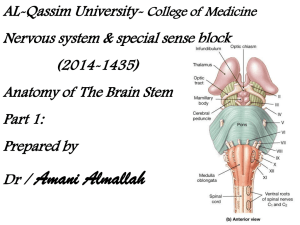
21-Spinal Cord Tracts I
... Motor Pathways • Contain a sequence of TWO neurons from the cerebral cortex or brain stem to the ...
... Motor Pathways • Contain a sequence of TWO neurons from the cerebral cortex or brain stem to the ...
28-1 Pt II - Southgate Community School District
... controls balance. – The medulla oblongata controls the functioning of many internal organs. – Optic lobes are involved in vision, and olfactory bulbs are involved in the sense of smell. – Vertebrate brains are connected to the rest of the body by a thick collection of nerves called a spinal cord ...
... controls balance. – The medulla oblongata controls the functioning of many internal organs. – Optic lobes are involved in vision, and olfactory bulbs are involved in the sense of smell. – Vertebrate brains are connected to the rest of the body by a thick collection of nerves called a spinal cord ...
Control and Communication
... b) Between weeks three and four the body gains most energy from protein c) Each food store decreases at a constant rate during week one d) Between weeks one and four the body only gains energy from lipid and protein 11. The diagram below shows some of the structures involved in a reflex action. ...
... b) Between weeks three and four the body gains most energy from protein c) Each food store decreases at a constant rate during week one d) Between weeks one and four the body only gains energy from lipid and protein 11. The diagram below shows some of the structures involved in a reflex action. ...
the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
... the brain of subjects while they were shown a series of letter navons. A letter navon is a large letter composed of smaller letters as shown in the side box. The researchers soon found out that while the subjects concentrated on the small F's, the left hemisphere showed greater activity; when they f ...
... the brain of subjects while they were shown a series of letter navons. A letter navon is a large letter composed of smaller letters as shown in the side box. The researchers soon found out that while the subjects concentrated on the small F's, the left hemisphere showed greater activity; when they f ...
Neuron File
... concentration differences of ions such as sodium, potassium, chloride, and calcium. Changes in the cross-membrane voltage can alter the function of voltage-dependent ion channels. If the voltage changes by a large enough amount, an all-ornone electrochemical pulse called anaction potential is genera ...
... concentration differences of ions such as sodium, potassium, chloride, and calcium. Changes in the cross-membrane voltage can alter the function of voltage-dependent ion channels. If the voltage changes by a large enough amount, an all-ornone electrochemical pulse called anaction potential is genera ...
Spinal cord 1
... that arise from several adjacent spinal roots. Nevertheless, lesions of a single spinal root, in many cases, can cause weakness and atrophy of a muscle ...
... that arise from several adjacent spinal roots. Nevertheless, lesions of a single spinal root, in many cases, can cause weakness and atrophy of a muscle ...
Results Introduction! Conclusions!
... experiments because they are very similar to their real counterparts in terms of their shape, size, and genetic expression levels. Furthermore, it is interesting to explore differences between IPSC cell lines because expression levels are different between the lines. It is important to note the chan ...
... experiments because they are very similar to their real counterparts in terms of their shape, size, and genetic expression levels. Furthermore, it is interesting to explore differences between IPSC cell lines because expression levels are different between the lines. It is important to note the chan ...
CURRICULUM OF PHYSIOLOGY
... and mean arterial pressure. Mechanism by which extracellular fluid volume elevates arterial blood pressure. – Pressure diuresis and natriuresis, mechanism. – Reninangiotensin-aldosterone system, components and activation. The principal effects of angiotensin II, mechanisms of water and salt retentio ...
... and mean arterial pressure. Mechanism by which extracellular fluid volume elevates arterial blood pressure. – Pressure diuresis and natriuresis, mechanism. – Reninangiotensin-aldosterone system, components and activation. The principal effects of angiotensin II, mechanisms of water and salt retentio ...
A soft-wired hypothalamus
... cocaine and amphetamine–regulated transcript (CART) in the arcuate nucleus and retrochiasmatic area and that provide innervation of the sympathetic ganglia at thoracic segments of the spinal cord28. This projection, which does not contact by NPY/AgRP fibers, is most likely to be important in the act ...
