File
... • Both elicit different responses on various effectors Terminating Autonomic Neurotransmitter Actions • The enzyme acetylcholinesterase rapidly decomposes the acetylcholine that cholinergic fibers release. • Norepinephrine from adrenergic fibers is removed by active transport. ...
... • Both elicit different responses on various effectors Terminating Autonomic Neurotransmitter Actions • The enzyme acetylcholinesterase rapidly decomposes the acetylcholine that cholinergic fibers release. • Norepinephrine from adrenergic fibers is removed by active transport. ...
Homework 12
... 10. Ahad Israfil lost the right side of his brain as a result of an accidental gun discharge at the age of 14 and was able to graduate a university. What would be your prediction on Ahad’s future accomplishments, if Ahad was to lose his left hemisphere? ...
... 10. Ahad Israfil lost the right side of his brain as a result of an accidental gun discharge at the age of 14 and was able to graduate a university. What would be your prediction on Ahad’s future accomplishments, if Ahad was to lose his left hemisphere? ...
Molecular Mechanisms of Appetite Regulation
... The PVN neurons synthesize and secrete neuropeptides that have a net catabolic action, including the corticotrophin-releasing hormone, thyrotropin-releasing hormone, somatostatin, vasopressin, and oxytocin. In addition, PVN sends sympathetic outflow to the peripheral metabolic organs, including li ...
... The PVN neurons synthesize and secrete neuropeptides that have a net catabolic action, including the corticotrophin-releasing hormone, thyrotropin-releasing hormone, somatostatin, vasopressin, and oxytocin. In addition, PVN sends sympathetic outflow to the peripheral metabolic organs, including li ...
Regulation of systemic circulation
... Role of rennin–angiotensin-aldosteron system in regulation of vessel tone Uxta glomerular cells of kidney produce enzyme rennin as the answer of decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin ...
... Role of rennin–angiotensin-aldosteron system in regulation of vessel tone Uxta glomerular cells of kidney produce enzyme rennin as the answer of decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin ...
Lecture 4 : Nervous System
... The dendrites of neurons receive information from sensory receptors or other neurons. This information is then passed down to the cell body and on to the axon. Once the information as arrived at the axon, it travels down the length of the axon in the form of an electrical signal known as an action p ...
... The dendrites of neurons receive information from sensory receptors or other neurons. This information is then passed down to the cell body and on to the axon. Once the information as arrived at the axon, it travels down the length of the axon in the form of an electrical signal known as an action p ...
Lecture 38 (Rhythms)
... The protein then changes the output of the neuron and inhibits further synthesis of the mRNA that created it. This cycle of expression/inhibition takes about 24 hours. ...
... The protein then changes the output of the neuron and inhibits further synthesis of the mRNA that created it. This cycle of expression/inhibition takes about 24 hours. ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... An Overview of Nervous Systems 1) Compare and contrast the nervous systems of the following animals and explain how variations in design and complexity relate to their phylogeny, natural history, and habitat: hydra, sea star, planarian, insect, squid and vertebrate. 2) Name the three stages in the p ...
... An Overview of Nervous Systems 1) Compare and contrast the nervous systems of the following animals and explain how variations in design and complexity relate to their phylogeny, natural history, and habitat: hydra, sea star, planarian, insect, squid and vertebrate. 2) Name the three stages in the p ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... An Overview of Nervous Systems 1) Compare and contrast the nervous systems of the following animals and explain how variations in design and complexity relate to their phylogeny, natural history, and habitat: hydra, sea star, planarian, insect, squid and vertebrate. 2) Name the three stages in the p ...
... An Overview of Nervous Systems 1) Compare and contrast the nervous systems of the following animals and explain how variations in design and complexity relate to their phylogeny, natural history, and habitat: hydra, sea star, planarian, insect, squid and vertebrate. 2) Name the three stages in the p ...
felix may 2nd year neuroscience Investigation into the response to
... times more glial cells than neurons. Glia are non-neuronal cells that support neuronal function by optimising the local environment and providing trophic factors and nutrients, having a homeostatic function. Unlike neurons glia continue to proliferate throughout life, especially during the reaction ...
... times more glial cells than neurons. Glia are non-neuronal cells that support neuronal function by optimising the local environment and providing trophic factors and nutrients, having a homeostatic function. Unlike neurons glia continue to proliferate throughout life, especially during the reaction ...
- Orange Coast College
... NE binds to receptor. G-protein dissociates into a subunit or bgcomplex. Depending upon tissue, either a subunit or bgcomplex produces the effects. ...
... NE binds to receptor. G-protein dissociates into a subunit or bgcomplex. Depending upon tissue, either a subunit or bgcomplex produces the effects. ...
Structural Biochemistry/Cell Signaling Pathways/Nervous System
... potential starts when voltage gated sodium channels are activated. These channels allow an influx of sodium. Potassium channels also open up, which causes an efflux of potassium ions. The efflux of potassium ions causes the membrane to hyperpolarize (makes more negative) the cell. If the current of ...
... potential starts when voltage gated sodium channels are activated. These channels allow an influx of sodium. Potassium channels also open up, which causes an efflux of potassium ions. The efflux of potassium ions causes the membrane to hyperpolarize (makes more negative) the cell. If the current of ...
Chapter 48 Nervous Systems
... (fMRI), which reconstructs a 3-D map of the subject’s brain activity. The results of brain imaging and other research methods show that groups of neurons function in specialized circuits dedicated to different tasks. The ability of cells to respond to the environment has evolved over billions of y ...
