ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes – the essentials!
... This is where two plates diverge and pull apart. As a gap appears between the two plates, lava can escape in a line or fissure. The lava creates new oceanic crust and forms mid-ocean ridges such as the one that runs down the centre of the Atlantic Ocean. Volcanoes can be found in certain locations b ...
... This is where two plates diverge and pull apart. As a gap appears between the two plates, lava can escape in a line or fissure. The lava creates new oceanic crust and forms mid-ocean ridges such as the one that runs down the centre of the Atlantic Ocean. Volcanoes can be found in certain locations b ...
Introduction Where Volcanoes Are Found
... Fluid lava flows down mountainsides. The rock that the flow becomes depends on which type of lava it is and where it cools. The three types of flows are a’a, pahoehoe, and pillow lava. A’a Lava A’a lava is the thickest of the non-explosive lavas. A'a forms a thick and brittle crust, which is torn in ...
... Fluid lava flows down mountainsides. The rock that the flow becomes depends on which type of lava it is and where it cools. The three types of flows are a’a, pahoehoe, and pillow lava. A’a Lava A’a lava is the thickest of the non-explosive lavas. A'a forms a thick and brittle crust, which is torn in ...
Volcanoes of Hawaii and the Planet-v1
... The Martian volcano Olympus Mons (18oN, 133oW) is one of the largest volcanoes in the Solar System. It is 600 km across and 27 km high. In this view, Olympus Mons is compared to the Hawaiian Islands at the same scale. Notice that the Island of Oahu would fit easily inside the summit crater (“caldera” ...
... The Martian volcano Olympus Mons (18oN, 133oW) is one of the largest volcanoes in the Solar System. It is 600 km across and 27 km high. In this view, Olympus Mons is compared to the Hawaiian Islands at the same scale. Notice that the Island of Oahu would fit easily inside the summit crater (“caldera” ...
File
... below the continental one. This area of downward movement is known as the subduction zone. The sinking plate melts due to the heat in the mantle. The magma rises and reaches the surface through vents, fissures or cracks in the continental plate forming volcanoes. ...
... below the continental one. This area of downward movement is known as the subduction zone. The sinking plate melts due to the heat in the mantle. The magma rises and reaches the surface through vents, fissures or cracks in the continental plate forming volcanoes. ...
Bundle 1 - Humble ISD
... Fact: The majority of volcanoes are located along tectonic plate boundaries. “Ring of Fire” is the name given to an area along the border of the Pacific Plate with a high concentration of volcanoes. Earthquakes happen randomly across the earth’s surface. Fact: As with volcanoes, most of the world’ ...
... Fact: The majority of volcanoes are located along tectonic plate boundaries. “Ring of Fire” is the name given to an area along the border of the Pacific Plate with a high concentration of volcanoes. Earthquakes happen randomly across the earth’s surface. Fact: As with volcanoes, most of the world’ ...
Plate Tectonics - Nutley Public Schools
... and the Pacific Ring of Fire Plate Boundaries Map – shows us the separation between plates and where earthquakes and volcanic activity might occur Divergent – divide or pull apart, ex. Mid Atlantic Ridge Convergent – collide and form mountains, ex. Himalayas Transform– slide next to one anot ...
... and the Pacific Ring of Fire Plate Boundaries Map – shows us the separation between plates and where earthquakes and volcanic activity might occur Divergent – divide or pull apart, ex. Mid Atlantic Ridge Convergent – collide and form mountains, ex. Himalayas Transform– slide next to one anot ...
Unit 3: Forces Within - Lemon Bay High School
... What kind of plate boundary occurs where two plates grind past each other without destroying or producing lithosphere? ...
... What kind of plate boundary occurs where two plates grind past each other without destroying or producing lithosphere? ...
Planetary Volcanism
... – N, H, S, F, Ar, CO, Cl – These can combine with hydrogen to produce toxic compounds such as – Hcl, HF, H2SO4,H2S ...
... – N, H, S, F, Ar, CO, Cl – These can combine with hydrogen to produce toxic compounds such as – Hcl, HF, H2SO4,H2S ...
volcano - Madison County Schools
... volcano forms. How spot volcanoes on the ocean floor can become islands. This is how the Hawai’ian Islands formed. As the Pacific Plate continues to move, the hot spot remains stationary, continuing to punch up through the crust. ...
... volcano forms. How spot volcanoes on the ocean floor can become islands. This is how the Hawai’ian Islands formed. As the Pacific Plate continues to move, the hot spot remains stationary, continuing to punch up through the crust. ...
yr9-end of year exams-revision-flash cards-evt
... Convergent (destructive) plate boundary where an oceanic (e.g. Nazca) and continental (e.g. South American) plate move towards each other due to convection currents. - Denser (heavier) oceanic crust is subducted below the continental plate, forming a deep ocean trench - Heat from the mantle & fricti ...
... Convergent (destructive) plate boundary where an oceanic (e.g. Nazca) and continental (e.g. South American) plate move towards each other due to convection currents. - Denser (heavier) oceanic crust is subducted below the continental plate, forming a deep ocean trench - Heat from the mantle & fricti ...
Chapter 5 lesson 1
... o Can produce volcanoes, such as those in the Andes Mountains and at Mt. Saint Helens Key Idea: The “Ring of Fire” is a major belt of volcanoes. Surrounds the Pacific Ocean Includes North and South America, as well as Japan, New Zealand, and the ...
... o Can produce volcanoes, such as those in the Andes Mountains and at Mt. Saint Helens Key Idea: The “Ring of Fire” is a major belt of volcanoes. Surrounds the Pacific Ocean Includes North and South America, as well as Japan, New Zealand, and the ...
Hot Spots
... constant, as the plate continues to move over it. • The result is a trail of volcanoes left behind, with older volcanoes moving away from the hot spot, and newer ones forming over top of the hot spot. ...
