Neural control of the circulation - Advances in Physiology Education
... parasympathetic fibers is acetylcholine, which binds to muscarinic acetylcholine receptors on target tissues. Effects of acetylcholine are discrete and short lived due to high local concentrations of acetylcholinesterase, which rapidly degrades the neurotransmitter and prevents its appearance in the ...
... parasympathetic fibers is acetylcholine, which binds to muscarinic acetylcholine receptors on target tissues. Effects of acetylcholine are discrete and short lived due to high local concentrations of acetylcholinesterase, which rapidly degrades the neurotransmitter and prevents its appearance in the ...
The Peripheral Nervous System
... sugar into the blood, and shuts down of activities not related to the body’s preparation to “fight or flight in response to stress • Parasympathetic system = causes the “rest and digest” responses o Activates digestion and pathways that store food molecules while lowering heart rate and blood pressu ...
... sugar into the blood, and shuts down of activities not related to the body’s preparation to “fight or flight in response to stress • Parasympathetic system = causes the “rest and digest” responses o Activates digestion and pathways that store food molecules while lowering heart rate and blood pressu ...
Poster No: 1064 - Orthopaedic Research Society
... reflects an alteration in the arrangement and concentration of RNAcontaining material in the cell, leading to changes in protein synthesis of importance for axonal regeneration.3 It seems likely that sustained mechanical compression of the nerve root could result in irreversible damage to the motor ...
... reflects an alteration in the arrangement and concentration of RNAcontaining material in the cell, leading to changes in protein synthesis of importance for axonal regeneration.3 It seems likely that sustained mechanical compression of the nerve root could result in irreversible damage to the motor ...
REM-off
... (e.g., NE, HA, ACh, DA, 5-HT). That is, the neuromodulator may change the ‘functional anatomy’ of the brain. For example, when neuron A (presynaptic), having fired an action potential, releases the neurotransmitter glutamate onto neuron B (postsynaptic), ionotropic receptors are activated resulting ...
... (e.g., NE, HA, ACh, DA, 5-HT). That is, the neuromodulator may change the ‘functional anatomy’ of the brain. For example, when neuron A (presynaptic), having fired an action potential, releases the neurotransmitter glutamate onto neuron B (postsynaptic), ionotropic receptors are activated resulting ...
pdf
... manipulation increased mitral cell responses to high-concentration odors, and it decreased responses to low-concentration odors. Taken together, these results show that excitation dominates at low odor concentrations, but inhibition dominates at high concentrations. Both effects are important for th ...
... manipulation increased mitral cell responses to high-concentration odors, and it decreased responses to low-concentration odors. Taken together, these results show that excitation dominates at low odor concentrations, but inhibition dominates at high concentrations. Both effects are important for th ...
The Brain (Handout)
... mammals solve the problem with maternal care (Figure 03b), shelter, warmth, and milk. In most birds, both parents cooperate to provide food and shelter to their young. The expanded forebrain and parental care provide mechanisms for the extra-genetic transmission of information from one generation ...
... mammals solve the problem with maternal care (Figure 03b), shelter, warmth, and milk. In most birds, both parents cooperate to provide food and shelter to their young. The expanded forebrain and parental care provide mechanisms for the extra-genetic transmission of information from one generation ...
rapid eye movement sleep deprivation induces acetylcholinesterase
... Acetylcholinesterase (AchE) is a large glycoprotein that, aside from its known cholinolytic activity, co-exists with other transmitter systems and possesses other functions. In the present study, the effects of short-tenn rapid-eye-movement sleep deprivation (REM-SD) on AchE activity in the anterior ...
... Acetylcholinesterase (AchE) is a large glycoprotein that, aside from its known cholinolytic activity, co-exists with other transmitter systems and possesses other functions. In the present study, the effects of short-tenn rapid-eye-movement sleep deprivation (REM-SD) on AchE activity in the anterior ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Much more complex than the parasympathetic division, both anatomically and functionally. Sympathetic preganglionic neuron cell bodies are housed in the lateral horn of the T1–L2 regions of the spinal cord. Preganglionic sympathetic axons travel with somatic motor neuron axons to exit the spinal cord ...
