Fundamentals on Peripheral Nerves
... Postganglionic Efferent Fibers (Efferent fibers to smooth muscle, glands, and cardiac muscle) All postganglionic efferent nerve fibers arise from nerve cell bodies located in autonomic ganglia. They terminate on smooth muscle cells, glands, or cardiac muscle cells. The postganglionic efferent fibers ...
... Postganglionic Efferent Fibers (Efferent fibers to smooth muscle, glands, and cardiac muscle) All postganglionic efferent nerve fibers arise from nerve cell bodies located in autonomic ganglia. They terminate on smooth muscle cells, glands, or cardiac muscle cells. The postganglionic efferent fibers ...
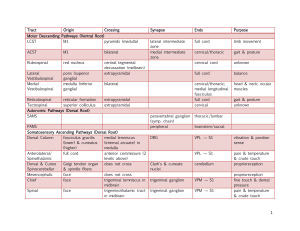
Tract Origin Crossing Synapse Ends Purpose Motor Descending
... inferior: fibers from ipsilateral spinocerebellar tract (proprioceptive), inferior olives, vestibular nuclei somatotopic input: repeats & layering provide multiple modes of coordination & interactions inner → outer::head → legs in posterior & anterior lobes audio/visual input in medial vermis motor ...
... inferior: fibers from ipsilateral spinocerebellar tract (proprioceptive), inferior olives, vestibular nuclei somatotopic input: repeats & layering provide multiple modes of coordination & interactions inner → outer::head → legs in posterior & anterior lobes audio/visual input in medial vermis motor ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... the parasympathetic division release acetylcholine and thus are called cholinergic. The preganglionic axon and a few postganglionic axons in the sympathetic division are also cholinergic. Most of the postganglionic axons of the sympathetic division release norepinephrine and are called ...
... the parasympathetic division release acetylcholine and thus are called cholinergic. The preganglionic axon and a few postganglionic axons in the sympathetic division are also cholinergic. Most of the postganglionic axons of the sympathetic division release norepinephrine and are called ...
Human Anatomy - Fisiokinesiterapia
... the parasympathetic division release acetylcholine and thus are called cholinergic. The preganglionic axon and a few postganglionic axons in the sympathetic division are also cholinergic. Most of the postganglionic axons of the sympathetic division release norepinephrine and are called ...
... the parasympathetic division release acetylcholine and thus are called cholinergic. The preganglionic axon and a few postganglionic axons in the sympathetic division are also cholinergic. Most of the postganglionic axons of the sympathetic division release norepinephrine and are called ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... – K+ inside and outside of the cell are attracted to the negative charges on the inside of the cell membrane, and repelled by the positive charges on the outside of the cell membrane • indicated in white on the next slide ...
... – K+ inside and outside of the cell are attracted to the negative charges on the inside of the cell membrane, and repelled by the positive charges on the outside of the cell membrane • indicated in white on the next slide ...
From Sensation to Perception
... the transmittal of autonomic impulses to lacrimal and salivary glands • Sensory function is __________________________ from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue ...
... the transmittal of autonomic impulses to lacrimal and salivary glands • Sensory function is __________________________ from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue ...
Membrane potential synchrony of simultaneously recorded striatal
... functionally de®ned region will be synchronous because they depend on the total number of active excitatory inputs. The moment-to-moment variations of membrane potential are generally not synchronous on the time scale of a few milliseconds, as can be seen in Fig. 3b. This could result from activatio ...
... functionally de®ned region will be synchronous because they depend on the total number of active excitatory inputs. The moment-to-moment variations of membrane potential are generally not synchronous on the time scale of a few milliseconds, as can be seen in Fig. 3b. This could result from activatio ...
Monitoring and switching of cortico-basal ganglia loop
... 4. Monitoring and switching of top-down biased control functions of cortico-basal ganglia loops through the thalamo-striatal system As described above, the CM and Pf receive signals from the internal segment of the globus pallidus and from the substantia nigra pars reticulata, respectively (Sidibé e ...
... 4. Monitoring and switching of top-down biased control functions of cortico-basal ganglia loops through the thalamo-striatal system As described above, the CM and Pf receive signals from the internal segment of the globus pallidus and from the substantia nigra pars reticulata, respectively (Sidibé e ...
2.1.2. The Purpose: Acquaint the student by subject to neurologies
... or an effector organ. Generally speaking, every neuron has a soma, an axon, and one or more dendrites. The structure and configuration of the nerve cell processes (especially the dendrites) vary depending on the function of the neuron. Thus, neurons can be classified into a number of morphological ...
... or an effector organ. Generally speaking, every neuron has a soma, an axon, and one or more dendrites. The structure and configuration of the nerve cell processes (especially the dendrites) vary depending on the function of the neuron. Thus, neurons can be classified into a number of morphological ...
PDF
... termination pattern could serve as a morphological substrate for relatively homogeneous effects on various CN cell types. The present data are the first direct demonstration that both principal cell types in the AVCN, bushy and stellate cells, receive functional inputs from the contralateral CN and ...
... termination pattern could serve as a morphological substrate for relatively homogeneous effects on various CN cell types. The present data are the first direct demonstration that both principal cell types in the AVCN, bushy and stellate cells, receive functional inputs from the contralateral CN and ...
ANS and sympathetic division pharm
... maintains body homeostasis by integrating signals from afferent somatic and visceral sensors to modulate organ perfusion and function. These signals are integrated in medulla and modulated by the central autonomic network which consists (in addition to the medulla) of the cerebral cortex, hypothalam ...
... maintains body homeostasis by integrating signals from afferent somatic and visceral sensors to modulate organ perfusion and function. These signals are integrated in medulla and modulated by the central autonomic network which consists (in addition to the medulla) of the cerebral cortex, hypothalam ...
