IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... Abstract: C-Mantec is a new neural network algorithm that adds competition between neurons with thermal perceptron learning rule. The neuron learning is ruled by the thermal perceptron rule that guarantees the stability of the learnt information while the architecture increases and while the neurons ...
... Abstract: C-Mantec is a new neural network algorithm that adds competition between neurons with thermal perceptron learning rule. The neuron learning is ruled by the thermal perceptron rule that guarantees the stability of the learnt information while the architecture increases and while the neurons ...
Somatic and Special Senses
... surrounded by columnar epithelial cells There are 400 types of olfactory receptor proteins Odorant molecules enter the nasal cavity as gases, dissolve in watery fluids, and then bind to the receptors in different patterns Stimulated olfactory receptors cells send nerve impulses along their axons whi ...
... surrounded by columnar epithelial cells There are 400 types of olfactory receptor proteins Odorant molecules enter the nasal cavity as gases, dissolve in watery fluids, and then bind to the receptors in different patterns Stimulated olfactory receptors cells send nerve impulses along their axons whi ...
Nervous System Basics: Neurons
... C. Transmitting the Impulse 1. When a stimulus excites an neuron, gates in the axon membrane open and let Na+ move in. a. This causes the inside to change to a slightly ...
... C. Transmitting the Impulse 1. When a stimulus excites an neuron, gates in the axon membrane open and let Na+ move in. a. This causes the inside to change to a slightly ...
central mechanisms underlying short-term and long
... the descending pathways from this region to the spinal sympathetic outflow. A further question is whether there is a common set of "command neurons" within this region of the hypothalamus that trigger both the somatomotor and autonomic changes. It is well known that acute emotional or threatening s ...
... the descending pathways from this region to the spinal sympathetic outflow. A further question is whether there is a common set of "command neurons" within this region of the hypothalamus that trigger both the somatomotor and autonomic changes. It is well known that acute emotional or threatening s ...
Nervous System - healthsciencesMBIT
... pain because it can stop us from continuing an activity that is needed for ...
... pain because it can stop us from continuing an activity that is needed for ...
neuro 13 descending tracts student
... Note: complete paralysis results if both pyramidal and extrapyramidal systems are involved (as is often the case). ...
... Note: complete paralysis results if both pyramidal and extrapyramidal systems are involved (as is often the case). ...
Chapter 15
... Motor neurons project from CNS through one or two synapses Effector—effects on smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
... Motor neurons project from CNS through one or two synapses Effector—effects on smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
rview
... C) The neuron's membrane is completely permeable, so all the various chemicals dissolved in the intracellular and extracellular fluid pass freely through it. D) The cell membranes of excitatory neurons produce action potentials, while the cell membranes of inhibitory neurons produce resting potentia ...
... C) The neuron's membrane is completely permeable, so all the various chemicals dissolved in the intracellular and extracellular fluid pass freely through it. D) The cell membranes of excitatory neurons produce action potentials, while the cell membranes of inhibitory neurons produce resting potentia ...
Chapter 2
... • Nervous System - an extensive network of specialized cells that carry information to and from all parts of the body. • Neuroscience – deals with the structure and function of the brain, neurons, nerves, and nervous tissue. • Relationship to behavior and learning. ...
... • Nervous System - an extensive network of specialized cells that carry information to and from all parts of the body. • Neuroscience – deals with the structure and function of the brain, neurons, nerves, and nervous tissue. • Relationship to behavior and learning. ...
Diseases of the Basal Ganglia
... subthalamic nucleus, which increases the tonic firing of nigral GABAergic neurons. Phasic increases in GPi/SNr discharge increases the inhibition in the superior colliculus or thalamic target nuclei, thus there is a reduced feedback to the cortex. The function of the arousing striatal disinhibition ...
... subthalamic nucleus, which increases the tonic firing of nigral GABAergic neurons. Phasic increases in GPi/SNr discharge increases the inhibition in the superior colliculus or thalamic target nuclei, thus there is a reduced feedback to the cortex. The function of the arousing striatal disinhibition ...
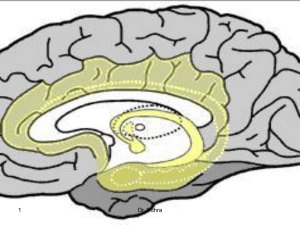
20-Limbic
... amygdala, or indirectly to the hippocampal formation, via entorhinal area. The amygdala appears to provide suggestion to experience & especially relevant to social stimuli. The affect is an evolutionary development from more primitive ‘feelings’, derived from sensory autonomic input bodily organs in ...
... amygdala, or indirectly to the hippocampal formation, via entorhinal area. The amygdala appears to provide suggestion to experience & especially relevant to social stimuli. The affect is an evolutionary development from more primitive ‘feelings’, derived from sensory autonomic input bodily organs in ...
Chapter 21
... b. monitoring actual movement c. comparing command signals (intentions for movements) with sensory information (actual performance) d. sending out corrective signals E. Integration of Sensory Input and Motor Output (p. 666) 1. Sensory input informs the CNS about changes in the external and internal ...
