An Introduction to the ANS and Higher
... • “Kicks in” only during exertion, stress, or emergency • “Fight or flight” • Parasympathetic Division • Controls during resting conditions • “Rest and digest” ...
... • “Kicks in” only during exertion, stress, or emergency • “Fight or flight” • Parasympathetic Division • Controls during resting conditions • “Rest and digest” ...
Intrinsic firing patterns of diverse neocortical neurons
... dusters of high-frequency spikes solely as a manifestation of its intrinsic membrane properties, and independent of its synaptic input. Almost any neuron might produce dusters of spikes in response to phasic synaptic input. However, this response pattern does not, of itself, justify dassifcafion as ...
... dusters of high-frequency spikes solely as a manifestation of its intrinsic membrane properties, and independent of its synaptic input. Almost any neuron might produce dusters of spikes in response to phasic synaptic input. However, this response pattern does not, of itself, justify dassifcafion as ...
III./2.2.: The pathology and etiology of headaches III./2.2.1.: Anatomy
... results in sterile inflammation (neurogenic inflammation), with a local increase in vessel wall permeability and plasma protein extravasation, vasodilation and histamine release. This process is self-propagatory as the sterile inflammation causes further trigeminal activation. According to animal st ...
... results in sterile inflammation (neurogenic inflammation), with a local increase in vessel wall permeability and plasma protein extravasation, vasodilation and histamine release. This process is self-propagatory as the sterile inflammation causes further trigeminal activation. According to animal st ...
Anatomy Lecture 3 Descending Motor Tracts In the last lecture the
... - It affects the medial group (axial and proximal muscles). - It supplies the same area and the opposite one as well; bilateral (if this tract is at the right side it will affect the alpha and gamma motor neuron that supply the right and left axial muscles). NOTE: - A person developed a stroke at th ...
... - It affects the medial group (axial and proximal muscles). - It supplies the same area and the opposite one as well; bilateral (if this tract is at the right side it will affect the alpha and gamma motor neuron that supply the right and left axial muscles). NOTE: - A person developed a stroke at th ...
Integrate-and-Fire Neurons and Networks
... Spiking neurons connected to each other by excitatory or inhibitory synapses exhibit non-trivial dynamical properties. The population may respond rapidly to external signals. The network activity may explode or die away. Neurons may spontaneously develop a tendency to fire synchronously or in groups ...
... Spiking neurons connected to each other by excitatory or inhibitory synapses exhibit non-trivial dynamical properties. The population may respond rapidly to external signals. The network activity may explode or die away. Neurons may spontaneously develop a tendency to fire synchronously or in groups ...
Peripheral Nervous System - cK-12
... The motor division of the peripheral system carries messages from the central nervous system to internal organs and muscles. The motor division is also divided into two parts (Figure 1.4), the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system carries messages that c ...
... The motor division of the peripheral system carries messages from the central nervous system to internal organs and muscles. The motor division is also divided into two parts (Figure 1.4), the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system carries messages that c ...
03/05 PPT
... • Different cells respond to the same guidance cues in different ways • Chemical cues exist at many points along the axon guidance pathway e.g the optic tectum and optic tract ...
... • Different cells respond to the same guidance cues in different ways • Chemical cues exist at many points along the axon guidance pathway e.g the optic tectum and optic tract ...
Chapter 11
... surrounding long nerve fibers Protects and insulates the fibers Increases transmission rate of ...
... surrounding long nerve fibers Protects and insulates the fibers Increases transmission rate of ...
NEUROTRANSMITTERS II.
... NUCLEI. THE RELEASING AND RELEASE INHIBITING HORMONES (LHRH, TRF, CRH, SRIF, GHRH) ...
... NUCLEI. THE RELEASING AND RELEASE INHIBITING HORMONES (LHRH, TRF, CRH, SRIF, GHRH) ...
Redalyc.Normal neuronal migration
... shape, direction of movement and speed of migration. The stages of radial migration are four: first, neurons generated at the ventricular zone move radially to the subventricular zone; in the second stage, neurons pause in the intermediate zone-SVZ for as long as 24h and become multipolar. A fractio ...
... shape, direction of movement and speed of migration. The stages of radial migration are four: first, neurons generated at the ventricular zone move radially to the subventricular zone; in the second stage, neurons pause in the intermediate zone-SVZ for as long as 24h and become multipolar. A fractio ...
Student Presentation - UNM Computer Science
... These comparisons between artificial and natural automata result in one question: “Our artificial automata are much smaller than natural automata in what they do and in the number of components they have, and they’re phenomenally more expensive in terms of space and energy. Why is this so?” Von Neum ...
... These comparisons between artificial and natural automata result in one question: “Our artificial automata are much smaller than natural automata in what they do and in the number of components they have, and they’re phenomenally more expensive in terms of space and energy. Why is this so?” Von Neum ...
LPN-C
... The SNS • consists of sensory neurons from the head, body wall, extremities, and motor neurons to skeletal muscle. • The motor responses are under conscious control and therefore the SNS is voluntary. • Certain peripheral nerves perform specialized functions and form the autonomic nervous system; t ...
... The SNS • consists of sensory neurons from the head, body wall, extremities, and motor neurons to skeletal muscle. • The motor responses are under conscious control and therefore the SNS is voluntary. • Certain peripheral nerves perform specialized functions and form the autonomic nervous system; t ...
gustatory and olfactory senses
... concentrations. The scala media is the compartment located between these outer two chambers. The scala media is filled with a fluid endolymph that had high concentrations of potassium. It also contains the organ of corti. The sound vibrations that pass by the oval window into the chochlear chambers ...
... concentrations. The scala media is the compartment located between these outer two chambers. The scala media is filled with a fluid endolymph that had high concentrations of potassium. It also contains the organ of corti. The sound vibrations that pass by the oval window into the chochlear chambers ...
