Q1 (from chapter 1)
... A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. Orbitofrontal cortex is responsible for social behavior Q2 ...
... A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. Orbitofrontal cortex is responsible for social behavior Q2 ...
210_Lecture6_motor
... Motor neurons in the spinal cord and brainstem degenerate. 5-10% of cases are due to genetic defects • The rest are sporadic: no known cause ...
... Motor neurons in the spinal cord and brainstem degenerate. 5-10% of cases are due to genetic defects • The rest are sporadic: no known cause ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Cerebral cortex motor areas – plan and control voluntary movement, affect spinal cord neurons ...
... Cerebral cortex motor areas – plan and control voluntary movement, affect spinal cord neurons ...
3cf1482f14bbaf7
... Descending Spinal Pathways extrapyramidal system - Coordination of head & eye movements, - Coordinated function of trunk & extremity musculature to maintaining posture and balance - Synapse in some intermediate nucleus rather than directly with lower motor neurons ...
... Descending Spinal Pathways extrapyramidal system - Coordination of head & eye movements, - Coordinated function of trunk & extremity musculature to maintaining posture and balance - Synapse in some intermediate nucleus rather than directly with lower motor neurons ...
Unit 3 Essential Vocabulary File - District 196 e
... You will also need to know (but are not required to complete flashcards for): the structure of the NERVOUS SYSTEM (peripheral and central). the parts and function of the NEURON. techniques for STUDYING THE BRAIN (MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG) Difference between identical and fraternal twins Genes, ...
... You will also need to know (but are not required to complete flashcards for): the structure of the NERVOUS SYSTEM (peripheral and central). the parts and function of the NEURON. techniques for STUDYING THE BRAIN (MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG) Difference between identical and fraternal twins Genes, ...
Brainstem*s involvement in Motor process
... • Contains ascending and descending pathways that carry motor (and sensory) information to other divisions of the central nervous system ...
... • Contains ascending and descending pathways that carry motor (and sensory) information to other divisions of the central nervous system ...
Basal nuclei
... Associated with 10 of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves (olfactory and optics) Does the same basic sensory and motor functions for the head that the spinal cord does for the rest of the body Reception and integration of all synaptic input from spinal cord Relaying sensory information to cerebellum, tha ...
... Associated with 10 of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves (olfactory and optics) Does the same basic sensory and motor functions for the head that the spinal cord does for the rest of the body Reception and integration of all synaptic input from spinal cord Relaying sensory information to cerebellum, tha ...
Slide ()
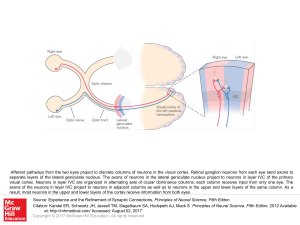
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
Connecting to your need For Rithme
... • Developing a child’s musical ability may actually improve her ability to learn and be successful at other disciplines, such as language, math and science. ...
... • Developing a child’s musical ability may actually improve her ability to learn and be successful at other disciplines, such as language, math and science. ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
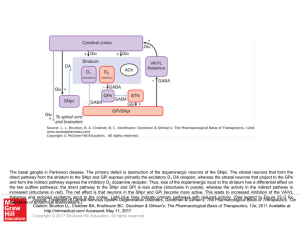
... The basal ganglia in Parkinson disease. The primary defect is destruction of the dopaminergic neurons of the SNpc. The striatal neurons that form the direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the ...
... The basal ganglia in Parkinson disease. The primary defect is destruction of the dopaminergic neurons of the SNpc. The striatal neurons that form the direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the ...
10-5 Infant Biosocial Development
... Germinal, embryonic, and fetal periods Teratogens: critical period, threshold, interaction Birth process ...
... Germinal, embryonic, and fetal periods Teratogens: critical period, threshold, interaction Birth process ...
Slide ()
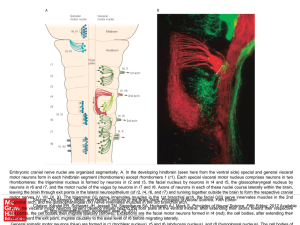
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
Lecture 15
... system (muscle length), muscle tension via Ib fibers and the Golgi tendon organ) can activate different reflex pathways by accessing specific interneurons with characteristic connectivity patterns (Ia and Ib interneurons). Some inhibitory interneurons are activated by axon collaterals of motor neuro ...
... system (muscle length), muscle tension via Ib fibers and the Golgi tendon organ) can activate different reflex pathways by accessing specific interneurons with characteristic connectivity patterns (Ia and Ib interneurons). Some inhibitory interneurons are activated by axon collaterals of motor neuro ...
27_LectureSlides
... CM neurons are preferentially recruited for tasks requiring topographical precision ...
... CM neurons are preferentially recruited for tasks requiring topographical precision ...
The motor system Outline Muscles Reflexes Disorders of movement
... Cost: BAD side effects Increases in dopamine levels throughout the body lead to issues with the liver and other organs ONLY treats the _________________________, not the cause Motor cortex Primary motor cortex _________________________ area (SMA) Premotor area SMA Involved in the ___________________ ...
... Cost: BAD side effects Increases in dopamine levels throughout the body lead to issues with the liver and other organs ONLY treats the _________________________, not the cause Motor cortex Primary motor cortex _________________________ area (SMA) Premotor area SMA Involved in the ___________________ ...
Input sources of alpha motor neurons
... • Alpha motor neurons receive input from sensory fibers located in the muscles themselves • Alpha motor neurons also receive input from the descending fibers of ...
... • Alpha motor neurons receive input from sensory fibers located in the muscles themselves • Alpha motor neurons also receive input from the descending fibers of ...
Anatomy of the Basal Ganglia
... Anatomy of the Basal Ganglia The striatum (caudaute/putamen) and subthalamic nucleus (STN) receive excitatory input from the cerebral cortex. Dopamine-releasing neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) connect to neurons in the striatum and modulate the inputs from the cortex. There is a ...
... Anatomy of the Basal Ganglia The striatum (caudaute/putamen) and subthalamic nucleus (STN) receive excitatory input from the cerebral cortex. Dopamine-releasing neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) connect to neurons in the striatum and modulate the inputs from the cortex. There is a ...
November 12
... Basal ganglia loop (near thalamus) gives the “go” signal Cerebellar loop – tells the motor cortex how to carry out the planned activity ...
... Basal ganglia loop (near thalamus) gives the “go” signal Cerebellar loop – tells the motor cortex how to carry out the planned activity ...
Slide ()
... The corticospinal and bulbospinal upper motor neuron pathways. Upper motor neurons have their cell bodies in layer V of the primary motor cortex (the precentral gyrus, or Brodmann’s area 4) and in the premotor and supplemental motor cortex (area 6). The upper motor neurons in the primary motor corte ...
... The corticospinal and bulbospinal upper motor neuron pathways. Upper motor neurons have their cell bodies in layer V of the primary motor cortex (the precentral gyrus, or Brodmann’s area 4) and in the premotor and supplemental motor cortex (area 6). The upper motor neurons in the primary motor corte ...
Control of Movement
... Innervates axial muscles and proximal part of limbs Vestibular nuclei – connection with cerebellum, receives sensory information from the ...
... Innervates axial muscles and proximal part of limbs Vestibular nuclei – connection with cerebellum, receives sensory information from the ...