Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis
... Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis • Bacterial cells are 50% protein by dry weight – Inhibition of protein synthesis leads to cessation of growth or cell death – Bacterial 70S ribosomes differ sufficiently from eukaryotic ribosomes to allow selective toxicity • Other properties of the antibiotics still ...
... Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis • Bacterial cells are 50% protein by dry weight – Inhibition of protein synthesis leads to cessation of growth or cell death – Bacterial 70S ribosomes differ sufficiently from eukaryotic ribosomes to allow selective toxicity • Other properties of the antibiotics still ...
Tuberculosis Chemotherapy
... Mechanism of action 1.The mechanism of action of streptomycin is inhibition of protein synthesis of mycobacteria in the ribosome. 2. Interfere with complex peptide formation. 3. Incorporation of incorrect amino acid into Peptide Resulting in Non functional toxic Protein. Adverse effects– nephrotoxi ...
... Mechanism of action 1.The mechanism of action of streptomycin is inhibition of protein synthesis of mycobacteria in the ribosome. 2. Interfere with complex peptide formation. 3. Incorporation of incorrect amino acid into Peptide Resulting in Non functional toxic Protein. Adverse effects– nephrotoxi ...
College of Medicine Microbiology
... 2. Obligatory dependence upon metabolic of host cell. Therefore , AVD interfere with cellular processes. Antiviral drugs are difficulty in obtaining selective toxicity against viruses without normal cell. 3. Some viruses become latent within host cells, and no antiviral drug can eradicate them. 4. D ...
... 2. Obligatory dependence upon metabolic of host cell. Therefore , AVD interfere with cellular processes. Antiviral drugs are difficulty in obtaining selective toxicity against viruses without normal cell. 3. Some viruses become latent within host cells, and no antiviral drug can eradicate them. 4. D ...
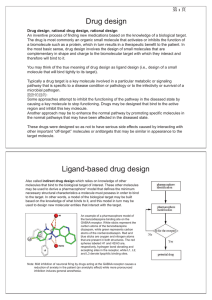
Drug design Ligand-based drug design
... biological activity has properties that would make it a likely orally active drug in humans. The rule was formulated by Christopher A. Lipinski in 1997, based on the observation that most medication drugs are relatively small and lipophilic molecules. The rule describes molecular properties importan ...
... biological activity has properties that would make it a likely orally active drug in humans. The rule was formulated by Christopher A. Lipinski in 1997, based on the observation that most medication drugs are relatively small and lipophilic molecules. The rule describes molecular properties importan ...
Handout- Enzyme Properties
... MOST enzymes are PROTEINS (Made of AMINO ACIDS) REQUIRED by all CHEMICAL PROCESSES in organisms (respiration, growth, photosynthesis, movement, etc.) They CONTROL the rate of METABOLIC (chemical reactions) in the body They lower ACTIVATION ENERGY (energy needed to start a reaction) They WEAKEN chemi ...
... MOST enzymes are PROTEINS (Made of AMINO ACIDS) REQUIRED by all CHEMICAL PROCESSES in organisms (respiration, growth, photosynthesis, movement, etc.) They CONTROL the rate of METABOLIC (chemical reactions) in the body They lower ACTIVATION ENERGY (energy needed to start a reaction) They WEAKEN chemi ...
ENZYMES – BIOLOGICAL CATALYSTS
... MOST enzymes are PROTEINS (Made of AMINO ACIDS) REQUIRED by all CHEMICAL PROCESSES in organisms (respiration, growth, photosynthesis, movement, etc.) They CONTROL the rate of METABOLIC (chemical reactions) in the body They lower ACTIVATION ENERGY (energy needed to start a reaction) They WEAKEN chemi ...