Nervous Nellie Circuit Lesson Summary: Neurons, or nerve cells
... 8. Ask students to describe how they knew which neurons were excitatory and inhibitory. 9. Ask students to write a reflection paragraph that describes how working with the Virtual Neurons software helped them learn about neurons and neuronal communication. 10. Ask for volunteers to share their refle ...
... 8. Ask students to describe how they knew which neurons were excitatory and inhibitory. 9. Ask students to write a reflection paragraph that describes how working with the Virtual Neurons software helped them learn about neurons and neuronal communication. 10. Ask for volunteers to share their refle ...
FREE Sample Here
... finally into the central canal of the spinal cord and the surrounding subarachnoid space where it is absorbed back into the blood supply. A primary function of the CSF is to protect the brain through floating the brain rather than attaching it to the skull. *See the Lecture Enrichment section for a ...
... finally into the central canal of the spinal cord and the surrounding subarachnoid space where it is absorbed back into the blood supply. A primary function of the CSF is to protect the brain through floating the brain rather than attaching it to the skull. *See the Lecture Enrichment section for a ...
Study Guide
... 2. Know the functions of sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. II. Organization of the Nervous System 1. Know the differences and similarities between SNS, ANS, and ENS. 2. What part of the nervous system are the SNS, ANS, and ENS a subdivision of? 3. Know the functions of SNS, ANS, and ...
... 2. Know the functions of sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. II. Organization of the Nervous System 1. Know the differences and similarities between SNS, ANS, and ENS. 2. What part of the nervous system are the SNS, ANS, and ENS a subdivision of? 3. Know the functions of SNS, ANS, and ...
Alveolar Process - student.ahc.umn.edu
... from the cementum surface to the blood vessels. Associated with neural elements. Most numerous in the cervical area. Function: Regulate vascular flow in relation to tooth function ...
... from the cementum surface to the blood vessels. Associated with neural elements. Most numerous in the cervical area. Function: Regulate vascular flow in relation to tooth function ...
Primary afferent neurons of the gut
... The endogenous compounds that mediate inflammation (autacoids) and related exogenous compounds including the synthetic prostaglandins. ...
... The endogenous compounds that mediate inflammation (autacoids) and related exogenous compounds including the synthetic prostaglandins. ...
NOT FOR SALE - Cengage Learning
... neurons. Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system that conduct impulses. Neurons can be visualized as having branches, trunks, and roots—something like trees. As we voyage through this forest, we see that many nerve cells lie alongside one another like a thicket of trees. But neurons can ...
... neurons. Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system that conduct impulses. Neurons can be visualized as having branches, trunks, and roots—something like trees. As we voyage through this forest, we see that many nerve cells lie alongside one another like a thicket of trees. But neurons can ...
26_1986 Wasilewska
... primates) belong to the mammalian basal ganglia. The St and GP are defined as the corpus striatum. A morphometric study of the mammalian St and GP has a long tradition and is related with different quantitative aspects. Data on the volumes of the brain and various brain parts in insectivores and pri ...
... primates) belong to the mammalian basal ganglia. The St and GP are defined as the corpus striatum. A morphometric study of the mammalian St and GP has a long tradition and is related with different quantitative aspects. Data on the volumes of the brain and various brain parts in insectivores and pri ...
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE
... Discuss the external structure of the spinal cord in terms of its length, start, end, number of segments, and enlarged areas. About 17 inches long, the start is the foramen magnum, it tapers to a point and terminates near the intervertebral disc that separates the first/ second lumbar vertebrae in a ...
... Discuss the external structure of the spinal cord in terms of its length, start, end, number of segments, and enlarged areas. About 17 inches long, the start is the foramen magnum, it tapers to a point and terminates near the intervertebral disc that separates the first/ second lumbar vertebrae in a ...
The Skeletal System
... The brain and spinal cord (in vertebrates) Carries out the body’s responses to stimuli ...
... The brain and spinal cord (in vertebrates) Carries out the body’s responses to stimuli ...
Nervous System Chapter 8 ppt copy
... your that from the spinal cord called central nervous spinal nerves. system to your Spinal nerves are skeletal muscles. made up of bundles The autonomic of sensory and the system controls Research Visit motor neurons involuntary actionsGlencoe Science bound together those not under by Web site at co ...
... your that from the spinal cord called central nervous spinal nerves. system to your Spinal nerves are skeletal muscles. made up of bundles The autonomic of sensory and the system controls Research Visit motor neurons involuntary actionsGlencoe Science bound together those not under by Web site at co ...
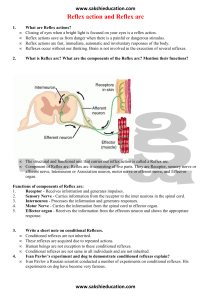
Reflex action and Reflex arc
... bell even if the food was not given. Dog associated with sound of the bell with food and assumed that whenever the bell rang food was given In expectation of food, saliva started flowing from its mouth. Human beings are no exception to this. Conditional reflexes are not same in all individuals and n ...
... bell even if the food was not given. Dog associated with sound of the bell with food and assumed that whenever the bell rang food was given In expectation of food, saliva started flowing from its mouth. Human beings are no exception to this. Conditional reflexes are not same in all individuals and n ...
Nervous System The master controlling and communicating system
... In motor neurons, the nerve impulse is generated at the junction of the axon hillock and axon (trigger zone) and conducted along the axon to the axon terminals which are the secretory regions of the neuron ...
... In motor neurons, the nerve impulse is generated at the junction of the axon hillock and axon (trigger zone) and conducted along the axon to the axon terminals which are the secretory regions of the neuron ...