A1985AUW1100002
... thought that, memory aside, the hippocampus offered several advantages. It has a cellular architecture that is remarkably conserved throughout mammals, and the main cetts, catted the pyramidal cells, are clustered in a discrete layer, an easy target for microelectrodes. These cells send their axons ...
... thought that, memory aside, the hippocampus offered several advantages. It has a cellular architecture that is remarkably conserved throughout mammals, and the main cetts, catted the pyramidal cells, are clustered in a discrete layer, an easy target for microelectrodes. These cells send their axons ...
Control and Coordination
... Imagine yourself to be Galan, the Greek physiologist (A.D.129 - 200). One day a patient came to you and told that he had fallen from his chariot and had a blow in the neck. He complained of loss of feeling in the arm while still retaining normal muscular control of its moment. What questions would a ...
... Imagine yourself to be Galan, the Greek physiologist (A.D.129 - 200). One day a patient came to you and told that he had fallen from his chariot and had a blow in the neck. He complained of loss of feeling in the arm while still retaining normal muscular control of its moment. What questions would a ...
The Nervous System
... conduction – myelinated or unmyelinated axons? 2. Which do you think would conduct an AP faster – an axon with a large diameter or an axon with a small diameter? The answer to #1 is a myelinated axon. If you can’t see why, then answer this question: could you move 100ft faster if you walked heel to ...
... conduction – myelinated or unmyelinated axons? 2. Which do you think would conduct an AP faster – an axon with a large diameter or an axon with a small diameter? The answer to #1 is a myelinated axon. If you can’t see why, then answer this question: could you move 100ft faster if you walked heel to ...
Neuroscience01_Introduction
... Commissure is a group of nerve fibers connecting one side of the ...
... Commissure is a group of nerve fibers connecting one side of the ...
Nervous System
... Gray and white matter. 4. Electrical signals in neuron. Ion channels Resting membrane potential (RMP) Graded potential. Action potential. ...
... Gray and white matter. 4. Electrical signals in neuron. Ion channels Resting membrane potential (RMP) Graded potential. Action potential. ...
Chapter 2
... All-or-None Response: When the depolarizing current exceeds the threshold, a neuron will fire. If the depolarizing current fails to exceed the threshold, a neuron will not fire. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... All-or-None Response: When the depolarizing current exceeds the threshold, a neuron will fire. If the depolarizing current fails to exceed the threshold, a neuron will not fire. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
File
... with each other and with muscle and gland cells they can coordinate, regulate, and integrate many body functions. The nervous tissue includes neurological cells. These cells support and bind components of nervous tissue, carry on phagocytosis, and help support nutrients to neurons by connecting them ...
... with each other and with muscle and gland cells they can coordinate, regulate, and integrate many body functions. The nervous tissue includes neurological cells. These cells support and bind components of nervous tissue, carry on phagocytosis, and help support nutrients to neurons by connecting them ...
The Nervous System - Appoquinimink High School
... opening and allowing positive sodium into the cell. This makes it positive. And is called DEPOLARIZATION 2. Soon after potassium channels open and allow potassium in ions in again bringing the charge back to negative. This is called REPOLARIZATION ...
... opening and allowing positive sodium into the cell. This makes it positive. And is called DEPOLARIZATION 2. Soon after potassium channels open and allow potassium in ions in again bringing the charge back to negative. This is called REPOLARIZATION ...
Nervous Regulation
... These 2 systems are antagonistic. The autonomic nervous system is made entirely of ________________. Impulses in this system start in motor neurons in the ______________ __________. The axons of these nerves ________________________ _________________________________________________________. The axon ...
... These 2 systems are antagonistic. The autonomic nervous system is made entirely of ________________. Impulses in this system start in motor neurons in the ______________ __________. The axons of these nerves ________________________ _________________________________________________________. The axon ...
Unit 3 "Cliff Notes" Review
... The hypothalamus directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking, body temperature, and control of emotions. It helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. Picture a HYPOdermic needle spraying two thirsty llamas with water to quench their thirst and cool them down. ...
... The hypothalamus directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking, body temperature, and control of emotions. It helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. Picture a HYPOdermic needle spraying two thirsty llamas with water to quench their thirst and cool them down. ...
The Brain
... control of the autonomic system. It maintains homeostasis by regulating such things as: 1. Hunger and body weight 2. Water and electrolytes through controlling thirst 3. Sleep and wakefulness 4. body temperature 5. blood pressure and heart rate 6. sexual response 7. secretion of hormones from the pi ...