The Nervous System - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Studies the effects of heredity on behavior ...
... Studies the effects of heredity on behavior ...
here
... Although the ANS is considered to be involuntary, this is not entirely true. A certain amount of conscious control can be exerted over it as has long been demonstrated by practitioners of yoga and Zen Buddhism. During their periods of meditation, these people are able to alter a numb ...
... Although the ANS is considered to be involuntary, this is not entirely true. A certain amount of conscious control can be exerted over it as has long been demonstrated by practitioners of yoga and Zen Buddhism. During their periods of meditation, these people are able to alter a numb ...
Peripheral Nervous System Structure of a Nerve Cranial Nerves
... motor subdivision of the PNS that controls body activities automatically. It is composed of a special group of neurons that regulate cardiac muscle (the heart), smooth muscles (found in the walls of the visceral organs and blood vessels), and glands. Although all body systems contribute to homeostas ...
... motor subdivision of the PNS that controls body activities automatically. It is composed of a special group of neurons that regulate cardiac muscle (the heart), smooth muscles (found in the walls of the visceral organs and blood vessels), and glands. Although all body systems contribute to homeostas ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Allows CNS to receive information and initiate action Sensory inputs and motor outputs categorized as Somatic or visceral General or special Basic Structure of PNS Sensory receptors—pick up stimuli from inside or outside the body Nerves and ganglia Nerves—bundles of peripheral axons Ganglia—clusters ...
... Allows CNS to receive information and initiate action Sensory inputs and motor outputs categorized as Somatic or visceral General or special Basic Structure of PNS Sensory receptors—pick up stimuli from inside or outside the body Nerves and ganglia Nerves—bundles of peripheral axons Ganglia—clusters ...
Skeletal Reflexes - University of Houston College of Optometry
... organs in number and structure They’re present because they are a natural constituent of striated muscle ...
... organs in number and structure They’re present because they are a natural constituent of striated muscle ...
Cranial nerves (L15)
... *also proprioceptive to these mm. *motor nucleus is in the midbrain -GVE parasympathetic motor to the sphincter pupillae & ciliary mm. *sphincter pupillae constricts pupil to control light input *ciliary changes shape of lens to accommodate changes in distance vision *primary neurons in Edinger-We ...
... *also proprioceptive to these mm. *motor nucleus is in the midbrain -GVE parasympathetic motor to the sphincter pupillae & ciliary mm. *sphincter pupillae constricts pupil to control light input *ciliary changes shape of lens to accommodate changes in distance vision *primary neurons in Edinger-We ...
Somatic and Special Senses
... project into the nasal cavity and are the sensitive parts of the receptors; chemicals enter the nasal cavity as gases, but they must dissolve at least partially in the watery fluids that surround the cilia before receptors can detect them ...
... project into the nasal cavity and are the sensitive parts of the receptors; chemicals enter the nasal cavity as gases, but they must dissolve at least partially in the watery fluids that surround the cilia before receptors can detect them ...
Somatic and Special Senses
... project into the nasal cavity and are the sensitive parts of the receptors; chemicals enter the nasal cavity as gases, but they must dissolve at least partially in the watery fluids that surround the cilia before receptors can detect them ...
... project into the nasal cavity and are the sensitive parts of the receptors; chemicals enter the nasal cavity as gases, but they must dissolve at least partially in the watery fluids that surround the cilia before receptors can detect them ...
ppt - Brain Dynamics Laboratory
... Functional consequences of oscillatory driving input to the motoneurons that relate to breathing have also been shown in rats in vitro. First, similar to the effect of correlated presynaptic inputs on other neurons, the timing of action potentials in motor neurons is crucially affected by oscillato ...
... Functional consequences of oscillatory driving input to the motoneurons that relate to breathing have also been shown in rats in vitro. First, similar to the effect of correlated presynaptic inputs on other neurons, the timing of action potentials in motor neurons is crucially affected by oscillato ...
Nervous System Ch 9
... • Second largest part of the human brain • Helps control muscle contractions to produce coordinated movements so that we can maintain balance, move smoothly, and sustain normal postures • Recent evidence shows the cerebellum may also have wider coordinating effects, assisting the cerebrum and other ...
... • Second largest part of the human brain • Helps control muscle contractions to produce coordinated movements so that we can maintain balance, move smoothly, and sustain normal postures • Recent evidence shows the cerebellum may also have wider coordinating effects, assisting the cerebrum and other ...
Simple model of spiking neurons
... Hoppensteadt and Izhikevich [1] and Wang [2] have proposed network models where the neural activity is described by differential equations. Both architectures can be used for pattern recognition via associative memory, which occurs when a group of neurons fires synchronously. These models were inspi ...
... Hoppensteadt and Izhikevich [1] and Wang [2] have proposed network models where the neural activity is described by differential equations. Both architectures can be used for pattern recognition via associative memory, which occurs when a group of neurons fires synchronously. These models were inspi ...
Simple model of spiking neurons
... One can see in Fig. 3 that the network exhibits cortical-like asynchronous dynamics; that is, neurons fire Poisson spike trains with mean firing rates around 8 Hz. Dark vertical lines indicate that there are occasional episodes of synchronized firings in the alpha and gamma frequency range (10 and 4 ...
... One can see in Fig. 3 that the network exhibits cortical-like asynchronous dynamics; that is, neurons fire Poisson spike trains with mean firing rates around 8 Hz. Dark vertical lines indicate that there are occasional episodes of synchronized firings in the alpha and gamma frequency range (10 and 4 ...
Analogy = Computer
... Diencephalon structures: • Thalamus (anterior thalamic nuclei) • Hypothalamus ...
... Diencephalon structures: • Thalamus (anterior thalamic nuclei) • Hypothalamus ...