... MOST enzymes are PROTEINS (Made of AMINO ACIDS) REQUIRED by all CHEMICAL PROCESSES in organisms (respiration, growth, photosynthesis, movement, etc.) They CONTROL the rate of METABOLIC (chemical reactions) in the body They lower ACTIVATION ENERGY (energy needed to start a reaction) They WEAKEN chemi ...
mst question paper - Entrance
... a) Proteins consisting of one polypeptide chain can have quaternary structure b) The formation of disulphide bond in a protein requires two cysteine residues that should be adjacent to each other in the primary sequence of the protein c) The denaturation of proteins always leads to an irreversible l ...
... a) Proteins consisting of one polypeptide chain can have quaternary structure b) The formation of disulphide bond in a protein requires two cysteine residues that should be adjacent to each other in the primary sequence of the protein c) The denaturation of proteins always leads to an irreversible l ...
Antiviral and Anti
... b. Ability to suppress resistant HIV strains by enhancement of PI plasma levels XXII. METABOLIS SIDE EFECTS OF PIs [S80] a. Side effects: “buffalo hump” (which can sometimes be reversed); similar in appearance to Cushing’s syndrome without the hypercorisolism; incidence is low. XXIII. PERIPHERAL LIP ...
... b. Ability to suppress resistant HIV strains by enhancement of PI plasma levels XXII. METABOLIS SIDE EFECTS OF PIs [S80] a. Side effects: “buffalo hump” (which can sometimes be reversed); similar in appearance to Cushing’s syndrome without the hypercorisolism; incidence is low. XXIII. PERIPHERAL LIP ...
Lecture 7 Bio3124 - University of Ottawa
... is difficult to specifically target viral cycle drugs currently used inhibit virus-specific enzymes and life cycle processes ...
... is difficult to specifically target viral cycle drugs currently used inhibit virus-specific enzymes and life cycle processes ...
Anti-HIV drugs: 25 compounds approved within 25 years after the
... be foreseen that within 25 years of the virus being discovered we would now, in 2008, have at hand 25 anti-HIV compounds licensed (thus formally approved) for the treatment of AIDS (Table 1). These compounds fall within different categories depending on the target within the HIV replicative cycle th ...
... be foreseen that within 25 years of the virus being discovered we would now, in 2008, have at hand 25 anti-HIV compounds licensed (thus formally approved) for the treatment of AIDS (Table 1). These compounds fall within different categories depending on the target within the HIV replicative cycle th ...
Antivirus agents. Agents used in AIDs treatment. Immunomodulators
... • Able to enter the cells infected with virus. • Interfere with viral nucleic acid synthesis and/or regulation. • Some agents interfere with ability of virus to bind to cells. ...
... • Able to enter the cells infected with virus. • Interfere with viral nucleic acid synthesis and/or regulation. • Some agents interfere with ability of virus to bind to cells. ...
Advances in antiviral drug discovery and development: Part I
... better therapeutics and antivirals in the future. The most important one is to address antiviral resistance, otherwise, like antibiotics, antivirals may also be rendered useless in future. Thus, there is a need to characterize newer molecules as antivirals for more specificity, less toxicity, proper ...
... better therapeutics and antivirals in the future. The most important one is to address antiviral resistance, otherwise, like antibiotics, antivirals may also be rendered useless in future. Thus, there is a need to characterize newer molecules as antivirals for more specificity, less toxicity, proper ...
Chapter 21
... Certain microbes are inherently resistant to the effects of a particular drug. This is termed innate or intrinsic resistance. If a previously sensitive organism develops resistance through spontaneous mutation, this is called acquired resistance. ...
... Certain microbes are inherently resistant to the effects of a particular drug. This is termed innate or intrinsic resistance. If a previously sensitive organism develops resistance through spontaneous mutation, this is called acquired resistance. ...
Alkylating agents
... • THF serves as the key one-carbon carrier for enzymatic processes involved in de novo synthesis of thymidylate, purine nucleotides, and the amino acids serine and methionine. • Inhibition of these various metabolic processes thereby interferes with the formation of DNA, RNA, and key cellular protei ...