... cocaine and amphetamine–regulated transcript (CART) in the arcuate nucleus and retrochiasmatic area and that provide innervation of the sympathetic ganglia at thoracic segments of the spinal cord28. This projection, which does not contact by NPY/AgRP fibers, is most likely to be important in the act ...
Neuro Anatomy
... ◦ A collection of nuclei involved in motivated behaviour (feeding, drinking, sexual behaviour) ...
... ◦ A collection of nuclei involved in motivated behaviour (feeding, drinking, sexual behaviour) ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 20.1 Time
... leads to redistribution of their dendrites. Source: From Sanes and Zipursky (2010). FIGURE 20.7 Four cellular processes that lead to regular arrangement of dendrites in the tangential plane of the retina’s inner plexiform layer. FIGURE 20.8 Schematic diagram of the effect of synaptic input on dendri ...
... leads to redistribution of their dendrites. Source: From Sanes and Zipursky (2010). FIGURE 20.7 Four cellular processes that lead to regular arrangement of dendrites in the tangential plane of the retina’s inner plexiform layer. FIGURE 20.8 Schematic diagram of the effect of synaptic input on dendri ...
Physiolgy of the nervous system
... - It acts as a barrier between neurons and blood capillaries to prevent harmful substances to reach neurons. ...
... - It acts as a barrier between neurons and blood capillaries to prevent harmful substances to reach neurons. ...
Comparison of Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions
... Postganglionic fibers produce long-lived, generalized, and specific activation of effector mechanisms by using norepinephrine neurotransmitter substance. Based on the transmitter substance used, most preganglionic fibers are classified as cholinergic and most postganglionic fibers as adrenergic (sw ...
... Postganglionic fibers produce long-lived, generalized, and specific activation of effector mechanisms by using norepinephrine neurotransmitter substance. Based on the transmitter substance used, most preganglionic fibers are classified as cholinergic and most postganglionic fibers as adrenergic (sw ...
1 Introduction to Nerve Cells and Nervous Systems
... experiments. It is the remaining ability of the nervous system that is being tested under such circumstances. Stimulation, by either electrical or chemical means,has also been much used and has been important in human studies (the brain can be stimulated in conscious patients under local anaesthesia ...
... experiments. It is the remaining ability of the nervous system that is being tested under such circumstances. Stimulation, by either electrical or chemical means,has also been much used and has been important in human studies (the brain can be stimulated in conscious patients under local anaesthesia ...
34a549e98b7b384
... supply spinothalamic tract, spinal trigeminal nucleus and tract, fibers from the nucleus ambiguous, dorsal motor nucleus of the Vagus (cranial nerve X) & inferior cerebellar peduncle. So Occlusion of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery will produce a lateral medullary syndrome or Wallenberg’s s ...
... supply spinothalamic tract, spinal trigeminal nucleus and tract, fibers from the nucleus ambiguous, dorsal motor nucleus of the Vagus (cranial nerve X) & inferior cerebellar peduncle. So Occlusion of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery will produce a lateral medullary syndrome or Wallenberg’s s ...
Midterm 1 - studyfruit
... ● -bigger the mammal= more area of cerebral cortex ● -bumps(Sulci) and grooves (gyri) on the cerebrum are caused by the cerebral cortex ...
... ● -bigger the mammal= more area of cerebral cortex ● -bumps(Sulci) and grooves (gyri) on the cerebrum are caused by the cerebral cortex ...
Central Nervous System
... Alternating cycles of sleep and wakefulness reflect a natural circadian rhythm The suprachiasmatic and preoptic nuclei of the hypothalamus regulate the sleep cycle Adenosine appears to be a sleep inducing chemical that accumulates in the brain ...
... Alternating cycles of sleep and wakefulness reflect a natural circadian rhythm The suprachiasmatic and preoptic nuclei of the hypothalamus regulate the sleep cycle Adenosine appears to be a sleep inducing chemical that accumulates in the brain ...