... Much more complex than the parasympathetic division, both anatomically and functionally. Sympathetic preganglionic neuron cell bodies are housed in the lateral horn of the T1–L2 regions of the spinal cord. Preganglionic sympathetic axons travel with somatic motor neuron axons to exit the spinal cord ...
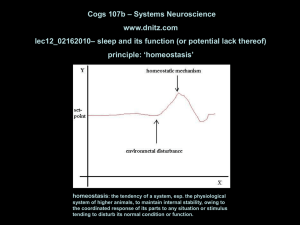
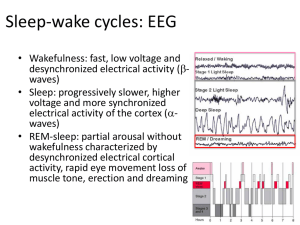
Sleep-wake cycles: EEG
... wakefulness characterized by desynchronized electrical cortical activity, rapid eye movement loss of muscle tone, erection and dreaming ...
... wakefulness characterized by desynchronized electrical cortical activity, rapid eye movement loss of muscle tone, erection and dreaming ...
Nervous System - AP Psychology: 2(A)
... information from the eyes. • Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and back of each cerebral hemisphere containing the centers for touch, taste, and temperature sensations. • Somatosensory cortex - ar ...
... information from the eyes. • Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and back of each cerebral hemisphere containing the centers for touch, taste, and temperature sensations. • Somatosensory cortex - ar ...
A táplálékfelvétel, a só- és vízháztartás neuroanatómiája
... - endogenous cannabinoid system may modulate the appetitive value of the food by affecting the activity of brain reward systems - high concentration of CB1 mRNA in the hypothalamic ventromedial nucleus - 2-AG is present in hypothalamic areas involved in feeding - CB1 receptor KO mice eat less and lo ...
... - endogenous cannabinoid system may modulate the appetitive value of the food by affecting the activity of brain reward systems - high concentration of CB1 mRNA in the hypothalamic ventromedial nucleus - 2-AG is present in hypothalamic areas involved in feeding - CB1 receptor KO mice eat less and lo ...
Sympathetically-correlated spinal cord neurons in rats
... nucleus, the posterior column nuclei, and the thalamus (spinothalamic tract) – Lamina 5 and 6 receives proprioceptive input AND sensory information relayed by lamina 4. These are the sites of origin of ascending projections to higher centres. • From T1 to L3 is Clarke’s column, which is within lamin ...
... nucleus, the posterior column nuclei, and the thalamus (spinothalamic tract) – Lamina 5 and 6 receives proprioceptive input AND sensory information relayed by lamina 4. These are the sites of origin of ascending projections to higher centres. • From T1 to L3 is Clarke’s column, which is within lamin ...
From neuroanatomy to behavior: central integration of peripheral
... Moreover, these data have provided a framework for the investigation of other metabolic cues that may regulate similar biological activities. The regulation of food intake, as well as glucose homeo stasis and energy expenditure, requires the coordinated response of various peripheral and central fa ...
... Moreover, these data have provided a framework for the investigation of other metabolic cues that may regulate similar biological activities. The regulation of food intake, as well as glucose homeo stasis and energy expenditure, requires the coordinated response of various peripheral and central fa ...
Neurons and Synapses
... Students will collect information from pre-set resources to develop understanding of the nervous system, neurons, synapses, and neurotransmitters. Information gather from this lesson will help them build models and participate in neuron related activities of future lessons. Time Needed: 1+ Period(s) ...
... Students will collect information from pre-set resources to develop understanding of the nervous system, neurons, synapses, and neurotransmitters. Information gather from this lesson will help them build models and participate in neuron related activities of future lessons. Time Needed: 1+ Period(s) ...
LESSON 3.3 WORKBOOK
... Note that these channels are different from the voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels we talked about on the axon and the presynaptic terminal because they are stimulated to open by a neurotransmitter binding to its receptor, and not by a change in voltage. When channels open that are permeable ...
... Note that these channels are different from the voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels we talked about on the axon and the presynaptic terminal because they are stimulated to open by a neurotransmitter binding to its receptor, and not by a change in voltage. When channels open that are permeable ...