... (fMRI), which reconstructs a 3-D map of the subject’s brain activity. The results of brain imaging and other research methods show that groups of neurons function in specialized circuits dedicated to different tasks. The ability of cells to respond to the environment has evolved over billions of y ...
YAPAY SİNİR AĞLARINA GİRİŞ
... This can potentially help us understand the nature of human intelligence, formulate better teaching strategies, or better remedial actions for brain damaged patients. Artificial System Building : The engineering goal of building efficient systems for real world applications. This may make machines m ...
... This can potentially help us understand the nature of human intelligence, formulate better teaching strategies, or better remedial actions for brain damaged patients. Artificial System Building : The engineering goal of building efficient systems for real world applications. This may make machines m ...
Chapter 15 Autonomic NS
... sensory receptor sensory neuron integrating center motor neurons (pre & postganglionic) visceral effectors ...
... sensory receptor sensory neuron integrating center motor neurons (pre & postganglionic) visceral effectors ...
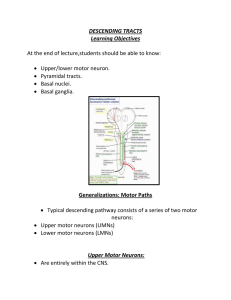
DESCENDING TRACTS Learning Objectives At the end of lecture
... Made up of corticospinal fibers that have crossed in medulla. Supply all levels of spinal cord. Anterior corticospinal tract: Made up of uncrossed corticospinal fibers of synapse with LMNs. Supply neck and upper limbs. ...
... Made up of corticospinal fibers that have crossed in medulla. Supply all levels of spinal cord. Anterior corticospinal tract: Made up of uncrossed corticospinal fibers of synapse with LMNs. Supply neck and upper limbs. ...
Supplementary material 4 – Unified probability of spike
... classification error was found (at 0.05 resolution). The reported Pmis value corresponds to the optimal Z-score for each SNR (see Figures S5, S7 and S9 for, respectively, the linear, inverse and inverse square models), and therefore underestimates the true misclassification rate if a standard cluste ...
... classification error was found (at 0.05 resolution). The reported Pmis value corresponds to the optimal Z-score for each SNR (see Figures S5, S7 and S9 for, respectively, the linear, inverse and inverse square models), and therefore underestimates the true misclassification rate if a standard cluste ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 35.1 Functional organization of the
... FIGURE 35.1 Functional organization of the CNS control of breathing. Circuitry centered within the medulla oblongata of the brainstem (blue oval) generates an oscillating inspiratory–expiratory rhythm. Neurons within the oscillator circuit generate rhythmic respiratory motor output without requiring ...
... FIGURE 35.1 Functional organization of the CNS control of breathing. Circuitry centered within the medulla oblongata of the brainstem (blue oval) generates an oscillating inspiratory–expiratory rhythm. Neurons within the oscillator circuit generate rhythmic respiratory motor output without requiring ...
Simulation with NEST, an example of a full
... the fast development of computer systems and the growing availability of experimental data, computational simulations get more important. The computational power, which is available now and will be available in the next years, allows simulations of mammalian brains. Even a simulation of the human br ...
... the fast development of computer systems and the growing availability of experimental data, computational simulations get more important. The computational power, which is available now and will be available in the next years, allows simulations of mammalian brains. Even a simulation of the human br ...
Neuronal Organization of the Cerebellar Cortex
... • Their axons travel into the deep cerebellar nuclei. • Purkinje cells use GABA as their neurotransmitter, and therefore exert inhibitory effects on their targets. ...
... • Their axons travel into the deep cerebellar nuclei. • Purkinje cells use GABA as their neurotransmitter, and therefore exert inhibitory effects on their targets. ...
Nervous
... throughout the ventricles, down the central canal of the spinal cord and throughout the subarachnoid space. CSF is reabsorbed back into blood primarily at the venous sinuses found within the dura mater. ...
... throughout the ventricles, down the central canal of the spinal cord and throughout the subarachnoid space. CSF is reabsorbed back into blood primarily at the venous sinuses found within the dura mater. ...
NAS 150 The Skeletal System Brilakis Fall, 2003
... broken down into pyruvic acid. The glucose is supplied by the stored glycogen in your muscles. This supplies enough energy for about 45 seconds. (if oxygen is absent, this process continues as lactic acid is formed) c. Aerobic respiration provides the rest of the ATP, assuming oxygen is present. The ...
... broken down into pyruvic acid. The glucose is supplied by the stored glycogen in your muscles. This supplies enough energy for about 45 seconds. (if oxygen is absent, this process continues as lactic acid is formed) c. Aerobic respiration provides the rest of the ATP, assuming oxygen is present. The ...
True or False Questions - Sinoe Medical Association
... produced by the arrival of an action potential in the synaptic terminal. b. Neurotransmitter is released from the synaptic terminal by exocytosis, when synaptic vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane of the terminal. c. An inhibitory neurotransmitter produces inhibition of a postsynaptic neuron by p ...
... produced by the arrival of an action potential in the synaptic terminal. b. Neurotransmitter is released from the synaptic terminal by exocytosis, when synaptic vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane of the terminal. c. An inhibitory neurotransmitter produces inhibition of a postsynaptic neuron by p ...
BIO 141 Unit 5 Learning Objectives
... 23. Explain why someone who receives damage to one side of their primary motor cortex, is unable to move the opposite side of their body. 24. Identify the cerebral lobe in which the following areas a ...
... 23. Explain why someone who receives damage to one side of their primary motor cortex, is unable to move the opposite side of their body. 24. Identify the cerebral lobe in which the following areas a ...