... • THF serves as the key one-carbon carrier for enzymatic processes involved in de novo synthesis of thymidylate, purine nucleotides, and the amino acids serine and methionine. • Inhibition of these various metabolic processes thereby interferes with the formation of DNA, RNA, and key cellular protei ...
Mechanism of Action
... Influenza A virus subtype H1N1, also known as A(H1N1), is a subtype of influenzavirus A and the most common cause of influenza (flu) in humans. Some strains of H1N1 are endemic in humans, including the strain(s) responsible for the 1918 flu pandemic which killed 50–100 million people worldwide. H1N1 ...
... Influenza A virus subtype H1N1, also known as A(H1N1), is a subtype of influenzavirus A and the most common cause of influenza (flu) in humans. Some strains of H1N1 are endemic in humans, including the strain(s) responsible for the 1918 flu pandemic which killed 50–100 million people worldwide. H1N1 ...
Metrifonate
... biotransformation of mertifonate occurs independently of the hepatic cytochrome P450 It is slowly and non-enzymatically transformed to DDVP which is PH dependent Serum t½ is 2 hours ...
... biotransformation of mertifonate occurs independently of the hepatic cytochrome P450 It is slowly and non-enzymatically transformed to DDVP which is PH dependent Serum t½ is 2 hours ...
Advanced Medicinal Chemistry
... Usually, the substrate & inhibitors bind at the active site Allosteric (non-competitive) binding occurs remotely to the active site ...
... Usually, the substrate & inhibitors bind at the active site Allosteric (non-competitive) binding occurs remotely to the active site ...
Advanced Medicinal Chemistry
... Usually, the substrate & inhibitors bind at the active site Allosteric (non-competitive) binding occurs remotely to the active site ...
... Usually, the substrate & inhibitors bind at the active site Allosteric (non-competitive) binding occurs remotely to the active site ...
Direct Link - TUSK: Tufts
... • M2 protein is a protein channel which enhances viral uncoating and thus inhibition of M2 protein inhibits viral replication • Resistance conferred by a single amino acid mutation in the M2 protein ...
... • M2 protein is a protein channel which enhances viral uncoating and thus inhibition of M2 protein inhibits viral replication • Resistance conferred by a single amino acid mutation in the M2 protein ...
Document
... toxicity in tests with cultured cells (anti-viral activity at 10,000 to 100,000-fold lower concentration than cytotoxic concentration) and have been shown to work synergistically with nucleoside analogs such as AZT. Thus, these drugs have high therapeutic index and also show good bioavailablity so t ...
... toxicity in tests with cultured cells (anti-viral activity at 10,000 to 100,000-fold lower concentration than cytotoxic concentration) and have been shown to work synergistically with nucleoside analogs such as AZT. Thus, these drugs have high therapeutic index and also show good bioavailablity so t ...
Design and Synthesis of Small Molecule Inhibitors of
... directed inhibition, or gene knock-out, has been shown to increase levels of HDL-C in rabbits and mice on both normal and high-fat diets. Because the active site of EL contains serine-protease like achitecture, we hypothesized that boronic acids could be used as small molecule inhibitors. Indeed, se ...
... directed inhibition, or gene knock-out, has been shown to increase levels of HDL-C in rabbits and mice on both normal and high-fat diets. Because the active site of EL contains serine-protease like achitecture, we hypothesized that boronic acids could be used as small molecule inhibitors. Indeed, se ...
ANTIVIRAL AGENTS
... Selective toxicity of these drugs depends on their ability to inhibit the HIV reverse transcriptase without inhibiting host cell DNA polymerases Some are capable of inhibiting human DNA polymerase γ Toxicities due to inhibition of mitochondrial DNA synthesis are frequently observed which are: anemia ...
... Selective toxicity of these drugs depends on their ability to inhibit the HIV reverse transcriptase without inhibiting host cell DNA polymerases Some are capable of inhibiting human DNA polymerase γ Toxicities due to inhibition of mitochondrial DNA synthesis are frequently observed which are: anemia ...