... constant, as the plate continues to move over it. • The result is a trail of volcanoes left behind, with older volcanoes moving away from the hot spot, and newer ones forming over top of the hot spot. ...
Wegener—Continental Drift
... currents. One example is that ocean water is heated by hydrothermal vents, becomes less dense and rises. As it reaches areas of lower temperature water, it cools, increases in density and sinks. Science Student 2: The atmosphere near the earth’s surface is heated, becomes less dense and rises. As th ...
... currents. One example is that ocean water is heated by hydrothermal vents, becomes less dense and rises. As it reaches areas of lower temperature water, it cools, increases in density and sinks. Science Student 2: The atmosphere near the earth’s surface is heated, becomes less dense and rises. As th ...
Volcano Vocabulary
... Steep sides, loosely packed volcano formed when tephra falls to the ground. Formed from andesitic lava. ...
... Steep sides, loosely packed volcano formed when tephra falls to the ground. Formed from andesitic lava. ...
VOLCANIC ACTIVITY
... 2) line of volcanic mountains form along edge of continent 3) major active area is Pacific Ring of Fire (Circum-Pacific Belt) b. two ocean plates 1) deep trench formed 2) line of volcanic islands form along trench = island arcs ...
... 2) line of volcanic mountains form along edge of continent 3) major active area is Pacific Ring of Fire (Circum-Pacific Belt) b. two ocean plates 1) deep trench formed 2) line of volcanic islands form along trench = island arcs ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... • The fragments ejected during eruptions range in _________ from very fine dust and volcanic ash (less than 2 millimeters) to pieces that weigh several tons. ...
... • The fragments ejected during eruptions range in _________ from very fine dust and volcanic ash (less than 2 millimeters) to pieces that weigh several tons. ...
Volcanoes - Geophile.net
... volcanic eruptions • Nuée Ardente (or pyroclastic flow) – Fiery pyroclastic flow made of hot gases infused with ash – Flows down sides of a volcano at speeds up to 200 km (125 miles) per hour ...
... volcanic eruptions • Nuée Ardente (or pyroclastic flow) – Fiery pyroclastic flow made of hot gases infused with ash – Flows down sides of a volcano at speeds up to 200 km (125 miles) per hour ...
Plate Tectonics - Cloudfront.net
... crust or mantle of the earth. • The hot, liquid rock will break through weak spots in the surface and form volcanoes or flood basalts. • Many volcanoes do not release lava, instead they spit ash and small bits of lava called lapilli. • Some eruptions are quiet with very fluid (low viscosity) lava fl ...
... crust or mantle of the earth. • The hot, liquid rock will break through weak spots in the surface and form volcanoes or flood basalts. • Many volcanoes do not release lava, instead they spit ash and small bits of lava called lapilli. • Some eruptions are quiet with very fluid (low viscosity) lava fl ...
Earthquakes/Mountain Building
... understanding of earth's processes. – Although it is known where earthquakes and volcanic eruptions are likely to happen, there is currently no reliable way to predict precisely when an event will occur. – Volcanoes and earthquakes indicate the high temperatures and pressures that exist in earth's i ...
... understanding of earth's processes. – Although it is known where earthquakes and volcanic eruptions are likely to happen, there is currently no reliable way to predict precisely when an event will occur. – Volcanoes and earthquakes indicate the high temperatures and pressures that exist in earth's i ...
Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire is an area in the basin of the Pacific Ocean where a large number of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur. In a 40,000 km (25,000 mi) horseshoe shape, it is associated with a nearly continuous series of oceanic trenches, volcanic arcs, and volcanic belts and/or plate movements. It has 452 volcanoes and is home to over 75% of the world's active and dormant volcanoes. The Ring of Fire is sometimes called the circum-Pacific belt.About 90% of the world's earthquakes and 81% of the world's largest earthquakes occur along the Ring of Fire. The next most seismically active region (5–6% of earthquakes and 17% of the world's largest earthquakes) is the Alpide belt, which extends from Java to the northern Atlantic Ocean via the Himalayas and southern Europe.All but 3 of the world's 25 largest volcanic eruptions of the last 11,700 years occurred at volcanoes in the Ring of Fire.The Ring of Fire is a direct result of plate tectonics and the movement and collisions of lithospheric plates. The eastern section of the ring is the result of the Nazca Plate and the Cocos Plate being subducted beneath the westward moving South American Plate. The Cocos Plate is being subducted beneath the Caribbean Plate, in Central America. A portion of the Pacific Plate along with the small Juan de Fuca Plate are being subducted beneath the North American Plate. Along the northern portion, the northwestward-moving Pacific plate is being subducted beneath the Aleutian Islands arc. Farther west, the Pacific plate is being subducted along the Kamchatka Peninsula arcs on south past Japan. The southern portion is more complex, with a number of smaller tectonic plates in collision with the Pacific plate from the Mariana Islands, the Philippines, Bougainville, Tonga, and New Zealand; this portion excludes Australia, since it lies in the center of its tectonic plate. Indonesia lies between the Ring of Fire along the northeastern islands adjacent to and including New Guinea and the Alpide belt along the south and west from Sumatra, Java, Bali, Flores, and Timor. The famous and very active San Andreas Fault zone of California is a transform fault which offsets a portion of the East Pacific Rise under southwestern United States and Mexico. The motion of the fault generates numerous small earthquakes, at multiple times a day, most of which are too small to be felt. The active Queen Charlotte Fault on the west coast of the Haida Gwaii, British Columbia, Canada, has generated three large earthquakes during the 20th century: a magnitude 7 event in 1929; a magnitude 8.1 in 1949 (Canada's largest recorded earthquake); and a magnitude 7.4 in 1970.