... b. monitoring actual movement c. comparing command signals (intentions for movements) with sensory information (actual performance) d. sending out corrective signals E. Integration of Sensory Input and Motor Output (p. 666) 1. Sensory input informs the CNS about changes in the external and internal ...
Lecture notes for Chapter 13
... above schema separate from Special sensory and Visceral sensory) Receives inputs from Exteroceptors, proprioceptors, and interoceptors Input relayed toward head, but processed along way ...
... above schema separate from Special sensory and Visceral sensory) Receives inputs from Exteroceptors, proprioceptors, and interoceptors Input relayed toward head, but processed along way ...
Principles of neural ensemble physiology underlying the operation
... spatiotemporal patterns of neural ensemble firing on the millisecond scale Following the nomenclature introduced by Reeke and Edelman, this principle, which states that identical behavioural outputs can be produced by distinct functional and transient neural ensembles, has been named the degeneracy ...
... spatiotemporal patterns of neural ensemble firing on the millisecond scale Following the nomenclature introduced by Reeke and Edelman, this principle, which states that identical behavioural outputs can be produced by distinct functional and transient neural ensembles, has been named the degeneracy ...
Nervous System
... which dendrites arise (also contains nucleus of cell) Axon terminals - end of axon/part that releases neurotransmitters to communicate with other neurons ...
... which dendrites arise (also contains nucleus of cell) Axon terminals - end of axon/part that releases neurotransmitters to communicate with other neurons ...
Brain Organization Simulation System
... For BOSS versions up to V6, each neuron is modeled as a simple McCullochPitts cell, a threshold element that sums arriving square-wave (2ms) input pulses sent by other neurons whenever one fires. For every (1ms) time step, if a neuron’s input sum exceeds its fixed threshold, that neuron fires and se ...
... For BOSS versions up to V6, each neuron is modeled as a simple McCullochPitts cell, a threshold element that sums arriving square-wave (2ms) input pulses sent by other neurons whenever one fires. For every (1ms) time step, if a neuron’s input sum exceeds its fixed threshold, that neuron fires and se ...
PNS Terminology
... – extend from the brain to the LMNs via two types of somatic motor pathways • 1. direct motor pathways: nerve impulses for precise voluntary movement – lateral corticospinal, anterior corticospinal and corticobulbar – cell bodies are located in motor cortex and travel down the spinal cord (corticosp ...
... – extend from the brain to the LMNs via two types of somatic motor pathways • 1. direct motor pathways: nerve impulses for precise voluntary movement – lateral corticospinal, anterior corticospinal and corticobulbar – cell bodies are located in motor cortex and travel down the spinal cord (corticosp ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 The Central Nervous
... The human nervous system is divided into three major divisions: the central nervous system (CNS), the autonomic nervous system (ANS), and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The central nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. Both the peripheral nervous system and the autonomic ner ...
... The human nervous system is divided into three major divisions: the central nervous system (CNS), the autonomic nervous system (ANS), and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The central nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. Both the peripheral nervous system and the autonomic ner ...
LESSON 1.2 WORKBOOK How does brain structure impact its function?
... The brain is also organized into areas of white matter where neurons travel and gray matter where connections between different neurons are made. In addition it can also be divided into distinct areas, each of which perform a specific function. Starting from the region where the spinal cord connects ...
... The brain is also organized into areas of white matter where neurons travel and gray matter where connections between different neurons are made. In addition it can also be divided into distinct areas, each of which perform a specific function. Starting from the region where the spinal cord connects ...
Chapter 11 Efferent Division: Autonomic and Somatic Motor Control
... Autonomic Synapse or Neuroeffector Junction (Figure 11-8, p. 392) Neurotransmitter release can be modulated here by hormones and paracrines (e.g. histamine) which can either facilitate or inhibit neurotransmitter release Some preganglionic neurons co-secrete neuropeptides along with ACh The peptide ...
... Autonomic Synapse or Neuroeffector Junction (Figure 11-8, p. 392) Neurotransmitter release can be modulated here by hormones and paracrines (e.g. histamine) which can either facilitate or inhibit neurotransmitter release Some preganglionic neurons co-secrete neuropeptides along with ACh The peptide ...
Chapter 4: The Cytology of Neurons
... Both excitatory and inhibitory input from interneurons driven by descending fibers from brain that control and coordinate movement Inhibitory input from Renshaw cells (an interneuron in spinal cord using L-glycine as neurotransmitters) ...
... Both excitatory and inhibitory input from interneurons driven by descending fibers from brain that control and coordinate movement Inhibitory input from Renshaw cells (an interneuron in spinal cord using L-glycine as neurotransmitters) ...
Effects of experience on brain development
... Radial migration – towards the outer wall of the tube (i.e. moving out – usually by moving along radial glial cells) – increase thickness? Tangential migration – at a right angle to radial migration, parallel to the tube walls (moving up – increase length?) Most cells engage in both types of m ...
... Radial migration – towards the outer wall of the tube (i.e. moving out – usually by moving along radial glial cells) – increase thickness? Tangential migration – at a right angle to radial migration, parallel to the tube walls (moving up – increase length?) Most cells engage in both types of m ...