Keeping Your Body Healthy -The Nervous System-
... The Nervous System • The body system that carries messages to and from the brain and spinal cord and all other parts of the body is the nervous system. • Composed of 2 divisions: – Central nervous system – Peripheral nervous system ...
... The Nervous System • The body system that carries messages to and from the brain and spinal cord and all other parts of the body is the nervous system. • Composed of 2 divisions: – Central nervous system – Peripheral nervous system ...
Spinal Cord and the Peripheral Nervous System
... transmitting sensory information about light touch, pain, and temperature. They travel to the thalamus in the dorsal column. Some tracts in the spinal cord are for neurons transmitting sensory information about vibration. They travel to the thalamus in the lateral column. Some tracts in the spin ...
... transmitting sensory information about light touch, pain, and temperature. They travel to the thalamus in the dorsal column. Some tracts in the spinal cord are for neurons transmitting sensory information about vibration. They travel to the thalamus in the lateral column. Some tracts in the spin ...
Alterations in Neurons of the Brainstem Due to Administration of
... Abstract: A Quantitative Histopathology study on rats’ brainstem was used to analyze morphological alterations in the neurons and glial cells of rats that received inhaled tetrahydrocanabinol for 4, 8 and 12 weeks. Puffing of smoke was performed with the use of a Hamilton syringe delivering 100ml pu ...
... Abstract: A Quantitative Histopathology study on rats’ brainstem was used to analyze morphological alterations in the neurons and glial cells of rats that received inhaled tetrahydrocanabinol for 4, 8 and 12 weeks. Puffing of smoke was performed with the use of a Hamilton syringe delivering 100ml pu ...
Somatosensory system
... • Medial pain system – Projection neurons synapse in medial locations in the central nervous system – Several pathways with variable numbers of projection neurons, not a three neuron pathway like fast pain. – The information from the medial pain systems is not somatotopically organized, so slow pain ...
... • Medial pain system – Projection neurons synapse in medial locations in the central nervous system – Several pathways with variable numbers of projection neurons, not a three neuron pathway like fast pain. – The information from the medial pain systems is not somatotopically organized, so slow pain ...
Memmler’s The Human Body in Health and Disease 11th edition
... of chemical messengers (hormones) secreted into to the blood ◦ nervous system - employs electrical and chemical means to send messages from cell to cell ...
... of chemical messengers (hormones) secreted into to the blood ◦ nervous system - employs electrical and chemical means to send messages from cell to cell ...
Participation of γ-Aminobutyric Acid Mechanism in the Nucleus
... Mentors: Stephanie Tjen-a-looi, John Longhurst In recent years, electroacupuncture (EA) has gained recognition as a safe and effective technique for treating several cardiovascular complications, and studies have validated its ability in manipulating blood pressure and heart rate. EA application at ...
... Mentors: Stephanie Tjen-a-looi, John Longhurst In recent years, electroacupuncture (EA) has gained recognition as a safe and effective technique for treating several cardiovascular complications, and studies have validated its ability in manipulating blood pressure and heart rate. EA application at ...
Answer Key Chapter 28 - Scarsdale Public Schools
... Two types of ion channels that inhibit action potentials are channels that bring Cl− ions into the cell and channels that release K+ ions out of the cell. 13. Briefly explain how a neuron can receive both excitatory and inhibitory signals and yet still fire an action potential in the receiving ...
... Two types of ion channels that inhibit action potentials are channels that bring Cl− ions into the cell and channels that release K+ ions out of the cell. 13. Briefly explain how a neuron can receive both excitatory and inhibitory signals and yet still fire an action potential in the receiving ...
Endocrinology – general, hypothalamus, pituitary
... The opiomelanocortins are structurally very similar to each other; they are all made from the precursor proopiomelanocortin. They include ACTH and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). The structural similarity means that overproduction of ACTH causes skin pigmentation. ...
... The opiomelanocortins are structurally very similar to each other; they are all made from the precursor proopiomelanocortin. They include ACTH and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). The structural similarity means that overproduction of ACTH causes skin pigmentation. ...