Saladin 5e Extended Outline
... reabsorbed and only 100 to 160 mL is normally present at one time. b. CSF production begins with filtration of blood plasma through the brain’s capillaries. i. Ependymal cells modify this filtrate so that CSF has more sodium and chloride, but less potassium, calcium, and glucose and very little prot ...
... reabsorbed and only 100 to 160 mL is normally present at one time. b. CSF production begins with filtration of blood plasma through the brain’s capillaries. i. Ependymal cells modify this filtrate so that CSF has more sodium and chloride, but less potassium, calcium, and glucose and very little prot ...
Use of rabies virus as a transneuronal tracer of neuronal
... 1 - Amplification of the signal: selfamplifying marker. 2 - Exclusive tropism for neurones in vivo. 3 - Absence of degeneration of infected neurones: possibility of combined visualisation of neurotransmitters & other tracers. 4 - Specificity: propagation exclusively by transneuronal transfer between ...
... 1 - Amplification of the signal: selfamplifying marker. 2 - Exclusive tropism for neurones in vivo. 3 - Absence of degeneration of infected neurones: possibility of combined visualisation of neurotransmitters & other tracers. 4 - Specificity: propagation exclusively by transneuronal transfer between ...
lungs – bronchia – pleura
... tissues of the body. Throughout this period the growing fetus passes through all the evolutionary stages from a single-celled organism to a complete human being. NOTE: The three germ layers give rise to the same tissue types in all organisms, including animals and plants. We know from the science of ...
... tissues of the body. Throughout this period the growing fetus passes through all the evolutionary stages from a single-celled organism to a complete human being. NOTE: The three germ layers give rise to the same tissue types in all organisms, including animals and plants. We know from the science of ...
Large-scale recording of neuronal ensembles
... actions from the spiking activity of its neurons? Early singleneuron recording research treated spike pattern variability as noise that needed to be averaged out to reveal the brain’s representation of invariant input. Another view is that variability of spikes is centrally coordinated and that this ...
... actions from the spiking activity of its neurons? Early singleneuron recording research treated spike pattern variability as noise that needed to be averaged out to reveal the brain’s representation of invariant input. Another view is that variability of spikes is centrally coordinated and that this ...
Skeletal System
... decreasing in strength as it travels If this depolarizing signal is strong enough when it reaches the initial segment of the axon, it acts as the trigger that initiates an action potential in the axon Signals from the receptive zone determine if the axon will fire an impulse ...
... decreasing in strength as it travels If this depolarizing signal is strong enough when it reaches the initial segment of the axon, it acts as the trigger that initiates an action potential in the axon Signals from the receptive zone determine if the axon will fire an impulse ...
Note - Reza Shadmehr
... Slide 3. The exact content of the myosin molecule determines the functional characteristics of the extrafusal muscle fiber. In adults, we see three varieties of the myosin molecule. These isoforms are designated as type I, IIa, and IIx. Type I fibers are known as slow fibers, while type II are fast ...
... Slide 3. The exact content of the myosin molecule determines the functional characteristics of the extrafusal muscle fiber. In adults, we see three varieties of the myosin molecule. These isoforms are designated as type I, IIa, and IIx. Type I fibers are known as slow fibers, while type II are fast ...
Module 3 Brain`s Building Blocks
... – GABA neurons have chemical locks that can be opened by chemical keys in the form of the neurotransmitter GABA GABA Keys – alcohol molecules so closely resemble those of the GABA neurotransmitter that alcohol can function like GABA keys and open GABA receptors – when GABA neurons are excited, they ...
... – GABA neurons have chemical locks that can be opened by chemical keys in the form of the neurotransmitter GABA GABA Keys – alcohol molecules so closely resemble those of the GABA neurotransmitter that alcohol can function like GABA keys and open GABA receptors – when GABA neurons are excited, they ...
Human Physiology/The Nervous System
... has the greatest hyperpolarized action potential threshold. While the axon and axon hillock are generally involved in information outflow, this region can also receive input from other neurons as well. The axon terminal is a specialized structure at the end of the axon that is used to release neurot ...
... has the greatest hyperpolarized action potential threshold. While the axon and axon hillock are generally involved in information outflow, this region can also receive input from other neurons as well. The axon terminal is a specialized structure at the end of the axon that is used to release neurot ...