... control of the autonomic system. It maintains homeostasis by regulating such things as: 1. Hunger and body weight 2. Water and electrolytes through controlling thirst 3. Sleep and wakefulness 4. body temperature 5. blood pressure and heart rate 6. sexual response 7. secretion of hormones from the pi ...
Paper: A differentially amplified motion in the ear for near
... The experiment demonstrated that vibrations at the reticular lamina, where stereocilia reside, were enhanced, had different frequency dependence and a different timing from the commonly measured vibrations of the basilar membrane. However, the full resolution of this conundrum will probably require ...
... The experiment demonstrated that vibrations at the reticular lamina, where stereocilia reside, were enhanced, had different frequency dependence and a different timing from the commonly measured vibrations of the basilar membrane. However, the full resolution of this conundrum will probably require ...
Biology of the Mind Powerpoint
... Structure of the Cortex Each brain hemisphere is divided into four lobes that are separated by prominent fissures. These lobes are the frontal lobe (forehead), parietal lobe (top to rear head), occipital lobe (back head) and temporal lobe (side of ...
... Structure of the Cortex Each brain hemisphere is divided into four lobes that are separated by prominent fissures. These lobes are the frontal lobe (forehead), parietal lobe (top to rear head), occipital lobe (back head) and temporal lobe (side of ...
Biology of Mind
... Structure of the Cortex Each brain hemisphere is divided into four lobes that are separated by prominent fissures. These lobes are the frontal lobe (forehead), parietal lobe (top to rear head), occipital lobe (back head) and temporal lobe (side of ...
... Structure of the Cortex Each brain hemisphere is divided into four lobes that are separated by prominent fissures. These lobes are the frontal lobe (forehead), parietal lobe (top to rear head), occipital lobe (back head) and temporal lobe (side of ...
brain and spinal cord
... enough to the NT to mimic its effects on the receiving neuron. Morphine, for example mimics the actions of endorphins*. ...
... enough to the NT to mimic its effects on the receiving neuron. Morphine, for example mimics the actions of endorphins*. ...
Slide ()
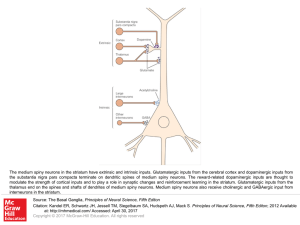
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
Nervous System: Levels of Organization Review and
... this unit. Could you demonstrate each of these objectives? If so, you will be ready for the assessment below. If not, consider reviewing content related to these objectives before attempting the assessment. ...
... this unit. Could you demonstrate each of these objectives? If so, you will be ready for the assessment below. If not, consider reviewing content related to these objectives before attempting the assessment. ...
The Nervous System
... Retrieved from http://iupucbio2.iupui.edu/ anatomy/images/Chapt13/FG13_10.jpg ...
... Retrieved from http://iupucbio2.iupui.edu/ anatomy/images/Chapt13/FG13_10.jpg ...
Chapter 19 The Neurological System
... a. The midbrain is located at the very top of the brain stem and acts as a reflex center. Visual and auditory reflexes are integrated here. When you turn your head to locate a sound, you are using the midbrain. The ‘righting reflex’ or the ability to hold your head upright and maintain balance is al ...
... a. The midbrain is located at the very top of the brain stem and acts as a reflex center. Visual and auditory reflexes are integrated here. When you turn your head to locate a sound, you are using the midbrain. The ‘righting reflex’ or the ability to hold your head upright and maintain balance is al ...
Teacher Guide
... cell body - the bulbous part of the neuron, also called the soma, that contains the nucleus. Dendrites and axons are processes off of the cell body. cerebellum - the highly folded part of the central nervous system above or dorsal to the brainstem that helps control movement, balance, and muscle coo ...
... cell body - the bulbous part of the neuron, also called the soma, that contains the nucleus. Dendrites and axons are processes off of the cell body. cerebellum - the highly folded part of the central nervous system above or dorsal to the brainstem that helps control movement, balance, and muscle coo ...
Nervous System
... Neurons send signals to other cells through thin fibers called axons, which cause chemicals known as neurotransmitters to be released at junctions called synapses, the NIH noted. A synapse gives a command to the cell and the entire communication process typically takes only a fraction of a milliseco ...
... Neurons send signals to other cells through thin fibers called axons, which cause chemicals known as neurotransmitters to be released at junctions called synapses, the NIH noted. A synapse gives a command to the cell and the entire communication process typically takes only a fraction of a milliseco ...
Brain - People
... PSTHs of all area studied show different periods of increased or decreased activity spanning across the whole length of trial ...
... PSTHs of all area studied show different periods of increased or decreased activity spanning across the whole length of trial ...